Thidiazuron decreases epithelial-mesenchymal transition activity through the NF-kB and PI3K/AKT signalling pathways in breast cancer
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Biological Sciences, College of Science, King Faisal University, Al-Ahsa, Saudi Arabia.
- Laboratory of Aromatic and Medicinal Plants, Center of Biotechnology, Technopole of Borj-Cedria, Hammam-Lif, Tunisia.
- Department of Nuclear Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Safat, Kuwait.
- Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Clinical Pharmacy, King Faisal University, Al-Ahsaa, Saudi Arabia.
- Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Zagazig, Zagazig, Egypt.
- Department of Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine, King Faisal University, Al-Ahsa, Saudi Arabia.
Abstract
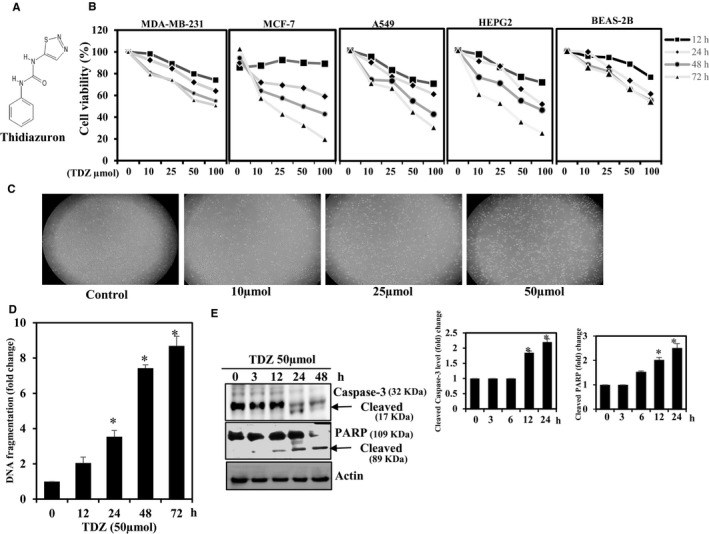
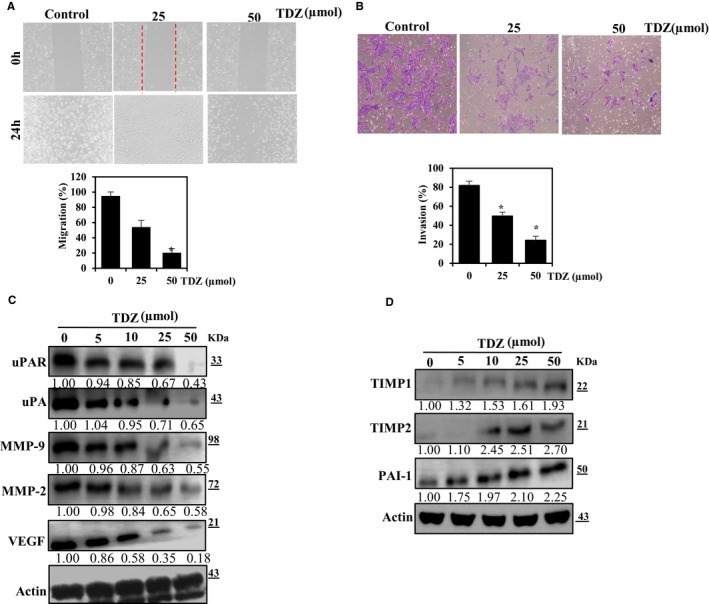
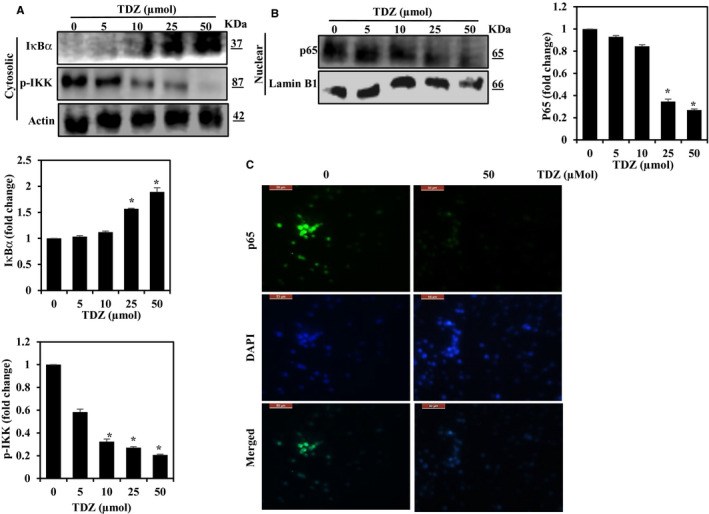
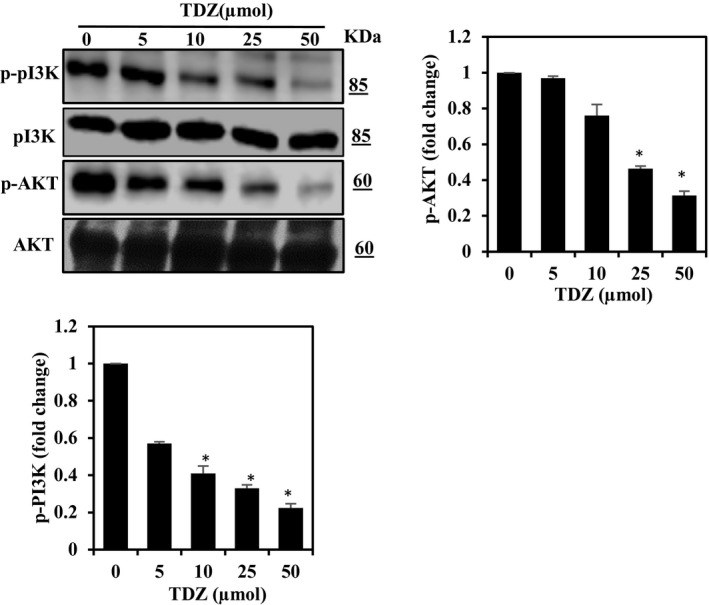
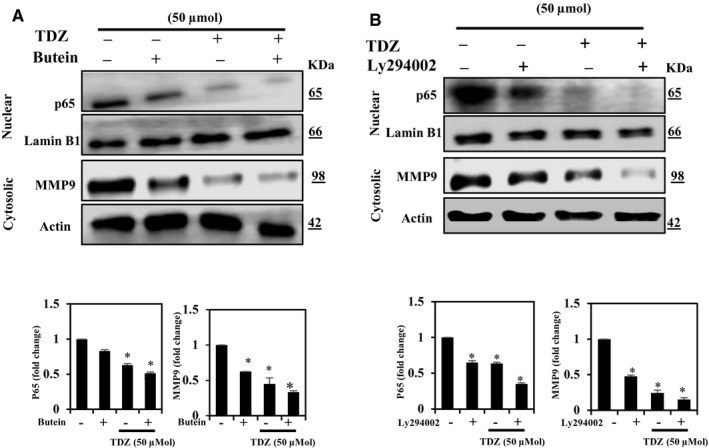
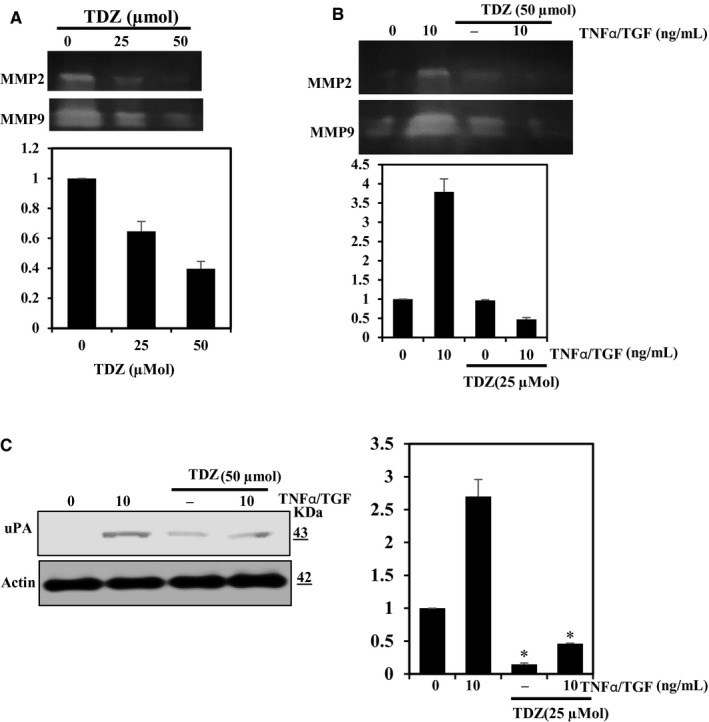
Breast cancer is the major type among the women population globally. The treatment of cancer metastasis has made modest progress due to multiple factors. Thidiazuron (TDZ) is a novel plant growth regulator that has been shown to have anticancer