Clinical remission of rheumatoid arthritis in a multicenter real-world study in Asia-Pacific region
Xing Sun 1, Ru Li 1, Yueming Cai 2, Adeeba Al-Herz 3, Manjari Lahiri 4, Minhaj Rahim Choudhury 5, Rudy Hidayat 6, Bagus Putu Putra Suryana 7, Yuko Kaneko 8, Keishi Fujio 9, Nguyen Van Hung 10, Sapan Pandya 11, Leong Khai Pang 12, Wanruchada Katchamart 13, Keshav Raj Sigdel 14, Buddhi Paudyal 14, Pongthorn Narongroeknawin 15, Parawee Chevaisrakul 16, Feng Sun 17, Yu Lu 18, Carmen Ho 19, Swan Sim Yeap 20, Zhanguo Li 1; APLAR RA SIG group
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Rheumatology & Immunology, Peking University People's Hospital, 11 Xizhimen South St., Beijing 100044, China.
- Department of Rheumatology & Immunology, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, China.
- Rheumatology Unit, Department of Internal Medicine, Al-Amiri Hospital, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
- Department of Medicine, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore.
- Department of Rheumatology, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- Department of Internal Medicine, Cipto Mangunkusumo National Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta.
- Rheumatology Division, Internal Medicine Department, Brawijaya University - Saiful Anwar Hospital, Indonesia.
- Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- Department of Allergy and Rheumatology, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan.
- Department of Rheumatology, Bach Mai Hospital, Giai Phong Road, Dong Da District, Hanoi, Vietnam.
- Vedanta institute of medical sciences and VS hospital, Ahmedabad, India.
- Department of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore.
- Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand.
- Department of Internal Medicine, Patan Academy of Health Sciences, Kathmandu, Nepal.
- Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, Phramongkutklao Hospital and College of Medicine, Bangkok, Thailand.
- Division of Allergy, Immunology and Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand.
- Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Peking University, 38 Xueyuan Road, Haidian District, Beijing 100191, China.
- School of Mathematical Science, Nankai University, No. 94 Weijin Road, Nankai District, Tianjin, 300071, China.
- Division of Rheumatology, Dept of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China.
- Department of Medicine, Subang Jaya Medical Centre, Selangor.
Abstract
Background: Clinical remission is an attainable goal for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). However, data on RA remission rates from multinational studies in the Asia-Pacific region are limited. We conducted a cross-sectional multicentric study to evaluate the clinical remission status and the related factors in RA patients in the Asia-Pacific region.
Methods: RA patients receiving standard care were enrolled consecutively from 17 sites in 11 countries from APLAR RA SIG group. Data were collected on-site by rheumatologists with a standardized case-report form. Remission was analyzed by different definitions including disease activity score using 28 joints (DAS28) based on ESR and CRP, clinical disease activity index (CDAI), simplified disease activity index (SDAI), Boolean remission definition, and clinical deep remission (CliDR). Logistic regression was used to determine related factors of remission.
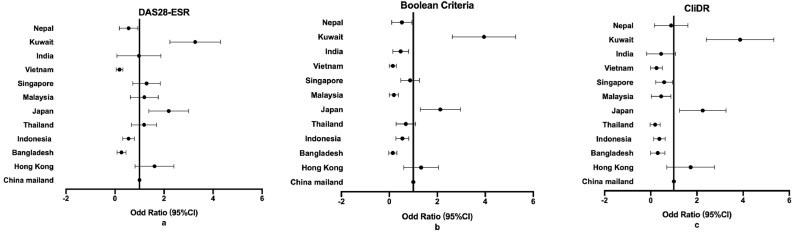
Findings: A total of 2010 RA patients was included in the study, the overall remission rates were 62•3% (DAS28-CRP), 35•5% (DAS28-ESR), 30•8% (CDAI), 26•5% (SDAI), 24•7% (Boolean), and 17•1% (CliDR), respectively, and varied from countries to countries in the Asia-Pacific region. Biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) prescription rate was low (17•9%). Compared to patients in non-remission, patients in remission had higher rates of b/tsDMARDs usage and lower rates of GC usage. The favorable related factors were male sex, younger age, fewer comorbidities, fewer extra-articular manifestations (EAM), and use of b/tsDMARDs, while treatment with GC was negatively related to remission.
