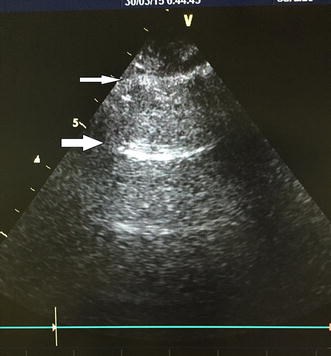
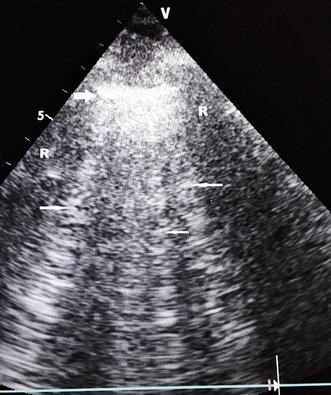
Sonographic chest B-lines anticipate elevated B-type natriuretic peptide level, irrespective of ejection fraction
Affiliations
Affiliations
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ahmadi Hospital, Kuwait Oil Company, Fahahil, Al Ahmadi, P.O. Box 46468, 64015, Kuwait city, Kuwait. zbitar2@hotmail.com.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Ahmadi Hospital, Kuwait Oil Company, Fahahil, Al Ahmadi, P.O. Box 46468, 64015, Kuwait city, Kuwait. ossamamaadarani@yahoo.com.
- 3Department of Cardiology, Chest Disease Hospital, Al Shuwaikh, Kuwait city, Kuwait. zbitar@kockw.com.
Abstract
Background: Echocardiography and the N-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level are important tests for assessing left ventricular function in patients presenting to the emergency department with acute dyspnea. Chest ultrasound is becoming an important tool in diagnosing acute pulmonary edema.
Aim: To assess the diagnostic accuracy of chest ultrasound examination using echocardiography and a curvilinear probe for detecting B-lines in patients presenting with acute pulmonary edema compared with assessment using NT-proBNP.
Methods: This paper reports a prospective observational study of 61 consecutive patients presenting with symptoms and signs of pulmonary edema and B-profile detected by echocardiography with a 5 MHz curvilinear probe. The emergency department physicians ordered NT-proBNP levels, and critical care physicians trained in ultrasound examination performed echocardiography and chest ultrasounds. The findings of the chest ultrasound were reviewed by another senior physician.
Results: Sixty-one participants were enrolled over a period of 6 months (49.2 % male, with a mean age 66.8). Forty-seven of the 61 patients had a B-profile. The median NT-proBNP level in the patients with B-profile was 6200, compared with the mean level in the patients with an A-profile of 180 (CI 0.33-0.82). The distributions in the two groups differed significantly (p = 0.034). Based on a threshold level of NT-proBNP in relation to age, the sensitivity and specificity (including the 95 % confidence interval) were determined; the sensitivity of finding B-profile on ultrasound was 92.0 %, and the specificity was 91.0 %. The positive predictive value of the B-profile was 97.0 %, and the negative predictive value was 71.0 %. The systolic function in the subjects with a B-profile was below 50 in 84.3 % of the subjects and normal in 15.7 % of the subjects. An A-profile was present in all of the subjects with systolic function >55 %. In the subjects with a B-profile, 94 % had a Framingham score of CHF >4; the subjects with all A-profile had scores <4, p < 0.0001. There was an NHANES score of >3 in 96 % of the subjects with a B-profile, and all of the subjects with an A-profile had scores <3 (p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Detecting the B-profile with an echocardiography probe (curvilinear 5 MHz) in lung ultrasound is highly sensitive and specific for elevated NT-proBNP helping in diagnosing pulmonary edema, although of resolution inferior to micro convex probes.
Keywords: B-lines; Ultrasound chest.
