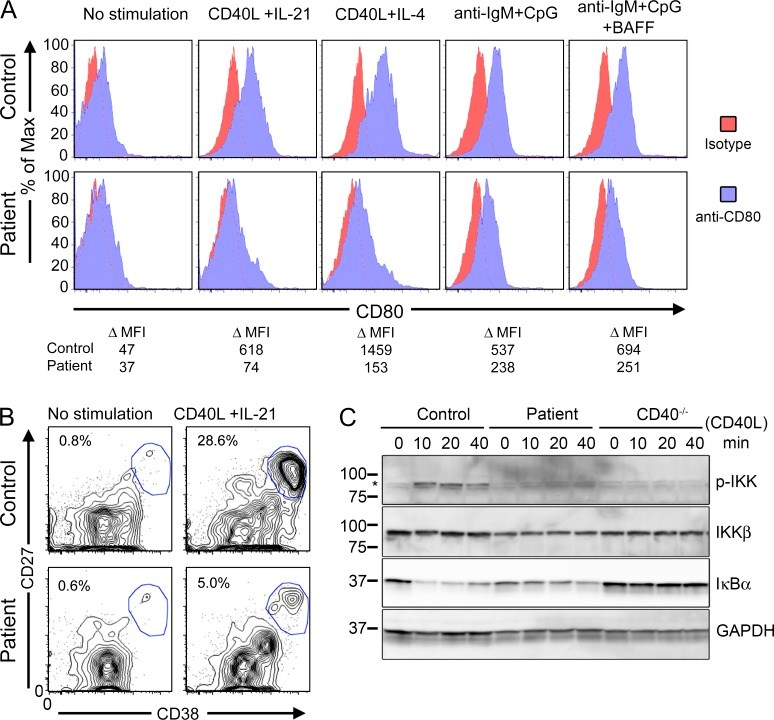
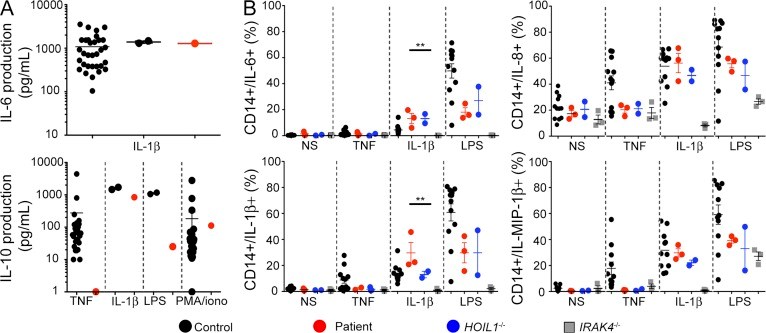
Human HOIP and LUBAC deficiency underlies autoinflammation, immunodeficiency, amylopectinosis, and lymphangiectasia
Bertrand Boisson 1, Emmanuel Laplantine 2, Kerry Dobbs 3, Aurélie Cobat 4, Nadine Tarantino 2, Melissa Hazen 3, Hart G W Lidov 3, Gregory Hopkins 3, Likun Du 3, Aziz Belkadi 4, Maya Chrabieh 4, Yuval Itan 1, Capucine Picard 5, Jean-Christophe Fournet 6, Hermann Eibel 7, Erdyni Tsitsikov 3, Sung-Yun Pai 3, Laurent Abel 8, Waleed Al-Herz 9, Jean-Laurent Casanova 10, Alain Israel 2, Luigi D Notarangelo 11
Affiliations
Affiliations
- St. Giles Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Rockefeller Branch, Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065.
- Laboratory of Signaling and Pathogenesis, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, UMR 3691, Institut Pasteur, 75724 Paris, France.
- Division of Immunology and The Manton Center for Orphan Disease Research, Department of Pathology, Division of Hematology-Oncology, Boston Children's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115.
- Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Necker Branch, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale UMR1163; Study Center of Immunodeficiencies, APHP; Pediatric Hematology-Immunology Unit, Necker Hospital for Sick Children, 75015 Paris, France Paris Descartes University, Imagine Institute, 75015 Paris, France.
