Skin manifestations of COVID-19 in children: Part 3
D Andina 1, A Belloni-Fortina 2, C Bodemer 3, E Bonifazi 4, A Chiriac 5, I Colmenero 6, A Diociaiuti 7, M El-Hachem 7, L Fertitta 3, D van Gysel 8, A Hernández-Martín 1, T Hubiche 9, C Luca 5, L Martos-Cabrera 1, A Maruani 10, F Mazzotta 4, A D Akkaya 11, M Casals 12, J Ferrando 13, R Grimalt 14, I Grozdev 15, V Kinsler 16, M A Morren 17, M Munisami 18, A Nanda 19, M P Novoa 20, H Ott 21, S Pasmans 22, C Salavastru 23, V Zawar 24, A Torrelo 1; ESPD Group for the Skin Manifestations of COVID-19
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Dermatology, Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, Spain.
- Pediatric Dermatology Unit, Department of Medicine DIMED, University of Padua, Padua, Italy.
- Department of Dermatology, Hospital Necker Enfants Malades, Paris Centre University, Paris, France.
- Dermatologia Pediatrica Association, Bari, Italy.
- Nicolina Medical Center, Iasi, Romania.
- Department of Pathology, Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, Spain.
- Dermatology Unit, Bambino Gesù Children's Hospital, IRCCS, Rome, Italy.
- Department of Pediatrics, O. L. Vrouw Hospital, Aalst, Belgium.
- Department of Dermatology, Université Côte d'Azur, Nice, France.
- Department of Dermatology, Unit of Pediatric Dermatology, University of Tours, SPHERE-INSERM1246, CHRU Tours, Tours, France.
- Department of Dermatology, Ulus Liv Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey.
- Department of Dermatology, Hospital Universitari de Sabadell, Barcelona, Spain.
- Department of Dermatology, Hospital Clìnic, Barcelona, Spain.
- Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universitat Internacional de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain.
- Department of Dermatology, Children's University Hospital Queen Fabiola, Brussels, Belgium.
- Department of Paediatric Dermatology, Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children, NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK.
- Pediatric Dermatology Unit, Department of Pediatrics and Dermato-Venereology, University Hospital Lausanne and University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland.
- Department of Dermatology and Sexually Transmitted Diseases, Jawaharlal Institute Of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Puducherry, India.
- As'ad Al-Hamad Dermatology Center, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
- Department of Dermatology, Hospital San Jose, Bogota, Colombia.
- Division of Pediatric Dermatology, Children's Hospital Auf der Bult, Hannover, Germany.
- Erasmus MC University Medical Center Rotterdam, Sophia Children's Hospital, Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- Department of Paediatric Dermatology, Colentina Clinical Hospital, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania.
- Department of Dermatology, Dr Vasantrao Pawar Medical College, Nashik, India.
Abstract
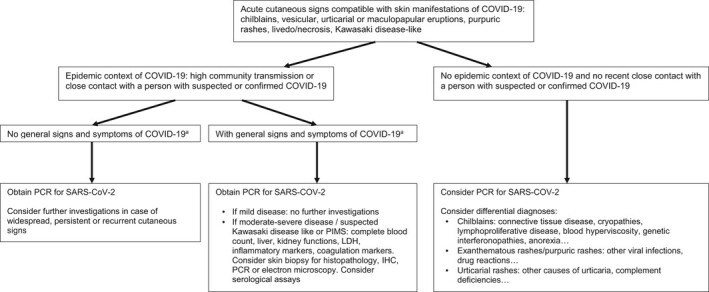
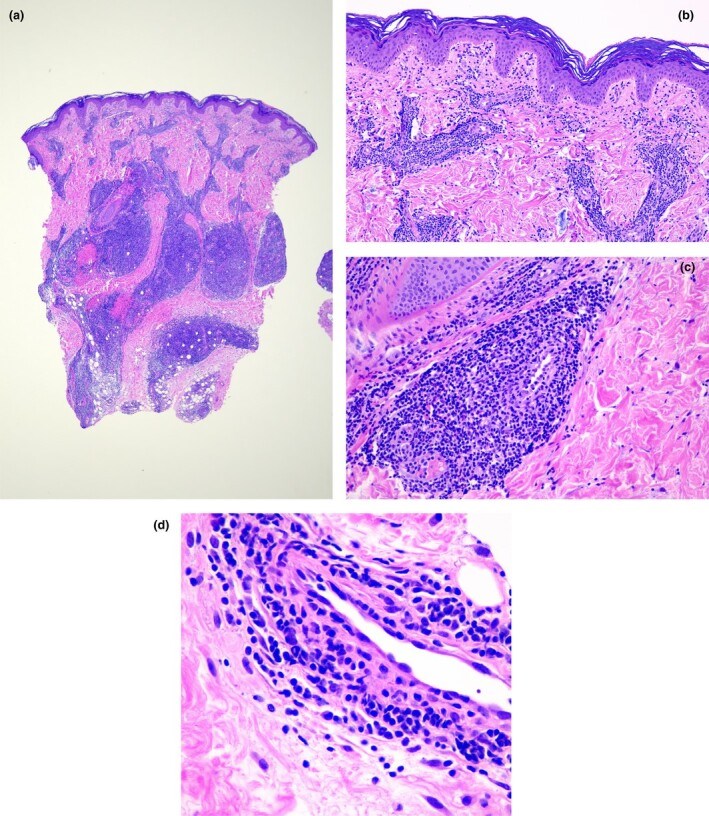
