The genetic regulatory signature of type 2 diabetes in human skeletal muscle
Laura J Scott 1, Michael R Erdos 2, Jeroen R Huyghe 1, Ryan P Welch 1, Andrew T Beck 1, Brooke N Wolford 2, Peter S Chines 2, John P Didion 2, Narisu Narisu 2, Heather M Stringham 1, D Leland Taylor 2 3, Anne U Jackson 1, Swarooparani Vadlamudi 4, Lori L Bonnycastle 2, Leena Kinnunen 5, Jouko Saramies 6, Jouko Sundvall 5, Ricardo D'Oliveira Albanus 7, Anna Kiseleva 7, John Hensley 7, Gregory E Crawford 8 9, Hui Jiang 1, Xiaoquan Wen 1, Richard M Watanabe 10 11, Timo A Lakka 12 13 14, Karen L Mohlke 4, Markku Laakso 15 16, Jaakko Tuomilehto 17 18 19 20, Heikki A Koistinen 5 21 22, Michael Boehnke 1, Francis S Collins 2, Stephen C J Parker 7 23
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Biostatistics and Center for Statistical Genetics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20892, USA.
- European Bioinformatics Institute, European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Wellcome Trust Genome Campus, Hinxton, Cambridgeshire CB10 1SD, UK.
- Department of Genetics, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, USA.
- Department of Health, National Institute for Health and Welfare, P.O. Box 30, Helsinki FI-00271, Finland.
- South Karelia Central Hospital, Lappeenranta 53130, Finland.
- Department of Computational Medicine &Bioinformatics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- Center for Genomic &Computational Biology, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina 27708, USA.
- Department of Pediatrics, Division of Medical Genetics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27708, USA.
- Department of Preventive Medicine, Keck School of Medicine of USC, Los Angeles, California 90089, USA.
- Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Keck School of Medicine of USC, Los Angeles, California 90089, USA.
- Institute of Biomedicine/Physiology, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio FI-00100, Finland.
- Kuopio Research Institute of Exercise Medicine, Kuopio FI-00100, Finland.
- Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine, Kuopio University Hospital, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio FI-00100, Finland.
- Department of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio FI-00100, Finland.
- Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio FI-00100, Finland.
- Chronic Disease Prevention Unit, National Institute for Health and Welfare, P.O. Box 30, Helsinki FI-00271, Finland.
- Center for Vascular Prevention, Danube University Krems, Krems 3500, Austria.
- Diabetes Research Group, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah 21589, Saudi Arabia.
- Dasman Diabetes Institute, Dasman 15461, Kuwait.
- Department of Medicine and Abdominal Center: Endocrinology, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Central Hospital, P.O. Box 340, Haartmaninkatu 4, Helsinki FI-00029, Finland.
- Minerva Foundation Institute for Medical Research, Biomedicum 2U, Tukholmankatu 8, Helsinki FI-00290, Finland.
- Department of Human Genetics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
Abstract
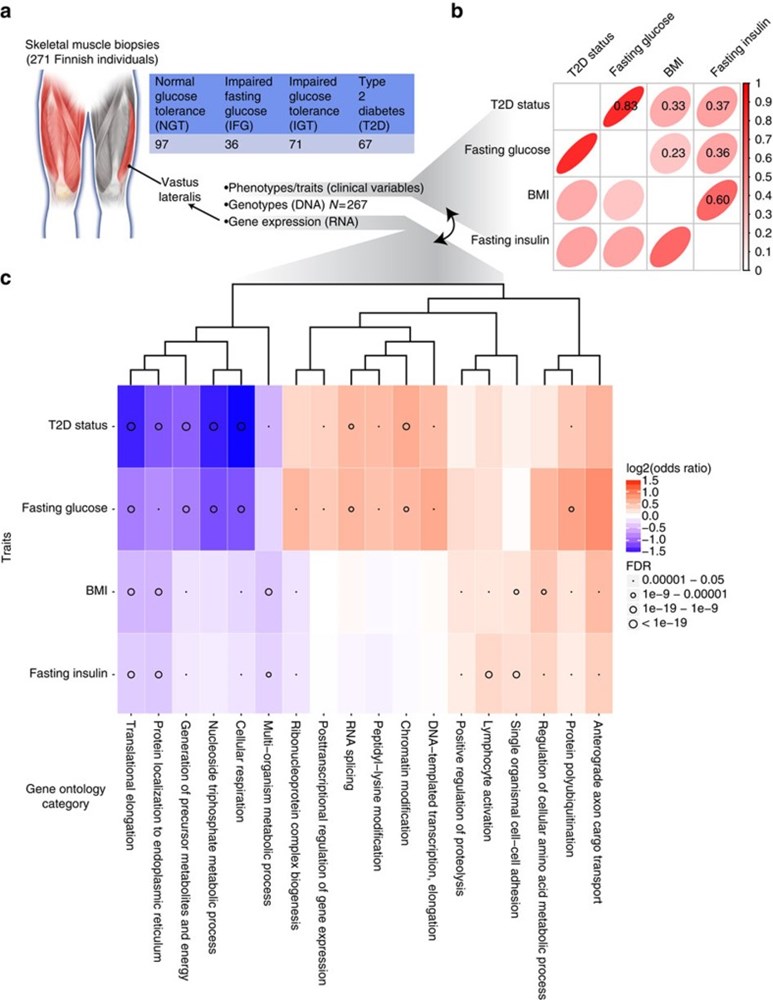
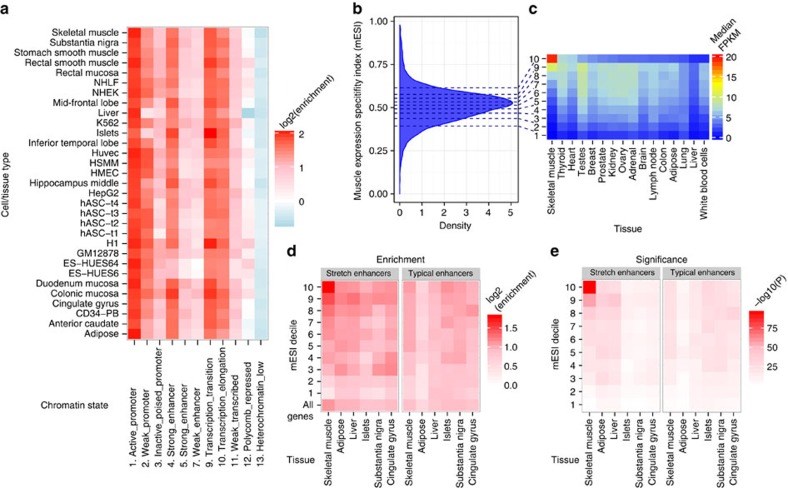
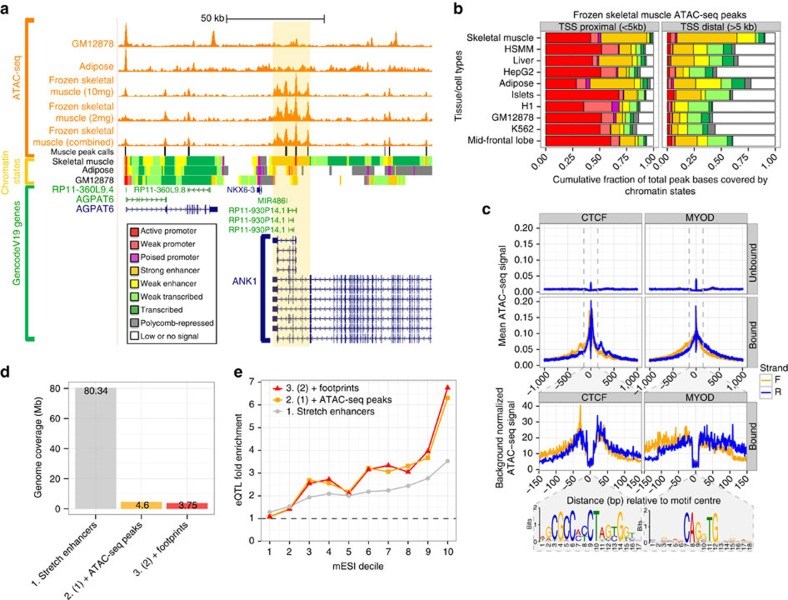
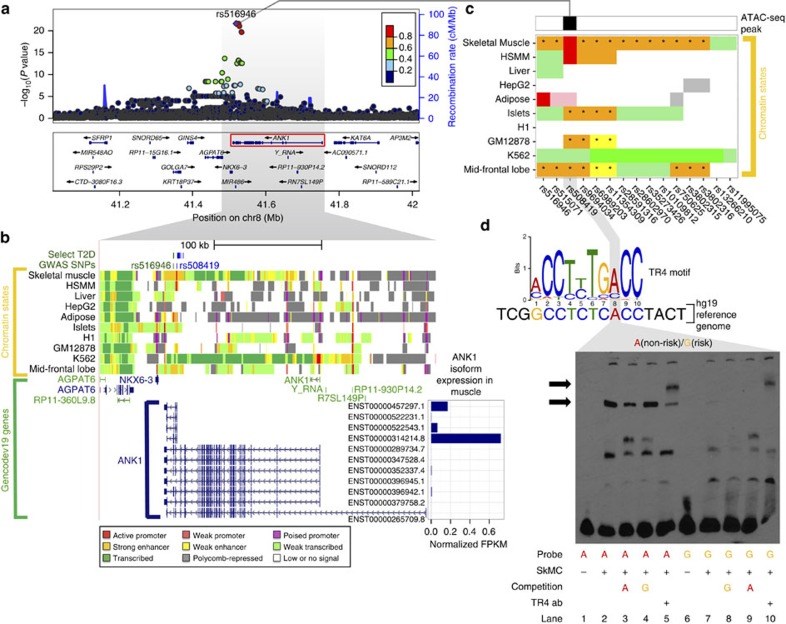
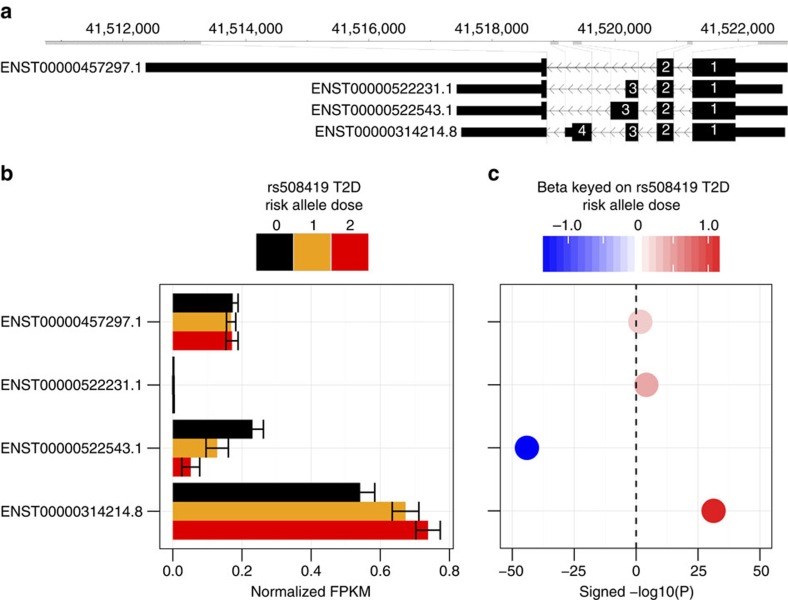
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) results from the combined effects of genetic and environmental factors on multiple tissues over time. Of the >100 variants associated with T2D and related traits in genome-wide association studies (GWAS), >90% occur in non-coding regions, suggesting a strong regulatory component to T2D risk. Here to understand how T2D status, metabolic traits and genetic variation influence gene expression, we analyse skeletal muscle biopsies from 271 well-phenotyped Finnish participants with glucose tolerance ranging from normal to newly diagnosed T2D. We perform high-depth strand-specific mRNA-sequencing and dense genotyping. Computational integration of these data with epigenome data, including ATAC-seq on skeletal muscle, and transcriptome data across diverse tissues reveals that the tissue-specific genetic regulatory architecture of skeletal muscle is highly enriched in muscle stretch/super enhancers, including some that overlap T2D GWAS variants. In one such example, T2D risk alleles residing in a muscle stretch/super enhancer are linked to increased expression and alternative splicing of muscle-specific isoforms of ANK1.