- St. Giles Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Rockefeller Branch, Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065 Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Necker Branch, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale UMR1163; Study Center of Immunodeficiencies, APHP; Pediatric Hematology-Immunology Unit, Necker Hospital for Sick Children, 75015 Paris, France Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Necker Branch, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale UMR1163; Study Center of Immunodeficiencies, APHP; Pediatric Hematology-Immunology Unit, Necker Hospital for Sick Children, 75015 Paris, France Paris Descartes University, Imagine Institute, 75015 Paris, France.
- Paris Descartes University, Imagine Institute, 75015 Paris, France.
- University Medical Centre Freiburg, Centre of Chronic Immunodeficiency, 79098 Freiburg, Germany.
- St. Giles Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Rockefeller Branch, Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065 Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Necker Branch, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale UMR1163; Study Center of Immunodeficiencies, APHP; Pediatric Hematology-Immunology Unit, Necker Hospital for Sick Children, 75015 Paris, France Paris Descartes University, Imagine Institute, 75015 Paris, France.
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology Unit, Department of Pediatrics, Al-Sabah Hospital, 70459 Kuwait City, Kuwait Department of Pediatrics, Kuwait University, 13110 Kuwait City, Kuwait.
- St. Giles Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Rockefeller Branch, Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065 Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Necker Branch, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale UMR1163; Study Center of Immunodeficiencies, APHP; Pediatric Hematology-Immunology Unit, Necker Hospital for Sick Children, 75015 Paris, France Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, Necker Branch, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale UMR1163; Study Center of Immunodeficiencies, APHP; Pediatric Hematology-Immunology Unit, Necker Hospital for Sick Children, 75015 Paris, France Paris Descartes University, Imagine Institute, 75015 Paris, France Howard Hughes Medical Institute, New York, NY 10065 casanova@rockefeller.edu luigi.notarangelo@childrens.harvard.edu.
