Effect of Causative Micro-organisms on Patterns of Labeled White Blood Cells in Osteomyelitis
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Nuclear Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Kuwait.
- Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Kuwait.
- Department of Laboratories, Microbiology Unit, Farwania Hospital, Kuwait.
- Department of Medicine, Farwania Hospital, Kuwait.
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of microbiological characteristics of causative organisms on the scintigraphic patterns of labeled-white blood cells (WBC) scan in cases of proven osteomyelitis.
Materials and methods: Retrospective analysis of 25 patients referred with suspected osteomyelitis and had both bone and labeled-WBC scans performed and complete records of the microbiological culture of the causative organism. The bone and labeled-WBC scans were retrieved and reviewed by two nuclear medicine physicians. Any definite focal accumulation of labeled WBCs within the bone was considered positive for osteomyelitis. Diagnosis of osteomyelitis in the discharge summary was considered the reference standard and was based on a combination of the clinical scenario, imaging, and laboratory findings including microbiology. Correlation of the pattern of labeled WBC and the type of microorganisms was done.
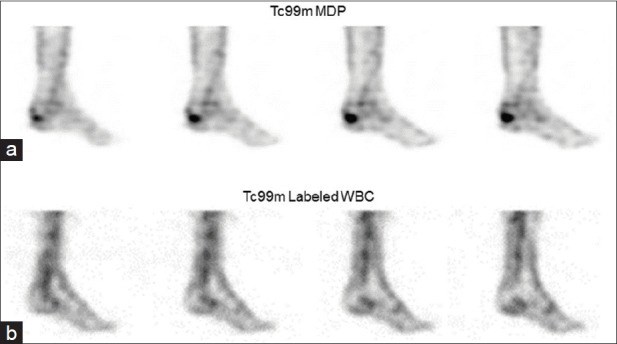
Results: A total of 16 patients were included in this study, seven females and nine males. Of these, seven patients had Gram-positive whereas nine patients had Gram-negative organisms. The majority (85.7%) of Gram-positive organisms showed increased accumulation of labeled WBCs, whereas only one-third (33.3%) of patients with Gram-negative organisms had such finding.
Conclusion: The pattern observed in this study shows that the false-negative results of labeled-WBC scans were mainly noted in patients with Gram-negative as opposed to Gram-positive infections. This confirms the experimental animal study findings that the secretion of anti-chemotactic factors by Gram-negative organisms, seems to be inhibiting the migration of labeled WBCs to the site of infection. The inhabitation is decreasing the accumulation of labeled WBCs and consequently resulting in a false-negative finding. The study adds to evidence that microbiological characteristics of the causative organisms are another explanation for the false-negative WBC in proven osteomyelitis.
Keywords: Bone scan; Gram-negative bacteria; Gram-positive bacteria; labeled white blood cells; osteomyelitis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
Elgazzar AH, Dannoon S, Sarikaya I, Farghali M, Junaid TA.Med Princ Pract. 2017;26(5):415-420. doi: 10.1159/000480083. Epub 2017 Aug 8.PMID: 28797001 Free PMC article.
Sonmezoglu K, Sonmezoglu M, Halac M, Akgün I, Türkmen C, Onsel C, Kanmaz B, Solanki K, Britton KE, Uslu I.J Nucl Med. 2001 Apr;42(4):567-74.PMID: 11337543
Seabold JE, Nepola JV, Marsh JL, Hawes DR, Justin EP, Ponto JA, Pettit WA, el-Khoury GY, Kirchner PT.Radiology. 1991 Sep;180(3):741-7. doi: 10.1148/radiology.180.3.1871288.PMID: 1871288
Nuclear medicine methods for evaluation of skeletal infection among other diagnostic modalities.
El-Maghraby TA, Moustafa HM, Pauwels EK.Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006 Sep;50(3):167-92.PMID: 16868532 Review.
