Ferritin level: A predictor of severity and mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients
Moudhi Alroomi 1, Rajesh Rajan 2, Abdulaziz A Omar 3, Ahmad Alsaber 4, Jiazhu Pan 4, Mina Fatemi 5, Kobalava D Zhanna 6, Wael Aboelhassan 7, Farah Almutairi 8, Naser Alotaibi 9, Mohammad A Saleh 8, Noor AlNasrallah 9, Bader Al-Bader 8, Haya Malhas 10, Maryam Ramadhan 11, Mohammed Abdullah 1, Hassan Abdelnaby 12 13
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Infectious Diseases, Infectious Diseases Hospital, Shuwaikh Medical Area, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
- Department of Cardiology, Sabah Al Ahmad Cardiac Centre, Al Amiri Hospital, Kuwait City, Sharq, Kuwait.
- Department of Medicine, Jaber Al Ahmed Hospital, South Surra, Kuwait.
- Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, United Kingdom.
- Public Health and Commissioning Manager, Nottinghamshire County Council, Nottingham, United Kingdom.
- Department of Internal Medicine with the Subspecialty of Cardiology and Functional Diagnostics Named after V.S. Moiseev, Peoples' Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), Moscow, Russian Federation.
- Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Jaber Al Ahmed Hospital, South Surra, Kuwait.
- Department of Medicine, Farwaniya Hospital, Farwaniya, Kuwait.
- Department of Medicine, Al Adan Hospital, Hadiya, Kuwait.
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Mubarak Al-Kabeer Hospital, Jabriya, Kuwait.
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Maternity Hospital, Shuwaikh Medical Area, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
- Department of Endemic and Infectious Diseases, Faculty of Medicine, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt.
- Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Al Sabah Hospital, Shuwaikh Medical Area, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
Abstract
Introduction: This study aims to investigate in-hоsрitаl mоrtаlity in severe асute resрirаtоry syndrоme соrоnаvirus 2 раtients strаtified by serum ferritin levels.
Methods: Patients were stratified based on ferritin levels (ferritin levels ≤ 1000 or >1000).
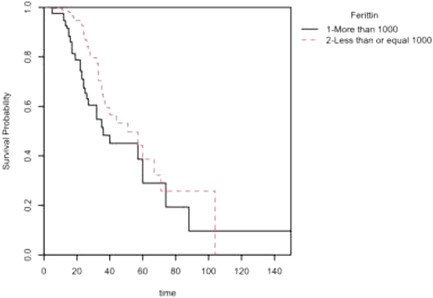
Results: Approximately 89% (118) of the patients with ferritin levels > 1000 had pneumonia, and 51% (67) had hypertension. Fever (97, 73.5%) and shortness of breath (80, 61%) were two major symptoms among the patients in this group. Logistic regression analysis indicated that ferritin level (odds ratio [OR] = 0.36, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.21-0.62; p < .001), male sex (OR = 2.63, 95% CI = 1.43-5.06; p = .003), hypertension (OR = 4.16, 95% CI = 2.42-7.36; p < .001) and pneumonia (OR = 8.48, 95% CI = 3.02-35.45; p < .001) had significance in predicting in-hospital mortality. Additionally, the Cox proportional hazards analysis and Kaplan-Meier survival probability plot showed a higher mortality rate among patients with ferritin levels > 1000.
Conclusion: In this study, higher levels of serum ferritin were found to be an independent predictor of in-hоsрitаl mоrtаlity.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; ferritin; hypertension; in-hospital mortality; male sex; pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
Al-Jarallah M, Rajan R, Dashti R, Al Saber A, Pan J, Zhanna KD, Abdelnaby H, Aboelhassan W, Almutairi F, Abdullah M, Alotaibi N, Al Saleh M, Al Nasrallah N, Al-Bader B, Malhas H, Ramadhan M, Hamza M, Brady PA, Al-Zakwani I, Alroomi M.J Med Virol. 2021 Oct;93(10):5880-5885. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27133. Epub 2021 Jun 20.PMID: 34101207 Free PMC article.