The current COVID-19 pandemic is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. The initial recognized symptoms were respiratory, sometimes culminating in severe respiratory distress requiring ventilation, and causing death in a percentage of those infected. As time has passed, other symptoms have been recognized. The initial reports of cutaneous manifestations were from Italian dermatologists, probably because Italy was the first European country to be heavily affected by the pandemic. The overall clinical presentation, course and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children differ from those in adults as do the cutaneous manifestations of childhood. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children after thorough and critical review of articles published in the literature and from the personal experience of a large panel of paediatric dermatologists in Europe. In Part 1, we discuss one of the first and most widespread cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19, chilblain-like lesions, and in Part 2 we expanded to other manifestations, including erythema multiforme, urticaria and Kawasaki disease-like inflammatory multisystemic syndrome. In this part of the review, we discuss the histological findings of COVID-19 manifestations, and the testing and management of infected children for both COVID-19 and any other pre-existing conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
Skin manifestations of COVID-19 in children: Part 2.
Andina D, Belloni-Fortina A, Bodemer C, Bonifazi E, Chiriac A, Colmenero I, Diociaiuti A, El-Hachem M, Fertitta L, van Gysel D, Hernández-Martín A, Hubiche T, Luca C, Martos-Cabrera L, Maruani A, Mazzotta F, Akkaya AD, Casals M, Ferrando J, Grimalt R, Grozdev I, Kinsler V, Morren MA, Munisami M, Nanda A, Novoa MP, Ott H, Pasmans S, Salavastru C, Zawar V, Torrelo A; ESPD Group for the Skin Manifestations of COVID-19.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021 Apr;46(3):451-461. doi: 10.1111/ced.14482. Epub 2020 Nov 9.PMID: 33166429 Free PMC article. Review.
Skin manifestations of COVID-19 in children: Part 1.
Andina D, Belloni-Fortina A, Bodemer C, Bonifazi E, Chiriac A, Colmenero I, Diociaiuti A, El-Hachem M, Fertitta L, van Gysel D, Hernández-Martín A, Hubiche T, Luca C, Martos-Cabrera L, Maruani A, Mazzotta F, Akkaya AD, Casals M, Ferrando J, Grimalt R, Grozdev I, Kinsler V, Morren MA, Munisami M, Nanda A, Novoa MP, Ott H, Pasmans S, Salavastru C, Zawar V, Torrelo A; ESPD Group for the Skin Manifestations of COVID-19.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021 Apr;46(3):444-450. doi: 10.1111/ced.14481. Epub 2020 Nov 12.PMID: 33180982 Free PMC article. Review.
[Cutaneous Manifestations Associated with COVID-19: A Narrative Review].
Relvas M, Calvão J, Oliveira R, Cardoso JC, Gonçalo M.Acta Med Port. 2021 Feb 1;34(2):128-136. doi: 10.20344/amp.14574. Epub 2020 Dec 14.PMID: 33315008 Review. Portuguese.
Skin Manifestations Associated with COVID-19: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.
Genovese G, Moltrasio C, Berti E, Marzano AV.Dermatology. 2021;237(1):1-12. doi: 10.1159/000512932. Epub 2020 Nov 24.PMID: 33232965 Free PMC article. Review.
Covid-19 pandemic and the skin.