effects. Therefore, we explored the anti-metastatic potentials of TDZ in cell lines by assessing its potential to suppress the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). We pretreated the BEAS-2B and breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cells with TDZ and deliberated alteration in a cell viability, mammosphere, migration, NF-кB signalling, PI3K/AKT signalling and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression and analysed the EMT induction by TGF-β/TNF-α-stimulated BEAS-2B cells. Treatment with TDZ (5-50 μmol) diminished the migration and invasion of the extremely metastatic MDA-MB-231 cells. Additionally, TDZ treatment led to down-regulation of uPAR, uPA, VEGF and MMP-2/-9 expression and up-regulation of TIMP-1/2 expression in these cells. Furthermore, TDZ treatment blocked invasion and EMT in non-tumorigenic BEAS-2B epithelial cells stimulated with TGF-β/TNF-α.TDZ prevents EMT and may thus block metastasis of breast cancer cells.
Keywords: Thidiazuron; breast cancer; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; matrix metalloproteinase; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicting interest.
Figures
Similar articles
Ibrahim HM, Ismail MB, Ammar RB, Ahmed EA.Biochem Cell Biol. 2021 Jun;99(3):374-384. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2020-0377. Epub 2020 Oct 24.PMID: 33103467
Sun Y, Zhou QM, Lu YY, Zhang H, Chen QL, Zhao M, Su SB.Molecules. 2019 Mar 21;24(6):1131. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061131.PMID: 30901941 Free PMC article.
Yang HL, Thiyagarajan V, Shen PC, Mathew DC, Lin KY, Liao JW, Hseu YC.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 8;38(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1196-x.PMID: 31068208 Free PMC article.
Wang L, Tang C, Cao H, Li K, Pang X, Zhong L, Dang W, Tang H, Huang Y, Wei L, Su M, Chen T.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(8):1220-30. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1056409. Epub 2015 Jun 29.PMID: 26121010 Free PMC article.
Genenger B, Perry JR, Ashford B, Ranson M.Discov Oncol. 2022 Jun 6;13(1):42. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00510-4.PMID: 35666359 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
Song L, Li X, Xu X, Huo X, Zheng Y, Wang X, Li D, Zhang J, Wang K, Wang L, Wu Z.Cells. 2022 Nov 18;11(22):3669. doi: 10.3390/cells11223669.PMID: 36429098 Free PMC article.
Glioblastoma multiforme: Diagnosis, treatment, and invasion.
Li J, Feng L, Lu Y.J Biomed Res. 2022 Oct 28;37(1):47-58. doi: 10.7555/JBR.36.20220156.PMID: 36403983 Free PMC article.