Figures
Similar articles
Genetic regulatory signatures underlying islet gene expression and type 2 diabetes.
Varshney A, Scott LJ, Welch RP, Erdos MR, Chines PS, Narisu N, Albanus RD, Orchard P, Wolford BN, Kursawe R, Vadlamudi S, Cannon ME, Didion JP, Hensley J, Kirilusha A; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Bonnycastle LL, Taylor DL, Watanabe R, Mohlke KL, Boehnke M, Collins FS, Parker SC, Stitzel ML.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 28;114(9):2301-2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1621192114. Epub 2017 Feb 13.PMID: 28193859 Free PMC article.
Rai V, Quang DX, Erdos MR, Cusanovich DA, Daza RM, Narisu N, Zou LS, Didion JP, Guan Y, Shendure J, Parker SCJ, Collins FS.Mol Metab. 2020 Feb;32:109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.12.006. Epub 2019 Dec 20.PMID: 32029221 Free PMC article.
Yan R, Lai S, Yang Y, Shi H, Cai Z, Sorrentino V, Du H, Chen H.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 28;6:25105. doi: 10.1038/srep25105.PMID: 27121283 Free PMC article.
Shared genetic etiology underlying Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes.
Hao K, Di Narzo AF, Ho L, Luo W, Li S, Chen R, Li T, Dubner L, Pasinetti GM.Mol Aspects Med. 2015 Jun-Oct;43-44:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2015.06.006. Epub 2015 Jun 23.PMID: 26116273 Free PMC article. Review.
The Contribution of Low-Frequency and Rare Coding Variation to Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes.
Flannick J.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Apr 8;19(5):25. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1142-5.PMID: 30957210 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
Skeletal muscle overexpression of sAnk1.5 in transgenic mice does not predispose to type 2 diabetes.