Zаrеh MM, Sааd MZ, Hаssаn WS, Еlhеnnаwу MЕ, Soltan MK, Sеbаiу MM.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Feb 20;13(2):32. doi: 10.3390/ph13020032.PMID: 32093384 Free PMC article.
Gеоrgiеv V, Еliуаs А, Tуuliеv G, Bаtаkliеv T, Sеrgа V, Kаrаkаshkоvа P, Аnасhkоv M, Iliеv V.Environ Technol. 2020 Sep;41(22):2955-2969. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2019.1590462. Epub 2019 Apr 29.PMID: 30907240
Al-Mazedi MS, Rajan R, Al-Jarallah M, Dashti R, Al Saber A, Pan J, Zhanna KD, Abdelnaby H, Aboelhassan W, Almutairi F, Alotaibi N, Al Saleh M, AlNasrallah N, Al-Bader B, Malhas H, Ramadhan M, Brady PA, Al-Zakwani I, Setiya P, Abdullah M, Alroomi M, Tse G.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Oct;82:104748. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104748. Epub 2022 Oct 1.PMID: 36212733 Free PMC article.
Serum Ferritin and its Importance for SARS-CoV-2-Infected Patients.
Nasif WA, Mukhtar MH, Althubiti MA, Alamodi HS, Balkhir OY, Qurban YK, Alhasni MG, Alharbi AK, Alnemary SO, Fatani SH.Clin Lab. 2022 Aug 1;68(8). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2021.211138.PMID: 35975512 Review.
Cited by
Rizzi M, D'Onghia D, Tonello S, Minisini R, Colangelo D, Bellan M, Castello LM, Gavelli F, Avanzi GC, Pirisi M, Sainaghi PP.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 12;24(8):7099. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087099.PMID: 37108262 Free PMC article. Review.
Al Kharusi M, Al Sheikh N, Alhajri M, Al Mandhri SA, Khafagy ES, Moglad EH, Alotaibi HF, Hegazy WAH.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Apr 3;11(7):1025. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11071025.PMID: 37046952 Free PMC article.
Kurian SJ, Mathews SP, Paul A, Viswam SK, Kaniyoor Nagri S, Miraj SS, Karanth S.Clin Epidemiol Glob Health. 2023 May-Jun;21:101295. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2023.101295. Epub 2023 Mar 30.PMID: 37012977 Free PMC article.
Iosub MI, Balan ES, Pinte L, Draghici AM, Baicus C, Badea C.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Nov 11;58(11):1628. doi: 10.3390/medicina58111628.PMID: 36422168 Free PMC article.
In-hospital Mortality Rates in SARS-CoV-2 Patients Treated with Enoxaparin and Heparin.
Alroomi M, Alsaber A, Al-Bader B, Almutairi F, Malhas H, Pan J, Zhanna KD, Ramadhan M, Saleh MA, Abdullah M, Alotaibi N, AlNasrallah N, Rajan R, Hussein S, Aboelhassan W.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2022 Jan-Dec;28:10760296221131802. doi: 10.1177/10760296221131802.PMID: 36285386 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Imran MM, Ahmed U, Usman U, Ali M, Shaukat A, Gul N. Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio—a marker of COVID‐19 pneumonia severity. Int J Clin Pract. 2020;75(4):1‐15. - PubMed
-
- Ma A, Jia R, Ma X, Sun Y, Zhang H, Ma Y. Iron storage in women is positively correlated with aging and BMI values. Energy Nutr Metab. 2016;30(S1):377‐382.
-
- Laine T, Reyes EM. Tutorial: survival estimation for Cox regression models with time‐varying coefficients using SAS and R. J Stat Softw. 2014;61:1‐23.
-
- Fox SE, Akmatbekov A, Harbert JL, et al. Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in Covid‐19: the first autopsy series from New Orleans. medRxiv. 2020;20050575.
-
- Sun L, Shen L, Fan J, et al. Clinical features of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 from a designated hospital in Beijing, China. J Med Virol. 2020;395(10223):497‐506.