Ramesh J, Thilakan RC, Gopalakrishnan RM, Vijayapoopathi S, Dorschel A, Venugopal B.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jun 24;13(7):1142. doi: 10.3390/genes13071142.PMID: 35885925 Free PMC article.
Cheng SW, Chen PC, Lin MH, Ger TR, Chiu HW, Lin YF.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 1;9(4):371. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040371.PMID: 33916322 Free PMC article.
Cheng SW, Chen PC, Ger TR, Chiu HW, Lin YF.J Pers Med. 2021 Mar 12;11(3):197. doi: 10.3390/jpm11030197.PMID: 33809079 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Kotsakis A, Ardavanis A, Koumakis G, Samantas E, Psyrri A, Papadimitriou C. Epidemiological characteristics, clinical outcomes and management patterns of metastatic breast cancer patients in routine clinical care settings of Greece: Results from the EMERGE multicenter retrospective chart review study. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:88. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deluche E, Onesti E, Andre F. Precision medicine for metastatic breast cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2015;35:e2‐e7. - PubMed
-
- Singh M, Yelle N, Venugopal C, Singh SK. EMT: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;182:80‐94. - PubMed
-
- Kim J, Kang HS, Lee Y‐J, et al. EGR1‐dependent PTEN upregulation by 2‐benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde attenuates cell invasion and EMT in colon cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;349:35‐44. - PubMed
-
- Vuoriluoto K, Haugen H, Kiviluoto S, et al. Vimentin regulates EMT induction by Slug and oncogenic H‐Ras and migration by governing Axl expression in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2011;30:1436‐1448. - PubMed
-
- Hseu Y‐C, Lin Y‐C, Rajendran P, et al. Antrodia salmonea suppresses invasion and metastasis in triple‐negative breast cancer cells by reversing EMT through the NF‐κB and Wnt/β‐catenin signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019;124:219‐230. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, Zhang X, Gang H, et al. Up‐regulation of gastric cancer cell invasion by Twist is accompanied by N‐cadherin and fibronectin expression. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 2007;358:925‐930. - PubMed
-
- Gilles C, Newgreen DF, Sato H, Thompson EW. Matrix Metalloproteases and Epithelial‐to‐Mesenchymal Transition. Rise and Fall of Epithelial Phenotype. Springer; 2005:297‐315.
-
- Park J‐H, Cho YY, Yoon SW, Park B. Suppression of MMP‐9 and FAK expression by pomolic acid via blocking of NF‐κB/ERK/mTOR signaling pathways in growth factor‐stimulated human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2016;49:1230‐1240. - PubMed
-
- Ko HS, Lee H‐J, Kim S‐H, Lee E‐O. Piceatannol suppresses breast cancer cell invasion through the inhibition of MMP‐9: involvement of PI3K/AKT and NF‐κB pathways. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:4083‐4089. - PubMed
-
- Peng B, He R, Xu Q, et al. Ginsenoside 20 (S)‐protopanaxadiol inhibits triple‐negative breast cancer metastasis in vivo by targeting EGFR‐mediated MAPK pathway. Pharmacol Res. 2019;142:1‐13. - PubMed
-
- Mamaghani MS, Assareh MH, Omidi M, et al. The effect of thidiazuron level on in vitro regeneration type and peroxidase profile in Eucalyptus microtheca F. Muell. Plant Growth Regul. 2009;59:199.
-
- Schulze J. Improvements in cereal tissue culture by thidiazuron: a review. Fruit Vegetable Cereal Sci Biotechnol. 2007;1:64‐79.
-
- Guo B, Abbasi BH, Zeb A, Xu L, Wei Y. Thidiazuron: a multi‐dimensional plant growth regulator. Afr J Biotech. 2011;10:8984‐9000.