Interpretation: Remission rates were low and varied in the Asia-Pacific region. Treatment with b/tsDMARDs and less GC usage were related to higher remission rate. There is an unmet need for RA remission in the Asia-Pacific region.
Conflict of interest statement
ML reports speaker fees from Abbvie and Johnson & Johnson, conference sponsorship from Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, and Sanofi, and has provided advisory services for Gilead, Eli Lilly. KF has received grants or contracts from Chugai, Bristol Myers, Abbvie, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Tsumura, Asahi Kasei, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Esai, Japan Blood Products Organization, Novartis, Sanofi, and Astellas, reports payments or honoraria from Astellas, Abbvie, Amgen, Ayumi, MSD, Esai, Ono, Gilead, Kowa, Sanofi, Japan Blood Products Organization, Novartis, Pfizer, Bristol Myers, Mylan EPD, Janssen, Asahi Kasei, Daiichi Sankyo, Chugai, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Eli Lilly, and Boehringer Ingelheim and has participated in the Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Asahi Kasei, Astellas, Abbvie, Amgen, Ono, Gilead, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Bristol Myers, and Mylan EPD. PC reports honoraria from Novartis and Johnson and Johnson, is a member of the advisory board for Johnson & Johnson, and reports samples of Amgevita, Baricitinib, and Ixekizumab. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
Koh JH, Lee Y, Kim HA, Kim J, Shin K.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2022 May 13;14:1759720X221096363. doi: 10.1177/1759720X221096363. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35586514 Free PMC article.
Clinical deep remission and related factors in a large cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Liu JJ, Li R, Gan YZ, Zhang RJ, Li J, Cai YM, Zhao JX, Liao H, Xu J, Shi LJ, Li J, Li SG, Sun XL, He J, Liu X, Ye H, Li ZG.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 May 5;132(9):1009-1014. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000227.PMID: 30946065 Free PMC article.
Cai YM, Li R, Ye H, He J, Sun XL, Jin JY, Liu JJ, Gan YZ, You XJ, Xu J, Shi LJ, Cheng G, Wang QW, Li ZG.Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Jun 20;133(12):1397-1403. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000811.PMID: 32496302 Free PMC article.
Leong JWY, Cheung PP, Dissanayake S, Fong WWS, Leong KH, Leung YY, Lim AYN, Lui NL, Manghani M, Santosa A, Sriranganathan MK, Suresh E, Tan TC, Teng GG, Lahiri M.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Feb;23(2):140-152. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13762. Epub 2019 Dec 19.PMID: 31859424 Review.
Gaujoux-Viala C, Mouterde G, Baillet A, Claudepierre P, Fautrel B, Le Loët X, Maillefert JF.Joint Bone Spine. 2012 Mar;79(2):149-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.04.008. Epub 2011 Jun 15.PMID: 21680221 Review.
Cited by
Al-Saleh J, Almarzooqi A, Negm AA.Open Access Rheumatol. 2023 May 10;15:51-63. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S408894. eCollection 2023.PMID: 37192954 Free PMC article.
Orthorexia Nervosa Practices in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The DORA Study.
Sifakaki M, Gkiouras K, Lindqvist HM, Marakis G, Petropoulou A, Donini LM, Bogdanos DP, Grammatikopoulou MG.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 31;15(3):713. doi: 10.3390/nu15030713.PMID: 36771419 Free PMC article.