Pierantozzi E, Raucci L, Buonocore S, Rubino EM, Ding Q, Laurino A, Fiore F, Soldaini M, Chen J, Rossi D, Vangheluwe P, Chen H, Sorrentino V.Sci Rep. 2023 May 20;13(1):8195. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35393-0.PMID: 37210436 Free PMC article.
Prioritization of genes associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus for functional studies.
Tan WX, Sim X, Khoo CM, Teo AKK.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023 May 11. doi: 10.1038/s41574-023-00836-1. Online ahead of print.PMID: 37169822 Review.
Hemerich D, Smit RAJ, Preuss M, Stalbow L, van der Laan SW, Asselbergs FW, van Setten J, Tragante V.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 2;13(1):3579. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30369-6.PMID: 36864090 Free PMC article.
Differential DNA methylation of steatosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescence.
Melton PE, Burton MA, Lillycrop KA, Godfrey KM, Rauschert S, Anderson D, Burdge GC, Mori TA, Beilin LJ, Ayonrinde OT, Craig JM, Olynyk JK, Holbrook JD, Pennell CE, Oddy WH, Moses EK, Adams LA, Huang RC.Hepatol Int. 2023 Jun;17(3):584-594. doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10469-7. Epub 2023 Feb 3.PMID: 36737504 Free PMC article.
Loci for insulin processing and secretion provide insight into type 2 diabetes risk.
Broadaway KA, Yin X, Williamson A, Parsons VA, Wilson EP, Moxley AH, Vadlamudi S, Varshney A, Jackson AU, Ahuja V, Bornstein SR, Corbin LJ, Delgado GE, Dwivedi OP, Fernandes Silva L, Frayling TM, Grallert H, Gustafsson S, Hakaste L, Hammar U, Herder C, Herrmann S, Højlund K, Hughes DA, Kleber ME, Lindgren CM, Liu CT, Luan J, Malmberg A, Moissl AP, Morris AP, Perakakis N, Peters A, Petrie JR, Roden M, Schwarz PEH, Sharma S, Silveira A, Strawbridge RJ, Tuomi T, Wood AR, Wu P, Zethelius B, Baldassarre D, Eriksson JG, Fall T, Florez JC, Fritsche A, Gigante B, Hamsten A, Kajantie E, Laakso M, Lahti J, Lawlor DA, Lind L, März W, Meigs JB, Sundström J, Timpson NJ, Wagner R, Walker M, Wareham NJ, Watkins H, Barroso I, O'Rahilly S, Grarup N, Parker SC, Boehnke M, Langenberg C, Wheeler E, Mohlke KL.Am J Hum Genet. 2023 Feb 2;110(2):284-299. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2023.01.002. Epub 2023 Jan 23.PMID: 36693378
KMEL References
References
-
- Scully T. Diabetes in numbers. Nature 485, S2–S3 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Lindholm M. E. et al.. The human skeletal muscle transcriptome: sex differences, alternative splicing, and tissue homogeneity assessed with RNA sequencing. FASEB J. 28, 4571–4581 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Mootha V. K. et al.. PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 34, 267–273 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Albert V. & Hall M. N. mTOR signaling in cellular and organismal energetics. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 33, 55–66 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Imamura M. et al.. A single-nucleotide polymorphism in ANK1 is associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in Japanese populations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 3042–3049 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Borzok M. A., Catino D. H., Nicholson J. D., Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A. & Bloch R. J. Mapping the binding site on small ankyrin 1 for obscurin. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 32384–32396 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Contreras-Ferrat A., Lavandero S., Jaimovich E. & Klip A. Calcium signaling in insulin action on striated muscle. Cell Calcium 56, 390–396 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Bouzakri K. et al.. siRNA-based gene silencing reveals specialized roles of IRS-1/Akt2 and IRS-2/Akt1 in glucose and lipid metabolism in human skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 4, 89–96 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Valle T. et al.. Mapping genes for NIDDM. Design of the Finland-United States Investigation of NIDDM Genetics (FUSION) Study. Diabetes Care 21, 949–958 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Väätäinen S. et al.. Quality of life along the diabetes continuum: a cross-sectional view of health-related quality of life and general health status in middle-aged and older Finns. Qual. Life Res. 23, 1935–1944 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Kouki R. et al.. Diet, fitness and metabolic syndrome--the DR's EXTRA study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 22, 553–560 (2012). - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) & International Diabetes Federation (IDF). Definition and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and Intermediate Hyperglycaemia: Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation. (WHO, Geneva, Switzerland, 2006).
-
- Gong T. & Szustakowski J. D. DeconRNASeq: a statistical framework for deconvolution of heterogeneous tissue samples based on mRNA-Seq data. Bioinformatics 29, 1083–1085 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Jolma A. et al.. DNA-binding specificities of human transcription factors. Cell 152, 327–339 (2013). - PubMed