-
- Enkhtaivan G, Kim DH, Pandurangan M. Cytotoxic effect of TDZ on human cervical cancer cells. J Photochem Photobiol, B. 2017;173:493‐498. - PubMed
-
- Shanmugam MK, Rajendran P, Li F, et al. Abrogation of STAT3 signaling cascade by zerumbone inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma xenograft mouse model. Mol Carcinog. 2015;54:971‐985. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak HF. Tumors: wounds that do not heal. N Engl J Med. 1986;315:1650‐1659. - PubMed
-
- Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T, Niedzwiecki A, Rath M. Modulation of uPA, MMPs and their inhibitors by a novel nutrient mixture in human glioblastoma cell lines. Int J Oncol. 2014;45:887‐894. - PubMed
-
- Kamitani S, Yamauchi Y, Kawasaki S, et al. Simultaneous stimulation with TGF‐β1 and TNF‐α induces epithelial mesenchymal transition in bronchial epithelial cells. Int Archives All Immunol. 2011;155:119‐128. - PubMed
-
- Das V, Bhattacharya S, Chikkaputtaiah C, Hazra S, Pal M. The basics of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT): a study from a structure, dynamics, and functional perspective. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:14535‐14555. - PubMed
-
- Thiery J, Sim W, Chua K, et al. Epithelial‐mesenchymal transition as a mechanism for the progression of breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13:O5.
-
- Weng C‐J, Yen G‐C. The in vitro and in vivo experimental evidences disclose the chemopreventive effects of Ganoderma lucidum on cancer invasion and metastasis. Clin Exp Metas. 2010;27:361‐369. - PubMed
-
- Lynch CC, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor–host cell communication. Differentiation: Rev. 2002;70:561‐573. - PubMed
-
- Osaki M, Ma O, Ito H. PI3K‐Akt pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis. 2004;9:667‐676. - PubMed
-
- Park K‐R, Nam D, Yun H‐M, et al. β‐Caryophyllene oxide inhibits growth and induces apoptosis through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 pathways and ROS‐mediated MAPKs activation. Cancer Lett. 2011;312:178‐188. - PubMed
-
- Lee W‐J, Chen W‐K, Wang C‐J, Lin W‐L, Tseng T‐H. Apigenin inhibits HGF‐promoted invasive growth and metastasis involving blocking PI3K/Akt pathway and β4 integrin function in MDA‐MB‐231 breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008;226:178‐191. - PubMed
-
- Arunasree K. Anti‐proliferative effects of carvacrol on a human metastatic breast cancer cell line, MDA‐MB 231. Phytomedicine. 2010;17:581‐588. - PubMed
-
- Fakai MI, Abd Malek SN, Karsani SA. Induction of apoptosis by chalepin through phosphatidylserine externalisations and DNA fragmentation in breast cancer cells (MCF7). Life Sci. 2019;220:186‐193. - PubMed
-
- Nelson AR, Fingleton B, Rothenberg ML, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases: biologic activity and clinical implications. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:1135. - PubMed
-
- Agliano A, Calvo A, Box C. The Challenge of Targeting Cancer Stem Cells to Halt Metastasis. Seminars in Cancer Biology. Elsevier; 2017:25‐42. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Yi M, Zhang R, et al. Vimentin is a crucial target for anti‐metastasis therapy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;438:47‐57. - PubMed
-
- Lee TK, Poon RT, Yuen AP, et al. Twist overexpression correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through induction of epithelial‐mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5369‐5376. - PubMed
-
- Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J, Lander ES, Weinberg RA. Loss of E‐cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Can Res. 2008;68:3645‐3654. - PubMed
-
- Méndez‐García LA, Nava‐Castro KE, Ochoa‐Mercado TDL, et al. Breast cancer metastasis: are cytokines important players during its development and progression? J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019;39:39‐55. - PubMed
-
- Saito T, Yoshida K, Matsumoto K, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce a reduction in E‐cadherin expression and morphological changes in MDCK cells. Res Vet Sci. 2014;96:288‐291. - PubMed