Combe BG, Tanaka Y, Buch MH, Nash P, Burmester GR, Kivitz AJ, Bartok B, Pechonkina A, Xia K, Emoto K, Kano S, Hendrikx TK, Landewé RBM, Aletaha D.Rheumatol Ther. 2023 Feb;10(1):53-70. doi: 10.1007/s40744-022-00498-x. Epub 2022 Oct 9.PMID: 36209441 Free PMC article.
Koh JH, Lee Y, Kim HA, Kim J, Shin K.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2022 May 13;14:1759720X221096363. doi: 10.1177/1759720X221096363. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35586514 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe RBM, Bijlsma JWJ. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):685–699. - PubMed
-
- Prevoo ML, van 't Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38(1):44–48. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Breedveld FC, Schiff MH. A simplified disease activity index for rheumatoid arthritis for use in clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003;42(2):244–257. - PubMed
-
- Dave B, Desai S, Ramadwar M. Kimura disease with proliferative squamous metaplasia: an unusual finding and a potential diagnostic pitfall. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2007;50(4):771–773. - PubMed
-
- Pincus T, Swearingen CJ, Bergman M, Yazici Y. RAPID3 (Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3), a rheumatoid arthritis index without formal joint counts for routine care: proposed severity categories compared to disease activity score and clinical disease activity index categories. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(11):2136–2147. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Rasker JJ, Boers M, Wells GA, Michaud K. Minimal disease activity, remission, and the long-term outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57(6):935–942. - PubMed
-
- Sokka T, Hetland ML, Makinen H. Remission and rheumatoid arthritis - Data on patients receiving usual care in twenty-four countries. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2008;58(9):2642–2651. - PubMed
-
- Chandrashekara S, Shobha V, Dharmanand BG. Factors influencing remission in rheumatoid arthritis patients: results from Karnataka rheumatoid arthritis comorbidity (KRAC) study. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases. 2018;21(11):1977–1985. - PubMed
-
- Darawankul B, Chaiamnuay S, Pakchotanon R, Asavatanabodee P, Narongroeknawin P. The good EULAR response at the first year is strongly predictive of clinical remission in rheumatoid arthritis: results from the TARAC cohort. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34(1):43–49. - PubMed
-
- Littlejohn G, Roberts L, Bird P. Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Australian OPAL Cohort Show Significant Improvement in Disease Activity over 5 Years: A Multicenter Observational Study. Journal of Rheumatology. 2015;42(9):1603–1609. - PubMed
-
- Aga A-B, Lie E, Uhlig T. Time trends in disease activity, response and remission rates in rheumatoid arthritis during the past decade: results from the NOR-DMARD study 2000-2010. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2015;74(2):381–388. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Li R, Da Z. Remission assessment of rheumatoid arthritis in daily practice in China: a cross-sectional observational study. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(3):597–605. - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Wang X, Zhong S, Florentinus S, Monastiriakos K, Smolen JS. Differences in disease activity measures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who achieved DAS, SDAI, or CDAI remission but not Boolean remission. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020;50(2):276–284. - PubMed
-
- Kuriya B, Xiong J, Boire G. Earlier time to remission predicts sustained clinical remission in early rheumatoid arthritis–results from the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) J Rheumatol. 2014;41(11):2161–2166. - PubMed
-
- Hetland ML, Jensen DV, Krogh NS. Monitoring patients with rheumatoid arthritis in routine care: experiences from a treat-to-target strategy using the DANBIO registry. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32 (5 Suppl 85): S-141-6. - PubMed
-
- Nam JL, Takase-Minegishi K, Ramiro S. Efficacy of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: a systematic literature review informing the 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2017;76(6):1113–1136. - PubMed
-
- Moller-Bisgaard S, Georgiadis S, Horslev-Petersen K. Predictors of joint damage progression and stringent remission in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis in clinical remission. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 2020 - PubMed
-
- Burmester GR, Buttgereit F, Bernasconi C. Continuing versus tapering glucocorticoids after achievement of low disease activity or remission in rheumatoid arthritis (SEMIRA): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;396(10246):267–276. - PubMed