Adipose Tissue Caveolin-1 Upregulation in Obesity Involves TNF-α/NF-κB Mediated Signaling
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Genetics and Bioinformatics, Dasman Diabetes Institute, Dasman 15462, Kuwait.
- Animal and Imaging Core Facilities, Dasman Diabetes Institute, Dasman 15462, Kuwait.
- Immunology & Microbiology Department, Dasman Diabetes Institute, Dasman 15462, Kuwait.
- Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Jabriya 046300, Kuwait.
Abstract
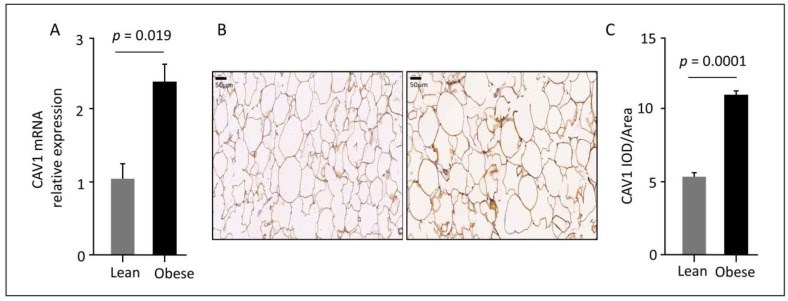
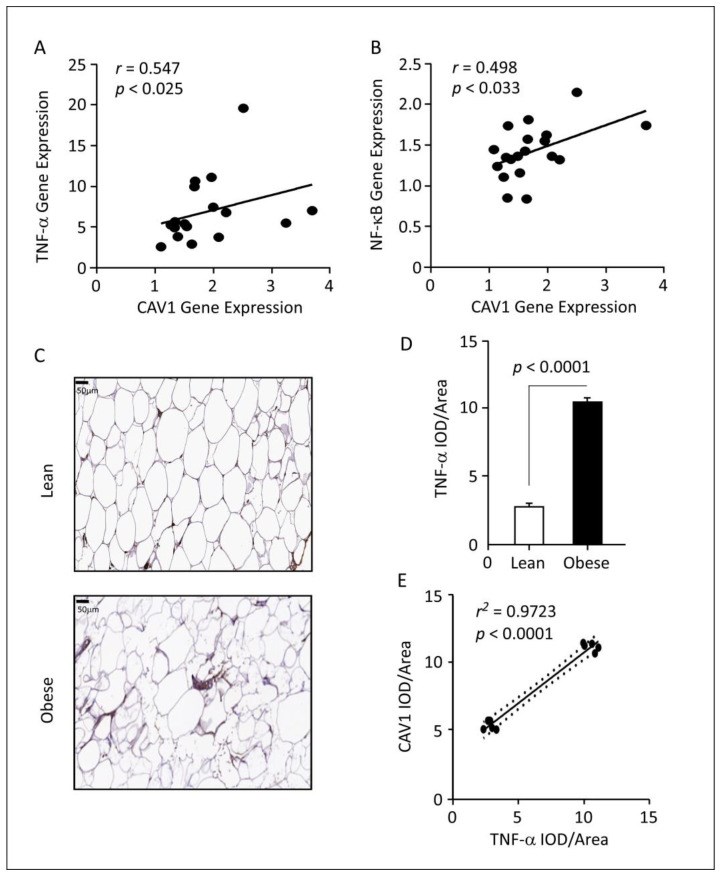
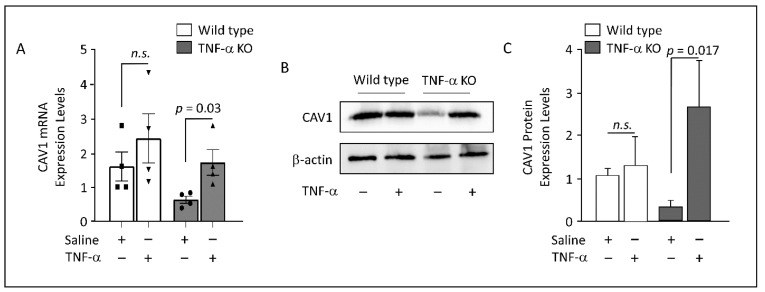
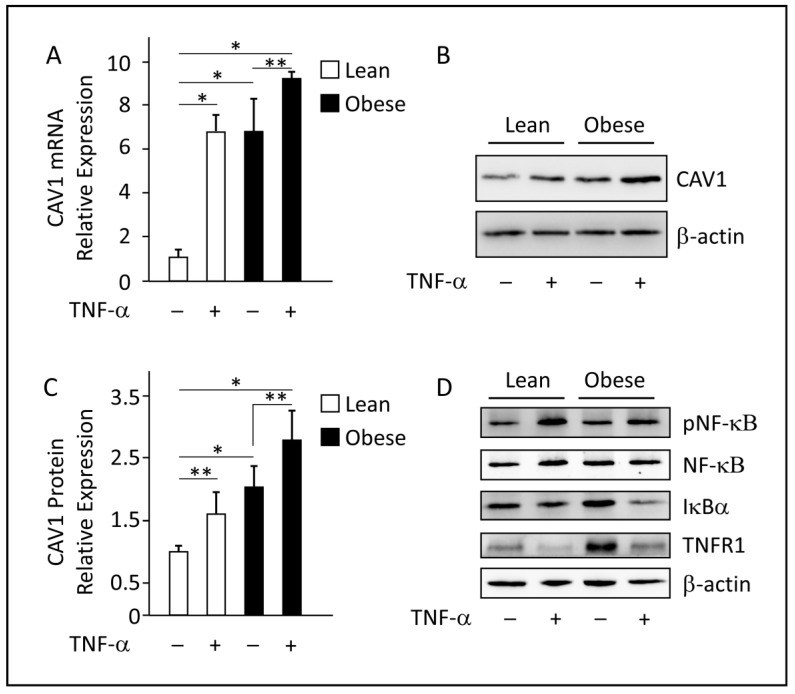
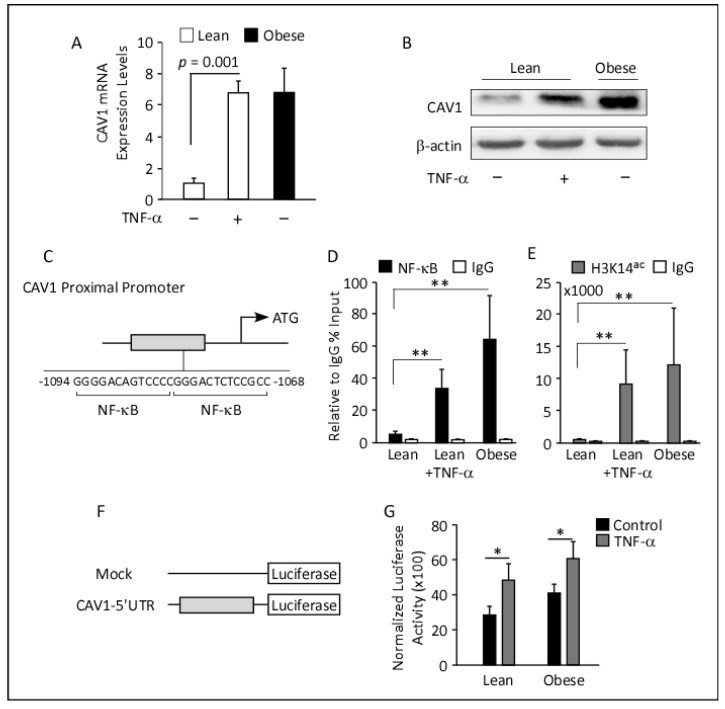
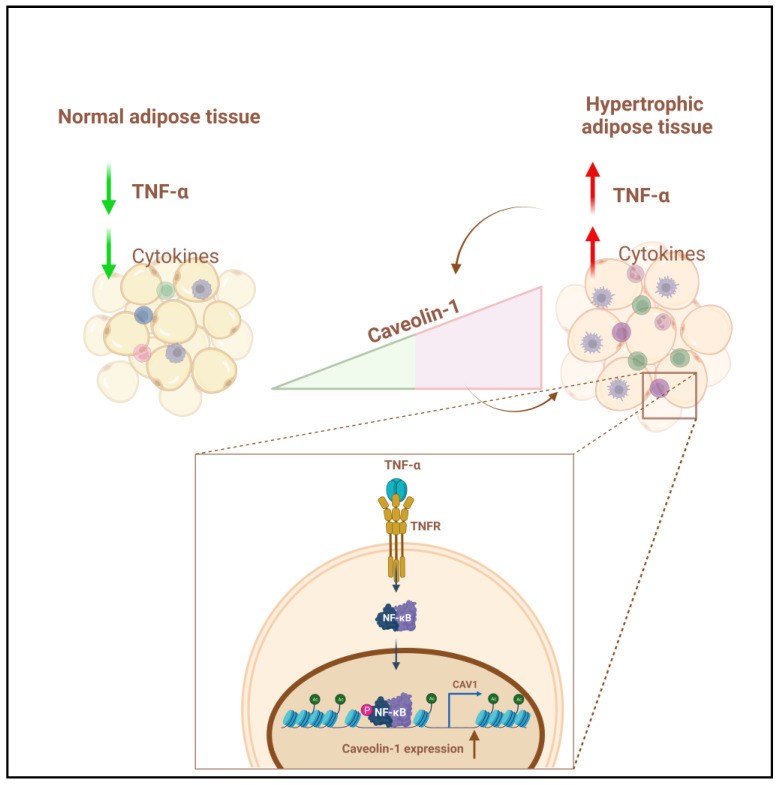
Obesity is characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation. Obese people have higher levels of caveolin-1 (CAV1), a structural and functional protein present in adipose tissues (ATs). We aimed to define the inflammatory mediators that influence CAV1 gene regulation and the associated mechanisms in obesity. Using subcutaneous AT from 27 (7 lean and 20 obese) normoglycemic individuals, in vitro human adipocyte models, and in vivo mice models, we found elevated CAV1 expression in obese AT and a positive correlation between the gene expression of CAV1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB). CAV1 gene expression was associated with proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines and their cognate receptors (r ≥ 0.447, p ≤ 0.030), but not with anti-inflammatory markers. CAV1 expression was correlated with CD163, indicating a prospective role for CAV1 in the adipose inflammatory microenvironment. Unlike wild-type animals, mice lacking TNF-α exhibited reduced levels of CAV1 mRNA/proteins, which were elevated by administering exogenous TNF-α. Mechanistically, TNF-α induces CAV1 gene transcription by mediating NF-κB binding to its two regulatory elements located in the CAV1 proximal regulatory region. The interplay between CAV1 and the TNF-α signaling pathway is intriguing and has potential as a target for therapeutic interventions in obesity and metabolic syndromes.
Keywords: NF-κB; TNF-α; adipose tissue; caveolin-1; cytokines; metabolic inflammation; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
Caveolin-1 prevents palmitate-induced NF-κB signaling by inhibiting GPRC5B-phosphorylation.
Kim YJ, Hirabayashi Y.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 18;503(4):2673-2677. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.022. Epub 2018 Aug 4.PMID: 30086884
Inducible Toll-like receptor and NF-kappaB regulatory pathway expression in human adipose tissue.
Vitseva OI, Tanriverdi K, Tchkonia TT, Kirkland JL, McDonnell ME, Apovian CM, Freedman J, Gokce N.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 May;16(5):932-7. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.25. Epub 2008 Feb 21.PMID: 18292749 Free PMC article.
Chemokine Expression in Inflamed Adipose Tissue Is Mainly Mediated by NF-κB.
Tourniaire F, Romier-Crouzet B, Lee JH, Marcotorchino J, Gouranton E, Salles J, Malezet C, Astier J, Darmon P, Blouin E, Walrand S, Ye J, Landrier JF.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 18;8(6):e66515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066515. Print 2013.PMID: 23824685 Free PMC article.
[Effect of electroacupuncture on SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway in adipose tissue of obese rats].
Huang Q, Chen R, Peng M, Li L, Li T, Liang FX, Xu F.Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2020 Feb 12;40(2):185-91. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20190324-00054.PMID: 32100506 Chinese.