Figures
Similar articles
Liteplo AS, Marill KA, Villen T, Miller RM, Murray AF, Croft PE, Capp R, Noble VE.Acad Emerg Med. 2009 Mar;16(3):201-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2008.00347.x. Epub 2009 Jan 29.PMID: 19183402
Miglioranza MH, Gargani L, Sant'Anna RT, Rover MM, Martins VM, Mantovani A, Weber C, Moraes MA, Feldman CJ, Kalil RA, Sicari R, Picano E, Leiria TL.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Nov;6(11):1141-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Oct 2.PMID: 24094830
Behnes M, Brueckmann M, Ahmad-Nejad P, Lang S, Wolpert C, Elmas E, Kaelsch T, Gruettner J, Weiss C, Borggrefe M, Neumaier M.Int J Cardiol. 2009 Jun 26;135(2):165-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.03.045. Epub 2008 Jul 7.PMID: 18603317 Clinical Trial.
Diagnosing Acute Heart Failure in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Martindale JL, Wakai A, Collins SP, Levy PD, Diercks D, Hiestand BC, Fermann GJ, deSouza I, Sinert R.Acad Emerg Med. 2016 Mar;23(3):223-42. doi: 10.1111/acem.12878. Epub 2016 Feb 13.PMID: 26910112 Review.
Januzzi JL Jr, Chen-Tournoux AA, Moe G.Am J Cardiol. 2008 Feb 4;101(3A):29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.11.017.PMID: 18243855 Review.
Cited by
Zaalouk TM, Bitar ZI, Maadarani OS, Ragab Elshabasy RD.Clin Case Rep. 2021 Mar 28;9(5):e04075. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.4075. eCollection 2021 May.PMID: 34084496 Free PMC article.
Glöckner E, Wening F, Christ M, Dechêne A, Singler K.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Jul 28;56(8):379. doi: 10.3390/medicina56080379.PMID: 32731477 Free PMC article.
Pardała A, Lupa M, Chudek J, Kolonko A.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Feb 12;55(2):45. doi: 10.3390/medicina55020045.PMID: 30759793 Free PMC article.
Li H, Li YD, Zhu WW, Kong LY, Ye XG, Cai QZ, Sun LL, Lu XZ.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jan 2;2018:8474839. doi: 10.1155/2018/8474839. eCollection 2018.PMID: 29487872 Free PMC article.
Feng SD, Jiang Y, Lin ZH, Lin PH, Lin SM, Liu QC.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Aug;96(34):e7526. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007526.PMID: 28834870 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Raymond I, Groenning BA, Hildebrandt PR, Nilsson JC, Baumann M, Trawinski J, et al. The influence of age, sex and other variables on the plasma level of N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide in a large sample of the general population. Heart. 2003;89:745. doi: 10.1136/heart.89.7.745. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Volpicelli G, Elbarbary M, Blaivas M, Lichtenstein DA, Mathis G, Kirkpatrick AW, et al. International liaison committee on lung ultrasound (ILC-LUS) for international consensus conference on lung ultrasound (ICC-LUS) Intensive Care Med. 2012;38:577–591. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2513-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Januzzi JL, van Kimmenade R, Lainchbury J, Bayes-Genis A, Ordonez-Llanos J, Santalo-Bel M, Pinto YM, Richards M. NT-proBNP testing for diagnosis and short-term prognosis in acute destabilized heart failure: an international pooled analysis of 1256 patients: the International Collaborative of NT-proBNP Study. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:330–337. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi631. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roberts E, Ludman AJ, Dworzynski K, Al-Mohammad A, Cowie MR, McMurray JJ, Mant J, NICE Guideline Development Group for Acute Heart Failure. The diagnostic accuracy of the natriuretic peptides in heart failure: systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis in the acute care setting. BMJ. 2015;350:h910. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h910. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liteplo AS, Marill KA, Villen T, Miller RM, Murray AF, Croft PE, et al. Emergency thoracic ultrasound in the differentiation of the etiology of shortness of breath (ETUDES): sonographic B-lines and N-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide in diagnosing congestive heart failure. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16:201–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2008.00347.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arques S, Roux E, Luccioni R. Current clinical applications of spectral tissue Doppler echocardiography (E/E’ ratio) as a noninvasive surrogate for left ventricular diastolic pressures in the diagnosis of heart failure with preserved left ventricular systolic function. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2007;5:16. doi: 10.1186/1476-7120-5-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed