Establishing a cerebral palsy registry in Kuwait: An exploratory study
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Physical Therapy Department, School of Allied Health, Kuwait University, Kuwait.
- Physical Therapy Department, Ministry of Health, Kuwait.
Abstract
Background: Cerebral palsy (CP), the most common motor disability in childhood, comprises a group of permanent non-progressive disorders affecting the antenatal, neonatal, or early postnatal development of areas in the brain responsible for posture and movement. Registries for children with CP, or surveillance programs, have been a source of consistently increasing research productivity; 38 related articles were published in 2013. In Kuwait, a CP registry would provide baseline information on children with CP and their parents. The registry could include demographic information obtained through parental interviews, or review of the mothers' and the children's medical charts.
Objective: This study was aimed at exploring the establishment of a pediatric CP registry in Kuwait.
Methods: In this exploratory study, caregivers of children with CP were recruited from rehabilitation clinics around Kuwait. The inclusion criteria were 1) boys or girls with a documented diagnosis of CP made between 6 months and 18 years of age, 2) caregivers with permanent residency in Kuwait, and 4) caregivers speaking Arabic and/or English fluently. The variables collected comprised registry and feasibility variables. Registry-associated variables comprised demographic and medical information about the children, and caregivers' willingness to be contacted for a follow-up or participation in other research projects. Feasibility variables were the percentage of information gathered, and the willingness of caregivers to participate in, and of therapists to recruit for, the registry.
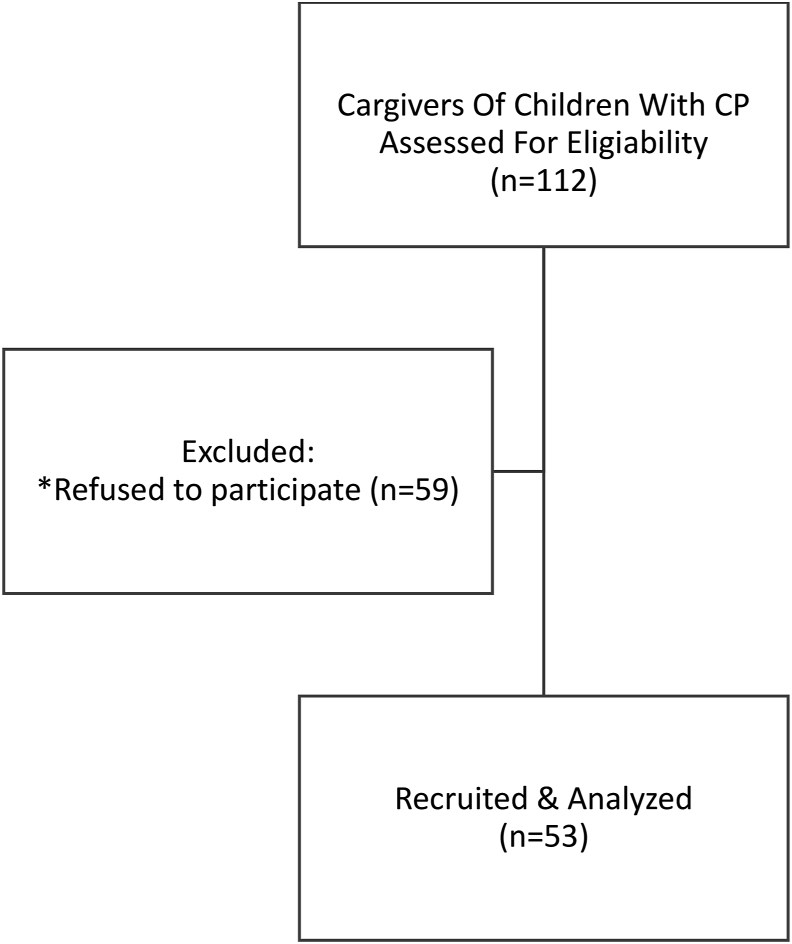
Results: Fifty-three caregivers of children with CP participated in this study. The mean age of the recruited children with CP was 5 years and 5 months (SD = 3 y 4 m, range = 11 m to 16 y 8 m/female n = 25). GMFCS level V was reported by half of the sample (n = 29/55.77%). Of the 112 caregivers screened, fewer than half (n = 53 of 112/47.32%) participated in the study. Most caregivers (n = 48/90.56%) used the Arabic version of the form.
Conclusion: The establishment of a pediatric CP registry in Kuwait is feasible, on the basis of our data.
Keywords: Cerebral palsy; Feasibility; Pediatrics; Registry; Surveillance.
Figures
Similar articles
The health and well-being of caregivers of children with cerebral palsy.
Raina P, O'Donnell M, Rosenbaum P, Brehaut J, Walter SD, Russell D, Swinton M, Zhu B, Wood E.Pediatrics. 2005 Jun;115(6):e626-36. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1689.PMID: 15930188
Hurley DS, Sukal-Moulton T, Gaebler-Spira D, Krosschell KJ, Pavone L, Mutlu A, Dewald JP, Msall ME.Int J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015 Apr;3(2):266. doi: 10.4172/2329-9096.1000266. Epub 2015 Mar 23.PMID: 27790626 Free PMC article.
Brehaut JC, Kohen DE, Raina P, Walter SD, Russell DJ, Swinton M, O'Donnell M, Rosenbaum P.Pediatrics. 2004 Aug;114(2):e182-91. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.2.e182.PMID: 15286255
Exercise interventions for cerebral palsy.
Ryan JM, Cassidy EE, Noorduyn SG, O'Connell NE.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 11;6(6):CD011660. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011660.pub2.PMID: 28602046 Free PMC article. Review.
Davidson B, Schoen N, Sedighim S, Haldenby R, Dalziel B, Breitbart S, Fehlings D, Milo-Manson G, Narayanan UG, Drake JM, Ibrahim GM.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2019 Oct 18:1-9. doi: 10.3171/2019.8.PEDS19282. Online ahead of print.PMID: 31628286 Review.
KMEL References
References
-
- Rosenbaum P., Paneth N., Leviton A., Goldstein M., Bax M., Damiano D., et al. A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. Feb 2007;109:8–14. - PubMed
-
- Hurley D.S., Sukal-Moulton T., Gaebler-Spira D., Krosschell K.J., Pavone L., Mutlu A., et al. Systematic review of cerebral palsy registries/surveillance groups: relationships between registry characteristics and knowledge dissemination. Int J Phys Med Rehabil. Apr 2015;3(2) doi: 10.4172/2329-9096.1000266. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khandaker G., Smithers-Sheedy H., Islam J., Alam M., Jung J., Novak I., et al. Bangladesh Cerebral Palsy Register (BCPR): a pilot study to develop a national cerebral palsy (CP) register with surveillance of children for CP. BMC Neurol. Sep 25 2015;15:173. doi: 10.1186/s12883-015-0427-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altonoby A., Tawfek M., Abdelaziem F., Kilany A. Establish registry of cerebral palsy in Tanta Egypt. Int J Ther Rehabil Res. 2017;6(2):174.