- Division of Immunology and The Manton Center for Orphan Disease Research, Department of Pathology, Division of Hematology-Oncology, Boston Children's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115 Harvard Stem Cell Institute, Harvard University, Boston, MA 02115 casanova@rockefeller.edu luigi.notarangelo@childrens.harvard.edu.
Abstract
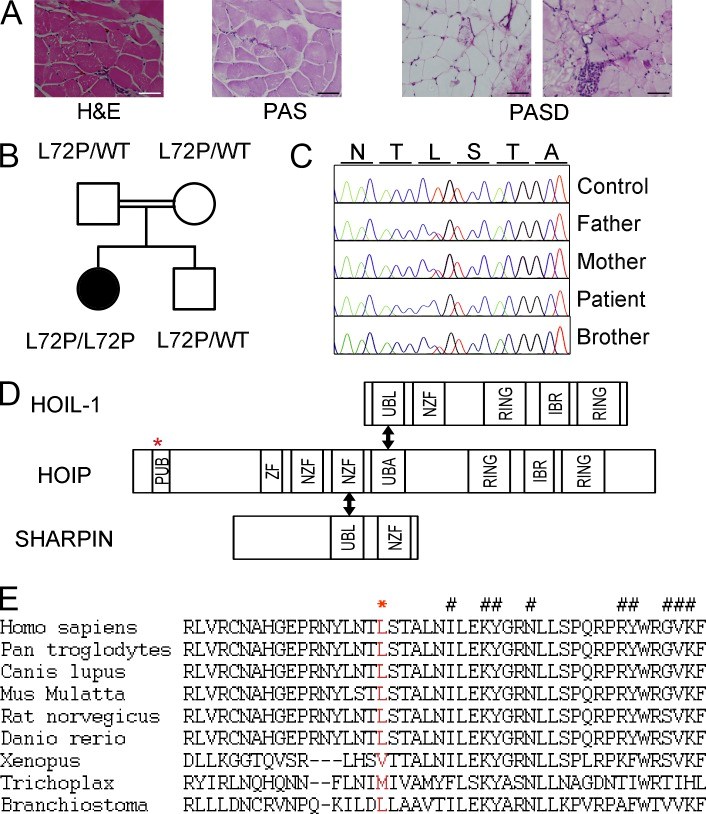
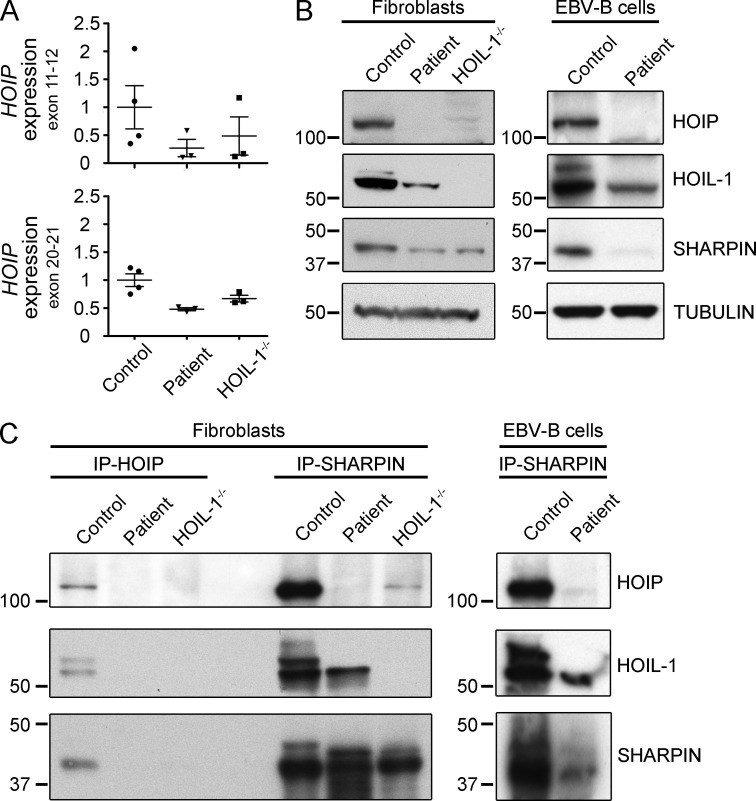
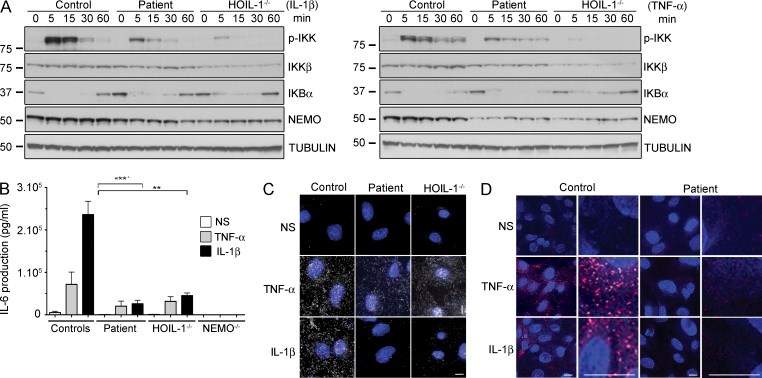
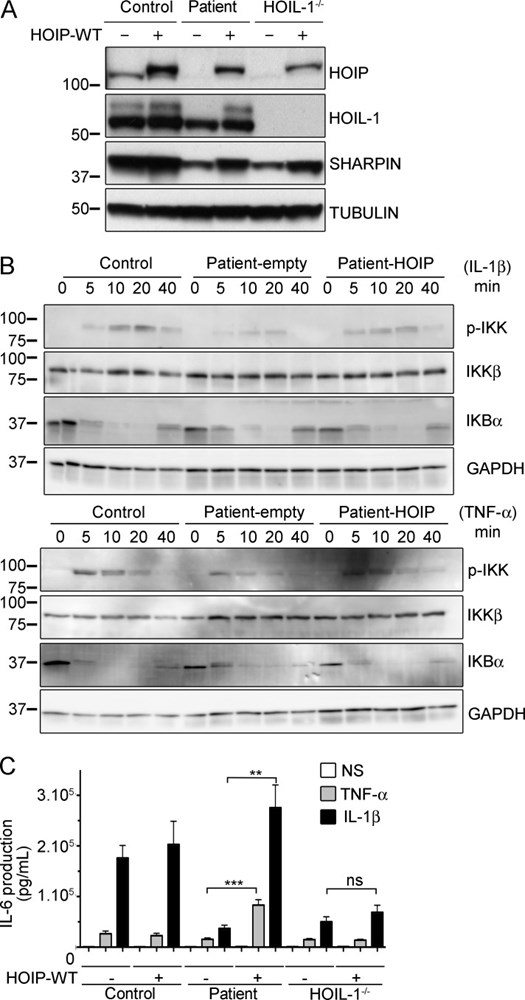
Inherited, complete deficiency of human HOIL-1, a component of the linear ubiquitination chain assembly complex (LUBAC), underlies autoinflammation, infections, and amylopectinosis. We report the clinical description and molecular analysis of a novel inherited disorder of the human LUBAC complex. A patient with multiorgan autoinflammation, combined immunodeficiency, subclinical amylopectinosis, and systemic lymphangiectasia, is homozygous for a mutation in HOIP, the gene encoding the catalytic component of LUBAC. The missense allele (L72P, in the PUB domain) is at least severely hypomorphic, as it impairs HOIP expression and destabilizes the whole LUBAC complex. Linear ubiquitination and NF-κB activation are impaired in the patient's fibroblasts stimulated by IL-1β or TNF. In contrast, the patient's monocytes respond to IL-1β more vigorously than control monocytes. However, the activation and differentiation of the patient's B cells are impaired in response to CD40 engagement. These cellular and clinical phenotypes largely overlap those of HOIL-1-deficient patients. Clinical differences between HOIL-1- and HOIP-mutated patients may result from differences between the mutations, the loci, or other factors. Our findings show that human HOIP is essential for the assembly and function of LUBAC and for various processes governing inflammation and immunity in both hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells.
Figures
Similar articles