Lauri C, Tamminga M, Glaudemans AWJM, Juárez Orozco LE, Erba PA, Jutte PC, Lipsky BA, IJzerman MJ, Signore A, Slart RHJA.Diabetes Care. 2017 Aug;40(8):1111-1120. doi: 10.2337/dc17-0532.PMID: 28733376 Review.
KMEL References
References
-
- Kumar JV, Robbins SL. Acute and chronic inflammation. In: Cotran RS, Kumar JV, Collins T, Robbins SL, editors. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 1999. pp. 25–46.
-
- Carek PJ, Dickerson LM, Sack JL. Diagnosis and management of osteomyelitis. Am Fam Physician. 2001;63:2413–20. - PubMed
-
- Kaim AH, Gross T, von Schulthess GK. Imaging of chronic posttraumatic osteomyelitis. Eur Radiol. 2002;12:1193–202. - PubMed
-
- Kruskal JB. Can USPIO-enhanced spinal MR imaging help distinguish acute infectious osteomyelitis from chronic infectious and inflammatory processes? Radiology. 2008;248:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Gold RH, Tong DJ, Crim JR, Seeger LL. Imaging the diabetic foot. Skeletal Radiol. 1995;24:563–71. - PubMed
-
- Hatzenbuehler J, Pulling TJ. Diagnosis and management of osteomyelitis. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:1027–33. - PubMed
-
- Ivancević V, Dodig D, Livaković M, Hancević J, Ivancević D. Comparison of three-phase bone scan, three-phase 99m-Tc-HM-PAO leukocyte scan and 67-gallium scan in chronic bone infection. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;355:189–98. - PubMed
-
- de Winter F, van de Wiele C, Vogelaers D, de Smet K, Verdonk R, Dierckx RA, et al. Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose-position emission tomography: A highly accurate imaging modality for the diagnosis of chronic musculoskeletal infections. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A:651–60. - PubMed
-
- Palestro CJ, Kim CK, Swyer AJ, Vallabhajosula S, Goldsmith SJ. Radionuclide diagnosis of vertebral osteomyelitis: Indium-111-leukocyte and technetium-99m-methylene diphosphonate bone scintigraphy. J Nucl Med. 1991;32:1861–5. - PubMed
-
- Whalen JL, Brown ML, McLeod R, Fitzgerald RH., Jr Limitations of indium leukocyte imaging for the diagnosis of spine infections. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1991;16:193–7. - PubMed
-
- Hovi I. Complicated bone and soft-tissue infections. Imaging with 0.1 T MR and 99mTc-HMPAO-labeled leukocytes. Ff. Acta Radiol. 1996;37:870–6. - PubMed
-
- Palestro CJ, Love C. Radionuclide imaging of musculoskeletal infection: Conventional agents. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2007;11:335–52. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Ulloa M, Vasavada PJ, Hanslits ML, Volarich DT, Elgazzar AH. Diagnosis of vertebral osteomyelitis: Clinical, radiological and scintigraphic features. Orthopedics. 1985;8:1144–50. - PubMed
-
- Waldvogel FA, Medoff G, Swartz MN. Osteomyelitis: A review of clinical features, therapeutic considerations and unusual aspects. N Engl J Med. 1970;282:198–206. - PubMed
-
- Kahn DS, Pritzker KP. The pathophysiology of bone infection. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973;96:12–9. - PubMed
-
- Kim EE, Pjura GA, Lowry PA, Gobuty AH, Traina JF. Osteomyelitis complicating fracture: Pitfalls of 111In leukocyte scintigraphy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;148:927–30. - PubMed
-
- Kumar JV, Abbas AK, Astor JC, editors. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier-Saunders; 2015. Inflammation and repair; pp. 69–112.
-
- Torda AJ, Gottlieb T, Bradbury R. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: Analysis of 20 cases and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:320–8. - PubMed
-
- Song KS, Ogden JA, Ganey T, Guidera KJ. Contiguous discitis and osteomyelitis in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997;17:470–7. - PubMed