Drenovska K, Schmidt E, Vassileva S.Int J Dermatol. 2020 Nov;59(11):1312-1319. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15189. Epub 2020 Sep 21.PMID: 32954488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
COVID-19 Associated Vasculitis Confirmed by the Tissues RT-PCR: A Case Series Report.
Belozerov KE, Avrusin IS, Andaryanova LI, Guseva AM, Shogenova ZS, Belanovich IN, Lobacheva AV, Kornishina TL, Isupova EA, Masalova VV, Kalashnikova OV, Nokhrin AV, Panova TF, Dutova YP, Myshkovskaya SL, Kostyunin KY, Komissarov AB, Chasnyk VG, Bregel LV, Kostik MM.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 13;11(3):870. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030870.PMID: 36979849 Free PMC article.
Dermatopathology of COVID-19 infection and vaccination.
Fernández-Figueras MT.Pathologie (Heidelb). 2022 Aug;43(Suppl 1):114-118. doi: 10.1007/s00292-022-01126-9. Epub 2022 Oct 5.PMID: 36197514 Free PMC article. Review.
Vansevičienė I, Krunkaitytė U, Dekerytė I, Beržanskis M, Lukošiūtė-Urbonienė A, Malcius D, Barauskas V.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Aug 14;58(8):1101. doi: 10.3390/medicina58081101.PMID: 36013568 Free PMC article.
Evolving Skin Rash as a Rare Cutaneous Manifestation in a Pediatric Patient With COVID-19 Infection.
Tilak K, Joung K, Apath M.Cureus. 2022 Jun 30;14(6):e26477. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26477. eCollection 2022 Jun.PMID: 35919370 Free PMC article.
COVID-19 Infection in Children: Diagnosis and Management.
Zhu F, Ang JY.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2022;24(4):51-62. doi: 10.1007/s11908-022-00779-0. Epub 2022 Apr 11.PMID: 35431658 Free PMC article. Review.
KMEL References
References
-
- Llamas‐Velasco M, Chicharro P, Rodríguez‐Jiménez P et al. Reply to "Clinical and histological characterization of vesicular COVID‐19 rashes: a prospective study in a tertiary care hospital": pseudoherpetic Grover disease seems to appear in patients with COVID‐19 infection. Clin Exp Dermatol 2020. 10.1111/ced.14305 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Epidemiology Working Group for NCIP Epidemic Response, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. [The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of novel coronavirus diseases (COVID‐19) in China] (in Chinese). Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2019; 2020(41): 141–51. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim guidelines for collecting, handling, and testing clinical specimens from persons for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019‐nCoV/lab/guidelines‐clinical‐specim... (accessed 5 June 2020).
-
- El Hachem M, Diociaiuti A, Concato C et al. A clinical, histopathological and laboratory study of 19 consecutive Italian paediatric patients with chilblain‐like lesions: lights and shadows on the relationship with COVID‐19 infection. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2020. 10.1111/jdv.16682 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hubiche T, Cardot‐Leccia N, Le Duff F et al. Chilblains appear as a manifestation of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and reveal features of type I interferonopathy and micro‐vasculopathy (in press). Preprint available at: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3586683 (accessed 26 August 2020).
-
- Xing Q, Li G, Xing Y et al. Precautions are needed for COVID‐19 patients with coinfection of common respiratory pathogens. MedRxiv 2020. 10.1101/2020.02.29.2002769 - DOI
-
- Wölfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID‐19. Nature 2020; 581: 465–9. - PubMed
-
- Lv H, Wu NC, Tsang OT et al. Cross‐reactive antibody response between SARS‐CoV‐2 and SARS‐CoV infections. Cell Rep 2020; 31: 107725. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds SD, Mathur AN, Chiu YE et al. Systemic immunosuppressive therapy for inflammatory skin diseases in children: expert consensus‐based guidance for clinical decision‐making during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Pediatr Dermatol 2020; 37: 424–4. - PubMed
-
- Wollenberg A, Flohr C, Simon D et al. European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis (ETFAD) statement on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐Cov‐2)‐infection and atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2020; 34: e241–2. - PubMed
-
- Cabrero‐Hernández M, García‐Salido A, Leoz‐Gordillo I et al. Severe SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in children with suspected acute abdomen: a case series from a tertiary hospital in Spain. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2020; 39: e195–8. - PubMed
-
- Villani A, Scalvenzi M, Fabbrocini G. Teledermatology: a useful tool to fight COVID‐19. J Dermatolog Treat 2020; 31: 325. - PubMed