Boisson B, Laplantine E, Prando C, Giliani S, Israelsson E, Xu Z, Abhyankar A, Israël L, Trevejo-Nunez G, Bogunovic D, Cepika AM, MacDuff D, Chrabieh M, Hubeau M, Bajolle F, Debré M, Mazzolari E, Vairo D, Agou F, Virgin HW, Bossuyt X, Rambaud C, Facchetti F, Bonnet D, Quartier P, Fournet JC, Pascual V, Chaussabel D, Notarangelo LD, Puel A, Israël A, Casanova JL, Picard C.Nat Immunol. 2012 Dec;13(12):1178-86. doi: 10.1038/ni.2457. Epub 2012 Oct 28.PMID: 23104095 Free PMC article.
Oda H, Beck DB, Kuehn HS, Sampaio Moura N, Hoffmann P, Ibarra M, Stoddard J, Tsai WL, Gutierrez-Cruz G, Gadina M, Rosenzweig SD, Kastner DL, Notarangelo LD, Aksentijevich I.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 18;10:479. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00479. eCollection 2019.PMID: 30936877 Free PMC article.
Bowman J, Rodgers MA, Shi M, Amatya R, Hostager B, Iwai K, Gao SJ, Jung JU.mBio. 2015 Nov 17;6(6):e01777-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01777-15.PMID: 26578682 Free PMC article.
An Update on Autoinflammatory Diseases: Relopathies.
Steiner A, Harapas CR, Masters SL, Davidson S.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018 May 30;20(7):39. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0749-x.PMID: 29846841 Review.
Linear ubiquitination-mediated NF-κB regulation and its related disorders.
Tokunaga F.J Biochem. 2013 Oct;154(4):313-23. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvt079. Epub 2013 Aug 21.PMID: 23969028 Review.
Cited by
RIPK1 in the inflammatory response and sepsis: Recent advances, drug discovery and beyond.
Liu X, Tang AL, Chen J, Gao N, Zhang G, Xiao C.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 5;14:1114103. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1114103. eCollection 2023.PMID: 37090690 Free PMC article. Review.
RNF31 promotes tumorigenesis via inhibiting RIPK1 kinase-dependent apoptosis.
Zhang J, Tu H, Zheng Z, Zhao X, Lin X.Oncogene. 2023 May;42(19):1585-1596. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02669-8. Epub 2023 Mar 30.PMID: 36997719
Dendritic cells in inborn errors of immunity.
Gupta S, Agrawal A.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 23;14:1080129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1080129. eCollection 2023.PMID: 36756122 Free PMC article. Review.
Innate and adaptive immune abnormalities underlying autoimmune diseases: the genetic connections.
