Ultrastructure of Hyperfunctioning Parathyroid Glands: Does it Explain Various Patterns of 99mTc-sestamibi Uptake
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Nuclear Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Safat, Kuwait.
- Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Safat, Kuwait.
- Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Safat, Kuwait.
Abstract
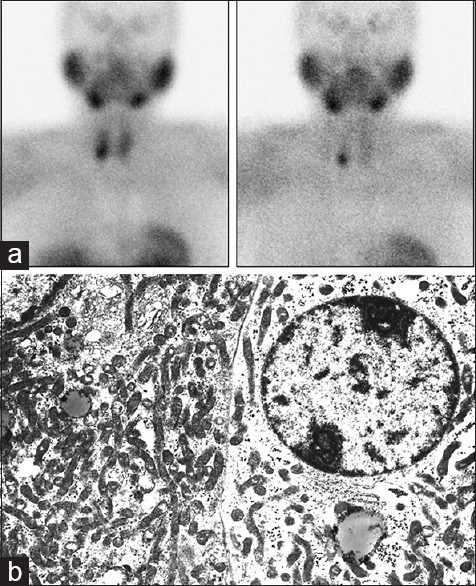
The aim of this study was to correlate the uptake of 99mTc-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile (MIBI) with ultra-structural features of parathyroid adenomas. Twenty patients with proven primary hyperparathyroidism were evaluated prospectively. Preoperative double-phase 99mTc-MIBI scintigraphy was performed in all patients and the degree of tracer uptake by the parathyroid lesions was assessed visually and semi-quantitatively. The excised glands were examined histologically and ultrastructurally, and their features were correlated with the degree of the radiotracer uptake. At surgery, 21 parathyroid adenomas were removed (double adenoma in one patient and a solitary adenoma in each of the remaining 19 patients). 99mTc-MIBI scan detected 18 of the 21 adenomas. There was positive correlation between the degree of 99mTc-MIBI uptake and the mitochondrial contents of the parathyroid adenoma cells. Four adenomas with intense uptake had high content of mitochondria in the cells. The three false-negative scans had low-to-moderate mitochondrial content. 99mTc-MIBI uptake is related to the mitochondrial content of the parathyroid adenoma cells.
Keywords: 99mTc- methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile; electron microscopy; mitochondria; parathyroid adenoma; radionuclide.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
Akin M, Atasever T, Kurukahvecioglu O, Dogan M, Gokaslan D, Poyraz A, Koksal H, Taneri F.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2009;110(3):166-9.PMID: 19507637
Dugonjić S, Šišić M, Radulović M, Ajdinović B.Hell J Nucl Med. 2017 Jan-Apr;20(1):46-50. doi: 10.1967/s002449910506. Epub 2017 Mar 20.PMID: 28315908
Yamaguchi S, Kobayashi Y, Tsujikawa K, Noma M, Mori N, Hara T, Takao T, Takada S, Sugao H, Yoshida S.Hinyokika Kiyo. 2001 Sep;47(9):619-23.PMID: 11692597 Japanese.
Martínez-Rodríguez I, Martínez-Amador N, de Arcocha-Torres M, Quirce R, Ortega-Nava F, Ibáñez-Bravo S, Lavado-Pérez C, Bravo-Ferrer Z, Carril JM.Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2014 Mar-Apr;33(2):93-8. doi: 10.1016/j.remn.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Oct 11.PMID: 24125595
Radionuclide imaging of the parathyroid glands.
Palestro CJ, Tomas MB, Tronco GG.Semin Nucl Med. 2005 Oct;35(4):266-76. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2005.06.001.PMID: 16150247 Review.
Cited by
Yu D, Zou L, Jin Y, Wei M, Wu X, Zuo L, Wu M, Jiang Y.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 8;13:915279. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.915279. eCollection 2022.PMID: 36157459 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Alenezi SA, Asa'ad SM, Elgazzar AH. Scintigraphic parathyroid imaging: Concepts and new developments. Res Rep Nucl Med. 2015;5:9–18.
-
- Elgazzar AH, Alenezi SA. Parathyroid gland. In: Elgazzar AH, editor. Pathophysiologic Basis of Nuclear Medicine. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer; 2014. pp. 9–18.
-
- Shaha AR, Jaffe BM. Cervical exploration for primary hyperparathyroidism. J Surg Oncol. 1993;52:14–7. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell BK, Merrell RC, Kinder BK. Localization studies in patients with hyperparathyroidism. Surg Clin North Am. 1995;75:483–98. - PubMed
-
- Denham DW, Norman J. Cost-effectiveness of preoperative sestamibi scan for primary hyperparathyroidism is dependent solely upon the surgeon's choice of operative procedure. J Am Coll Surg. 1998;186:293–305. - PubMed
-
- O'Doherty MJ, Kettle AG. Parathyroid imaging: Preoperative localization. Nucl Med Commun. 2003;24:125–31. - PubMed
-
- Hindié E, Ugur O, Fuster D, O'Doherty M, Grassetto G, Ureña P, et al. 2009 EANM parathyroid guidelines. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;36:1201–16. - PubMed
-
- Kim YI, Jung YH, Hwang KT, Lee HY. Efficacy of 99mTc-sestamibi SPECT/CT for minimally invasive parathyroidectomy: Comparative study with 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy, SPECT, US and CT. Ann Nucl Med. 2012;26:804–10. - PubMed
-
- Mihai R, Simon D, Hellman P. Imaging for primary hyperparathyroidism – An evidence-based analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2009;394:765–84. - PubMed
-
- Patel CN, Salahudeen HM, Lansdown M, Scarsbrook AF. Clinical utility of ultrasound and 99mTc sestamibi SPECT/CT for preoperative localization of parathyroid adenoma in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Clin Radiol. 2010;65:278–87. - PubMed
-
- Bleier BS, LiVolsi VA, Chalian AA, Gimotty PA, Botbyl JD, Weber RS. Technetium Tc 99m sestamibi sensitivity in oxyphil cell-dominant parathyroid adenomas. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;132:779–82. - PubMed
-
- McBiles M, Lambert AT, Cote MG, Kim SY. Sestamibi parathyroid imaging. Semin Nucl Med. 1995;25:221–34. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Monte JE, Brown ML, Shah AN, Ranger NT, Watson CG, Carty SE, et al. Parathyroid adenomas: Accurate detection and localization with Tc-99m sestamibi SPECT. Radiology. 1996;201:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Hindié E, Melliére D, Perlemuter L, Jeanguillaume C, Galle P. Primary hyperparathyroidism: Higher success rate of first surgery after preoperative Tc-99m sestamibi-I-123 subtraction scanning. Radiology. 1997;204:221–8. - PubMed
-
- Bénard F, Lefebvre B, Beuvon F, Langlois MF, Bisson G. Rapid washout of technetium-99m-MIBI from a large parathyroid adenoma. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:241–3. - PubMed
-
- Kao A, Shiau YC, Tsai SC, Wang JJ, Ho ST. Technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile imaging for parathyroid adenoma: Relationship to P-glycoprotein or multidrug resistance-related protein expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29:1012–5. - PubMed
-
- Carpentier A, Jeannotte S, Verreault J, Lefebvre B, Bisson G, Mongeau CJ, et al. Preoperative localization of parathyroid lesions in hyperparathyroidism: Relationship between technetium-99m-MIBI uptake and oxyphil cell content. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:1441–4. - PubMed
-
- Ishibashi M, Nishida H, Okuda S, Suekane S, Hayabuchi N. Localization of parathyroid glands in hemodialysis patients using Tc-99m sestamibi imaging. Nephron. 1998;78:48–53. - PubMed
-
- Piñero A, Rodriguez JM, Ortiz S, Soria T, Bermejo J, Claver MA, et al. Relation of biochemical, cytologic, and morphologic parameters to the result of gammagraphy with technetium 99m sestamibi in primary hyperparathyroidism. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;122:851–5. - PubMed
-
- Hetrakul N, Civelek AC, Stagg CA, Udelsman R. In vitro accumulation of technetium-99m-sestamibi in human parathyroid mitochondria. Surgery. 2001;130:1011–8. - PubMed