18F-Sodium Fluoride (NaF) Uptake in Calcified Bladder Carcinoma: Double Density Sign
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Kuwait Cancer Control Center, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Shuwaikh, Kuwait
- Jack Brignall PET/CT Centre, Castle Hill Hospital, Cottingham, United Kingdom
Abstract
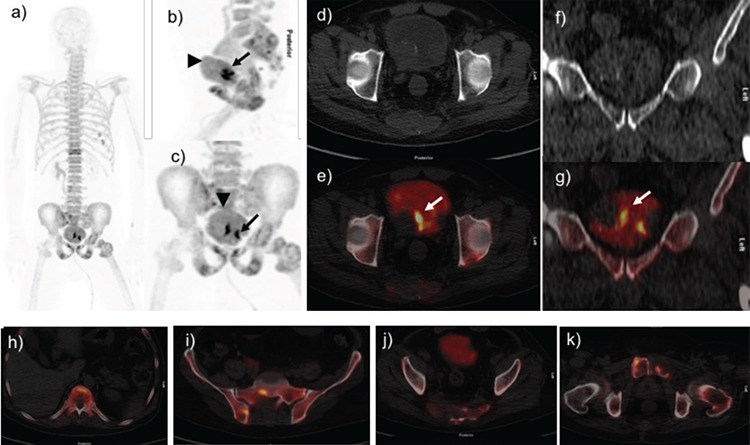
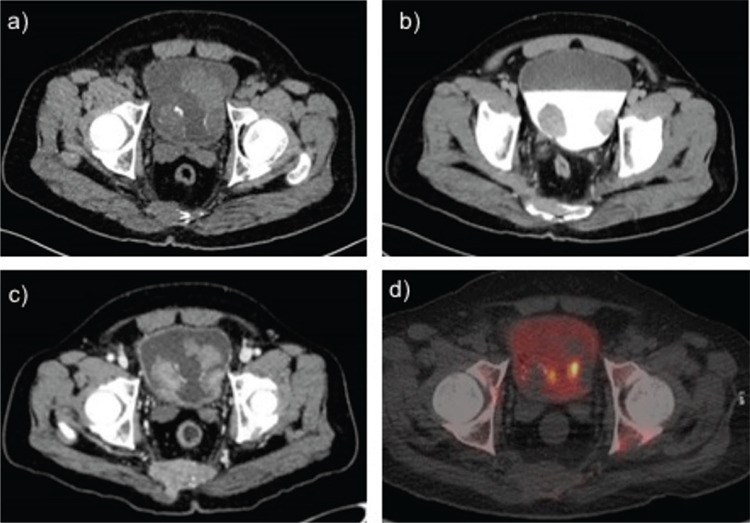
18F-Sodium fluoride (NaF) is primarily a skeletal imaging agent which can be localized in extraosseous calcified foci. Here, we describe a case of a 48-year-old man with bladder carcinoma referred for staging using 18F-NaF positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT). 18F-NaF PET/CT detected a calcified soft tissue mass in the urinary bladder. Extraosseous 18F-NaF uptake is often encountered and these non-osseous findings could possibly provide important diagnostic information. Thus, recognition of extraosseous 18F-NaF activity has implications for accurate staging and management.
Keywords: 18F-NaF PET/CT; bladder carcinoma; extraosseous uptake; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
Verma P, Chandra P, Agrawal A, Purandare N, Shah S, Rangarajan V.Indian J Nucl Med. 2016 Apr-Jun;31(2):152-3. doi: 10.4103/0972-3919.178333.PMID: 27095869 Free PMC article.
Incidental brain metastasis of breast cancer detected on 18F-Sodium Fluoride (NaF) PET-CT.
Usmani S, Ahmed N, Muzaffar S, Kandari FA.J Pak Med Assoc. 2020 Oct;70(10):1867-1868.PMID: 33159774
Pianou NK, Stavrou PZ, Vlontzou E, Rondogianni P, Exarhos DN, Datseris IE.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7.PMID: 30843003
Newer PET application with an old tracer: role of 18F-NaF skeletal PET/CT in oncologic practice.
Bastawrous S, Bhargava P, Behnia F, Djang DS, Haseley DR.Radiographics. 2014 Sep-Oct;34(5):1295-316. doi: 10.1148/rg.345130061.PMID: 25208282 Review.
Kulshrestha RK, Vinjamuri S, England A, Nightingale J, Hogg P.J Nucl Med Technol. 2016 Dec;44(4):217-222. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.116.176859. Epub 2016 Sep 15.PMID: 27634981 Review.
KMEL References
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Babaian RJ, Johnson DE, Llamas L, Ayala AG. Metastases from transitional cell carcinoma of urinary bladder. Urology. 1980;16:142–144. - PubMed
-
- Kirkali Z, Chan T, Manoharan M, Algaba F, Busch C, Cheng L, Kiemeney L, Kriegmair M, Montironi R, Murphy WM, Sesterhenn IA, Tachibana M, Weider J. Bladder cancer: epidemiology, staging and grading, and diagnosis. Urology. 2005;66(6 Suppl 1):4–34. - PubMed
-
- Usmani S, Gnanasegaran G, Marafi F, Esmail A, Ahmed N, Van den Wyngaert T. The clinical significance of incidental soft tissue uptake on whole body 18F-sodium fluoride bone PET-CT. Clin Radiol. 2019;74:95–110. - PubMed
-
- Sheth S, Colletti PM. Atlas of sodium fluoride PET bone scans: atlas of NaF PET bone scans. Clin Nucl Med. 2012;37:e110–116. - PubMed
-
- Van Der Gucht A, Galat A, Rosso J, Guellich A, Garot J, Bodez D, et al. [18F]-NaF PET/CT imaging in cardiac amyloidosis. J Nucl Cardiol. 2016;23:846–849. - PubMed