Chi X, Huang M, Tu H, Zhang B, Lin X, Xu H, Dong C, Hu X.Sci China Life Sci. 2023 Feb 3:1-36. doi: 10.1007/s11427-021-2187-3. Online ahead of print.PMID: 36738430 Free PMC article. Review.
Du Y, Liu M, Nigrovic PA, Dedeoglu F, Lee PY.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Mar;151(3):607-618. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.12.816. Epub 2023 Jan 25.PMID: 36707349 Review.
KMEL References
References
-
- Al-Herz W., Bousfiha A., Casanova J.L., Chatila T., Conley M.E., Cunningham-Rundles C., Etzioni A., Franco J.L., Gaspar H.B., Holland S.M., et al. . 2014. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update on the classification from the international union of immunological societies expert committee for primary immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 5:162 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00162 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alsina L., Israelsson E., Altman M.C., Dang K.K., Ghandil P., Israel L., von Bernuth H., Baldwin N., Qin H., Jin Z., et al. . 2014. A narrow repertoire of transcriptional modules responsive to pyogenic bacteria is impaired in patients carrying loss-of-function mutations in MYD88 or IRAK4. Nat. Immunol. 15:1134–1142. 10.1038/ni.3028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashida N., Senbanerjee S., Kodama S., Foo S.Y., Coggins M., Spencer J.A., Zamiri P., Shen D., Li L., Sciuto T., et al. . 2011. IKKβ regulates essential functions of the vascular endothelium through kinase-dependent and -independent pathways. Nat. Commun. 2:318 10.1038/ncomms1317 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boisson B., Laplantine E., Prando C., Giliani S., Israelsson E., Xu Z., Abhyankar A., Israël L., Trevejo-Nunez G., Bogunovic D., et al. . 2012. Immunodeficiency, autoinflammation and amylopectinosis in humans with inherited HOIL-1 and LUBAC deficiency. Nat. Immunol. 13:1178–1186. 10.1038/ni.2457 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Byun M., Abhyankar A., Lelarge V., Plancoulaine S., Palanduz A., Telhan L., Boisson B., Picard C., Dewell S., Zhao C., et al. . 2010. Whole-exome sequencing-based discovery of STIM1 deficiency in a child with fatal classic Kaposi sarcoma. J. Exp. Med. 207:2307–2312. 10.1084/jem.20101597 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Courtois G., Smahi A., Reichenbach J., Döffinger R., Cancrini C., Bonnet M., Puel A., Chable-Bessia C., Yamaoka S., Feinberg J., et al. . 2003. A hypermorphic IkappaBalpha mutation is associated with autosomal dominant anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and T cell immunodeficiency. J. Clin. Invest. 112:1108–1115. 10.1172/JCI18714 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Döffinger R., Smahi A., Bessia C., Geissmann F., Feinberg J., Durandy A., Bodemer C., Kenwrick S., Dupuis-Girod S., Blanche S., et al. . 2001. X-linked anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia with immunodeficiency is caused by impaired NF-kappaB signaling. Nat. Genet. 27:277–285. 10.1038/85837 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dubois S.M., Alexia C., Wu Y., Leclair H.M., Leveau C., Schol E., Fest T., Tarte K., Chen Z.J., Gavard J., and Bidère N.. 2014. A catalytic-independent role for the LUBAC in NF-κB activation upon antigen receptor engagement and in lymphoma cells. Blood. 123:2199–2203. 10.1182/blood-2013-05-504019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferrari S., Giliani S., Insalaco A., Al-Ghonaium A., Soresina A.R., Loubser M., Avanzini M.A., Marconi M., Badolato R., Ugazio A.G., et al. . 2001. Mutations of CD40 gene cause an autosomal recessive form of immunodeficiency with hyper IgM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 98:12614–12619. 10.1073/pnas.221456898 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fuss I.J., Strober W., Cuccherini B.A., Pearlstein G.R., Bossuyt X., Brown M., Fleisher T.A., and Horgan K.. 1998. Intestinal lymphangiectasia, a disease characterized by selective loss of naive CD45RA+ lymphocytes into the gastrointestinal tract. Eur. J. Immunol. 28:4275–4285. 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199812)28:12<4275::AID-IMMU4275>3.0.CO;2-P - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haas T.L., Emmerich C.H., Gerlach B., Schmukle A.C., Cordier S.M., Rieser E., Feltham R., Vince J., Warnken U., Wenger T., et al. . 2009. Recruitment of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex stabilizes the TNF-R1 signaling complex and is required for TNF-mediated gene induction. Mol. Cell. 36:831–844. 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.10.013 - DOI - PubMed