Gong W, Jiao Q, Yuan J, Luo H, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Xu X, Bai L, Zhang X.Clin Sci (Lond). 2023 Mar 31;137(6):511-525. doi: 10.1042/CS20220874.PMID: 36929208
KMEL References
References
-
- Ahmad R., Al-Roub A., Kochumon S., Akther N., Thomas R., Kumari M., Koshy M.S., Tiss A., Hannun Y.A., Tuomilehto J., et al. The Synergy between Palmitate and TNF-alpha for CCL2 Production Is Dependent on the TRIF/IRF3 Pathway: Implications for Metabolic Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2018;200:3599–3611. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701552. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Catalan V., Gomez-Ambrosi J., Rodriguez A., Silva C., Rotellar F., Gil M.J., Cienfuegos J.A., Salvador J., Fruhbeck G. Expression of caveolin-1 in human adipose tissue is upregulated in obesity and obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus and related to inflammation. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008;68:213–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.03021.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Popko K., Gorska E., Stelmaszczyk-Emmel A., Plywaczewski R., Stoklosa A., Gorecka D., Pyrzak B., Demkow U. Proinflammatory cytokines Il-6 and TNF-α and the development of inflammation in obese subjects. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2010;15((Suppl. S2)):120–122. doi: 10.1186/2047-783X-15-S2-120. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palacios-Ortega S., Varela-Guruceaga M., Algarabel M., Milagro F.I., Martínez J.A., De Miguel C. Effect of TNF-Alpha on Caveolin-1 Expression and Insulin Signaling during Adipocyte Differentiation and in Mature Adipocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015;36:1499–1516. doi: 10.1159/000430314. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ruan H., Hacohen N., Golub T.R., Van Parijs L., Lodish H.F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppresses adipocyte-specific genes and activates expression of preadipocyte genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: Nuclear factor-kappaB activation by TNF-alpha is obligatory. Diabetes. 2002;51:1319–1336. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.5.1319. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Serrano-Marco L., Chacón M.R., Maymó-Masip E., Barroso E., Salvadó L., Wabitsch M., Garrido-Sánchez L., Tinahones F.J., Palomer X., Vendrell J., et al. TNF-α inhibits PPARβ/δ activity and SIRT1 expression through NF-κB in human adipocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012;1821:1177–1185. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akhter N., Kochumon S., Hasan A., Wilson A., Nizam R., Al Madhoun A., Al-Rashed F., Arefanian H., Alzaid F., Sindhu S., et al. IFN-γ and LPS Induce Synergistic Expression of CCL2 in Monocytic Cells via H3K27 Acetylation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022;15:4291–4302. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S368352. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kochumon S., Hasan A., Al-Rashed F., Sindhu S., Thomas R., Jacob T., Al-Sayyar A., Arefanian H., Al Madhoun A., Al-Ozairi E., et al. Increased Adipose Tissue Expression of IL-23 Associates with Inflammatory Markers in People with High LDL Cholesterol. Cells. 2022;11:3072. doi: 10.3390/cells11193072. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad R., Shihab P.K., Thomas R., Alghanim M., Hasan A., Sindhu S., Behbehani K. Increased expression of the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)-1 is associated with adipose tissue inflammatory state in obesity. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2015;7:71. doi: 10.1186/s13098-015-0067-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Madhoun A., Haddad D., Nizam R., Miranda L., Kochumon S., Thomas R., Thanaraj T.A., Ahmad R., Bitar M.S., Al-Mulla F. Caveolin-1 rs1997623 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Creates a New Binding Site for the Early B-Cell Factor 1 That Instigates Adipose Tissue CAV1 Protein Overexpression. Cells. 2022;11:3937. doi: 10.3390/cells11233937. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Madhoun A., Marafie S.K., Haddad D., Melhem M., Abu-Farha M., Ali H., Sindhu S., Atari M., Al-Mulla F. Comparative Proteomic Analysis Identifies EphA2 as a Specific Cell Surface Marker for Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:6437. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176437. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sindhu S., Akhter N., Wilson A., Thomas R., Arefanian H., Al Madhoun A., Al-Mulla F., Ahmad R. MIP-1alpha Expression Induced by Co-Stimulation of Human Monocytic Cells with Palmitate and TNF-alpha Involves the TLR4-IRF3 Pathway and Is Amplified by Oxidative Stress. Cells. 2020;9:1799. doi: 10.3390/cells9081799. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maher A., Nunez-Toldra R., Carrio N., Ferres-Padro E., Ali H., Montori S., Al Madhoun A. The Effect of Commercially Available Endodontic Cements and Biomaterials on Osteogenic Differentiation of Dental Pulp Pluripotent-Like Stem Cells. Dent. J. 2018;6:48. doi: 10.3390/dj6040048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Madhoun A.S., Voronova A., Ryan T., Zakariyah A., McIntire C., Gibson L., Shelton M., Ruel M., Skerjanc I.S. Testosterone enhances cardiomyogenesis in stem cells and recruits the androgen receptor to the MEF2C and HCN4 genes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013;60:164–171. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.04.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Roub A., Al Madhoun A., Akhter N., Thomas R., Miranda L., Jacob T., Al-Ozairi E., Al-Mulla F., Sindhu S., Ahmad R. IL-1β and TNFα Cooperativity in Regulating IL-6 Expression in Adipocytes Depends on CREB Binding and H3K14 Acetylation. Cells. 2021;10:3228. doi: 10.3390/cells10113228. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kochumon S., Al Madhoun A., Al-Rashed F., Thomas R., Sindhu S., Al-Ozairi E., Al-Mulla F., Ahmad R. Elevated adipose tissue associated IL-2 expression in obesity correlates with metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73347-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad R., Al-Mass A., Atizado V., Al-Hubail A., Al-Ghimlas F., Al-Arouj M., Bennakhi A., Dermime S., Behbehani K. Elevated expression of the toll like receptors 2 and 4 in obese individuals: Its significance for obesity-induced inflammation. J. Inflamm. 2012;9:48. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-9-48. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akhter N., Wilson A., Thomas R., Al-Rashed F., Kochumon S., Al-Roub A., Arefanian H., Al-Madhoun A., Al-Mulla F., Ahmad R., et al. ROS/TNF-α Crosstalk Triggers the Expression of IL-8 and MCP-1 in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells via the NF-κB and ERK1/2 Mediated Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:10519. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910519. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kopp A., Buechler C., Neumeier M., Weigert J., Aslanidis C., Scholmerich J., Schaffler A. Innate immunity and adipocyte function: Ligand-specific activation of multiple Toll-like receptors modulates cytokine, adipokine, and chemokine secretion in adipocytes. Obesity. 2009;17:648–656. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.607. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schaeffler A., Gross P., Buettner R., Bollheimer C., Buechler C., Neumeier M., Kopp A., Schoelmerich J., Falk W. Fatty acid-induced induction of Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in adipocytes links nutritional signalling with innate immunity. Immunology. 2009;126:233–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02892.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Remels A.H., Gosker H.R., Schrauwen P., Hommelberg P.P., Sliwinski P., Polkey M., Galdiz J., Wouters E.F., Langen R.C., Schols A.M. TNF-alpha impairs regulation of muscle oxidative phenotype: Implications for cachexia? Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. J. 2010;24:5052–5062. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-150714. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ouchi N., Kihara S., Arita Y., Okamoto Y., Maeda K., Kuriyama H., Hotta K., Nishida M., Takahashi M., Muraguchi M., et al. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-kappaB signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. Circulation. 2000;102:1296–1301. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.11.1296. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hube F., Birgel M., Lee Y.M., Hauner H. Expression pattern of tumour necrosis factor receptors in subcutaneous and omental human adipose tissue: Role of obesity and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1999;29:672–678. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.1999.00520.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kochumon S., Madhoun A.A., Al-Rashed F., Azim R., Al-Ozairi E., Al-Mulla F., Ahmad R. Adipose tissue gene expression of CXCL10 and CXCL11 modulates inflammatory markers in obesity: Implications for metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020;11:2042018820930902. doi: 10.1177/2042018820930902. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Rashed F., Sindhu S., Arefanian H., Al Madhoun A., Kochumon S., Thomas R., Al-Kandari S., Alghaith A., Jacob T., Al-Mulla F., et al. Repetitive Intermittent Hyperglycemia Drives the M1 Polarization and Inflammatory Responses in THP-1 Macrophages Through the Mechanism Involving the TLR4-IRF5 Pathway. Cells. 2020;9:1892. doi: 10.3390/cells9081892. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sindhu S., Akhter N., Kochumon S., Thomas R., Wilson A., Shenouda S., Tuomilehto J., Ahmad R. Increased Expression of the Innate Immune Receptor TLR10 in Obesity and Type-2 Diabetes: Association with ROS-Mediated Oxidative Stress. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018;45:572–590. doi: 10.1159/000487034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nakajima S., Koh V., Kua L.F., So J., Davide L., Lim K.S., Petersen S.H., Yong W.P., Shabbir A., Kono K. Accumulation of CD11c+CD163+ Adipose Tissue Macrophages through Upregulation of Intracellular 11beta-HSD1 in Human Obesity. J. Immunol. 2016;197:3735–3745. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600895. - DOI - PubMed