-
- HogenEsch H., Janke S., Boggess D., and Sundberg J.P.. 1999. Absence of Peyer’s patches and abnormal lymphoid architecture in chronic proliferative dermatitis (cpdm/cpdm) mice. J. Immunol. 162:3890–3896. - PubMed
-
- HogenEsch H., Torregrosa S.E., Boggess D., Sundberg B.A., Carroll J., and Sundberg J.P.. 2001. Increased expression of type 2 cytokines in chronic proliferative dermatitis (cpdm) mutant mice and resolution of inflammation following treatment with IL-12. Eur. J. Immunol. 31:734–742. 10.1002/1521-4141(200103)31:3<734::AID-IMMU734>3.0.CO;2-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee C.E., Fulcher D.A., Whittle B., Chand R., Fewings N., Field M., Andrews D., Goodnow C.C., and Cook M.C.. 2014. Autosomal-dominant B-cell deficiency with alopecia due to a mutation in NFKB2 that results in nonprocessable p100. Blood. 124:2964–2972. 10.1182/blood-2014-06-578542 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M.L., Dong K.C., Yu C., Phu L., Gao X., Hannoush R.N., Hymowitz S.G., Kirkpatrick D.S., Dixit V.M., and Kelley R.F.. 2012. Engineering and structural characterization of a linear polyubiquitin-specific antibody. J. Mol. Biol. 418:134–144. - PubMed
-
- McKenna A., Hanna M., Banks E., Sivachenko A., Cibulskis K., Kernytsky A., Garimella K., Altshuler D., Gabriel S., Daly M., and DePristo M.A.. 2010. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 20:1297–1303. 10.1101/gr.107524.110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peltzer N., Rieser E., Taraborrelli L., Draber P., Darding M., Pernaute B., Shimizu Y., Sarr A., Draberova H., Montinaro A., et al. . 2014. HOIP deficiency causes embryonic lethality by aberrant TNFR1-mediated endothelial cell death. Cell Reports. 9:153–165. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.066 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Recher M., Berglund L.J., Avery D.T., Cowan M.J., Gennery A.R., Smart J., Peake J., Wong M., Pai S.Y., Baxi S., et al. . 2011. IL-21 is the primary common γ chain-binding cytokine required for human B-cell differentiation in vivo. Blood. 118:6824–6835. 10.1182/blood-2011-06-362533 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smahi A., Courtois G., Vabres P., Yamaoka S., Heuertz S., Munnich A., Israël A., Heiss N.S., Klauck S.M., Kioschis P., et al. . The International Incontinentia Pigmenti (IP) Consortium. 2000. Genomic rearrangement in NEMO impairs NF-kappaB activation and is a cause of incontinentia pigmenti. Nature. 405:466–472. 10.1038/35013114 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang K., Kim C., Bradfield J., Guo Y., Toskala E., Otieno F.G., Hou C., Thomas K., Cardinale C., Lyon G.J., et al. . 2013. Whole-genome DNA/RNA sequencing identifies truncating mutations in RBCK1 in a novel Mendelian disease with neuromuscular and cardiac involvement. Genome Med. 5:67 10.1186/gm471 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Willmann K.L., Klaver S., Doğu F., Santos-Valente E., Garncarz W., Bilic I., Mace E., Salzer E., Conde C.D., Sic H., et al. . 2014. Biallelic loss-of-function mutation in NIK causes a primary immunodeficiency with multifaceted aberrant lymphoid immunity. Nat. Commun. 5:5360 10.1038/ncomms6360 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zak D.E., Schmitz F., Gold E.S., Diercks A.H., Peschon J.J., Valvo J.S., Niemistö A., Podolsky I., Fallen S.G., Suen R., et al. . 2011. Systems analysis identifies an essential role for SHANK-associated RH domain-interacting protein (SHARPIN) in macrophage Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 108:11536–11541. 10.1073/pnas.1107577108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed