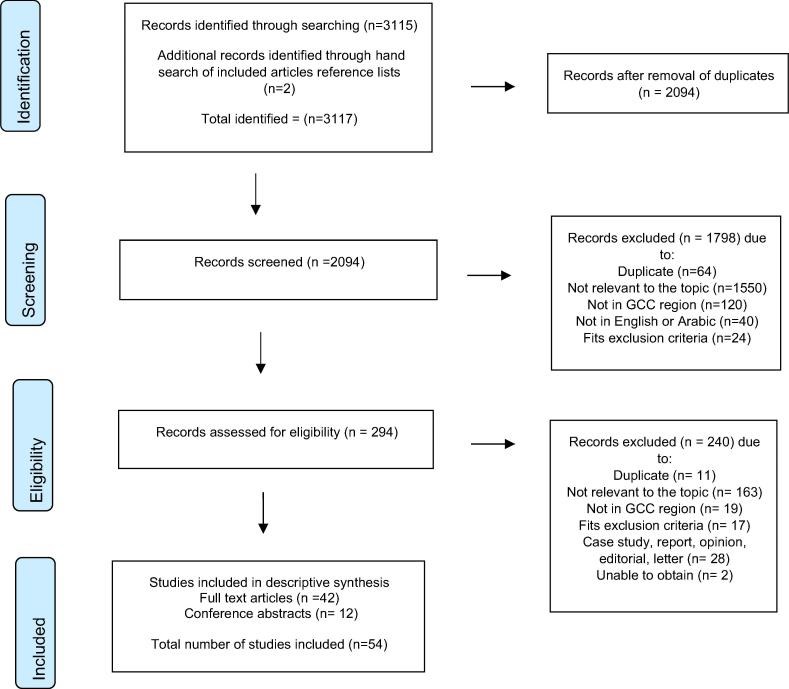
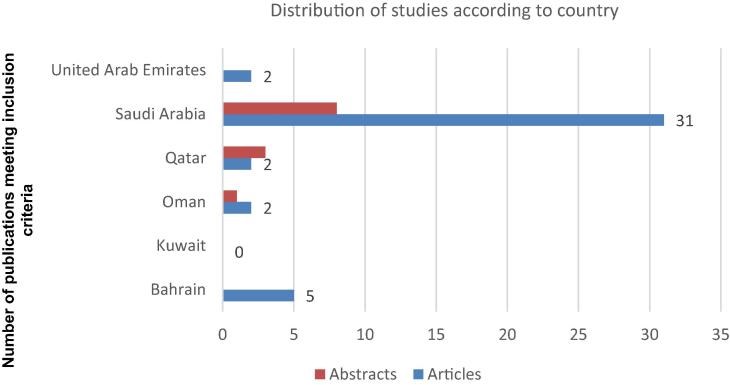
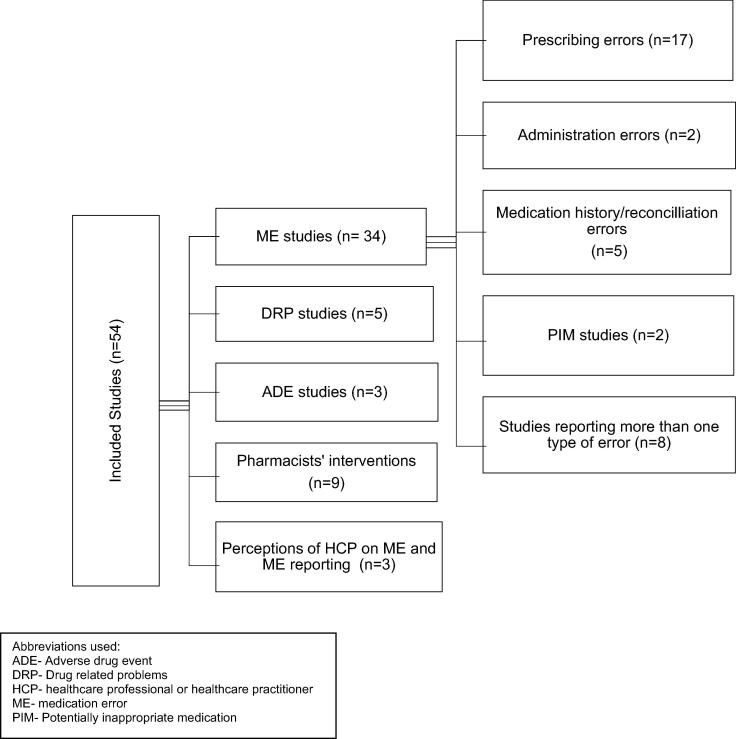
Systematic review of the safety of medication use in inpatient, outpatient and primary care settings in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries
Figures
Similar articles
Alghamdi AA, Keers RN, Sutherland A, Ashcroft DM.Drug Saf. 2019 Dec;42(12):1423-1436. doi: 10.1007/s40264-019-00856-9.PMID: 31410745 Free PMC article.
Interventions to ensure medication safety in acute care: an umbrella review.
Khalil H, Kynoch K, Hines S.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2020 Jun;18(2):188-211. doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000232.PMID: 32487967
Narayanan J, Balan S, Li Ling O, Kasim N, Johny P.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2022 Aug;42(6):2360-2366. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2022.2049729. Epub 2022 Apr 27.PMID: 35476628
Noibi S, Mohy A, Gouhar R, Shaker F, Lukic T, Al-Jahdali H.BMC Public Health. 2020 Aug 8;20(1):1211. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09259-3.PMID: 32770967 Free PMC article. Review.
The epidemiology of preventable adverse drug events: a review of the literature.
von Laue NC, Schwappach DL, Koeck CM.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2003 Jul 15;115(12):407-15. doi: 10.1007/BF03040432.PMID: 12918183 Review.
Cited by
Obaid D, El-Dahiyat F, Babar ZU.J Pharm Policy Pract. 2022 Jun 8;15(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s40545-022-00434-y.PMID: 35676727 Free PMC article.
Aljuaid M, Alajman N, Alsafadi A, Alnajjar F, Alshaikh M.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2021 Jun 21;14:2571-2578. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S311638. eCollection 2021.PMID: 34188568 Free PMC article.
Koeck JA, Young NJ, Kontny U, Orlikowsky T, Bassler D, Eisert A.Front Pediatr. 2021 May 26;9:633064. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.633064. eCollection 2021.PMID: 34123962 Free PMC article.
Prescribing errors among adult patients in a large tertiary care system in Saudi Arabia.
Alharaibi MA, Alhifany AA, Asiri YA, Alwhaibi MM, Ali S, Jaganathan PP, Alhawassi TM.Ann Saudi Med. 2021 May-Jun;41(3):147-156. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2021.147. Epub 2021 Jun 1.PMID: 34085548 Free PMC article.
Thomas B, Pallivalapila A, El Kassem W, Al Hail M, Paudyal V, McLay J, MacLure K, Stewart D.Int J Clin Pharm. 2021 Feb;43(1):77-84. doi: 10.1007/s11096-020-01108-y. Epub 2020 Aug 7.PMID: 32767219 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Abushaiqa M., Zaran F., Bach D., Smolarek R., Farber M. Educational interventions to reduce use of unsafe abbreviations. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2007;64:1170–1173. - PubMed
-
- Ackroyd-Stolarz S., Hartnell N., MacKinnon N. Demystifying medication safety: making sense of the terminology. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2006;2:280–289. - PubMed
-
- Alakhali Ansari, Alavudeen Medication errors at the outpatient pharmacy in a hospital in Aseer region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Eur. J. Clin. Pharm. 2014;16(2):144–146.
-
- Al Anany R., Badran H., Al Tamimi H., El Hamid M., Khudair I., Alabad O. Making the case for early medication reconciliation by clinical pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy. 2012;32(10):e267.
-
- Al Anazi M., Al-Jeraisy M. Perspectives of healthcare professionals on reasons for medication errors: a cross-sectional study. J. Infec. Public Health. 2015;8(4):398.
-
- Aljadhey H., Al-Rashoud I. Medication discrepancy at discharge in a tertiary hospital in Saudi Arabia. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2013;22(S1):75–76.
-
- Aljadhey H., Mahmoud M., Mayet A., Alshaikh M., Ahmed Y., Murray M.D., Bates D.W. Incidence of adverse drug events in an academic hospital: a prospective cohort study. Int. J. Qual. Health C. 2013;25(6):648–655. - PubMed
-
- Aljamal M. Medication administration errors at a major hospital in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2012;35:876.
-
- Al-Jazairi A., Al-Agil A., Asiri Y. The impact of clinical pharmacist in a cardiac surgery intensive care unit. Saudi Med. J. 2008;29(2):277–281. - PubMed
-
- Al Khaja K., Al-Ansari T., Damanhori A., Sequeiraa R. Rational use of antimicrobials in infants in primary care of Bahrain. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2006;52(6):390–393. - PubMed
-
- Al Khaja K., Al-Ansari T., Damanhori A., Sequeira R. Evaluation of drug utilization and prescribing errors in infants: a primary care prescription based study. Health Policy (New York) 2007;52(6):350–357. - PubMed
-
- Al Khaja K., Al-Ansari T., Sequeira R. An evaluation of prescribing errors in primary care in Bahrain. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005;43(6):294–301. - PubMed
-
- Al Khaja K., Sequeira R., Al-Ansari T., Damanhori A. Prescription writing skills of residents in a family practice residency programme in Bahrain. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84:198–204. - PubMed
-
- Al Khaja K., Sequeira R., Damanhori A. Medication prescribing errors pertaining to cardiovascular/antidiabetic medications: a prescription audit in primary care. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012;26(410–417):118. - PubMed
-
- Allan E.L., Barker K.N. Fundamentals of medication error research. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1990;47:555–571. - PubMed
-
- Al-Omar H., Al-Sultan M., Abu-Auda H. Prescribing of potentially inappropriate medications among the elderly population in an ambulatory care setting in a Saudi Military hospital: trend and cost. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2013;13:616–621. - PubMed
-
- Al-Rashdi I.S., Victoria M., Susan S. Analysis of pharmacists’ interventions of electronic prescriptions at Sultan Qaboos University hospital in Oman. Value in Health. 2010;13(7):A425.
-
- Al-Rowibah F., Younis M., Parkash J. The Impact of Computerized Physician Order Entry on Medication Errors and Adverse Drug Events. J. Health Care Finance. 2013;40(1):93–102. - PubMed
-
- Alshaikh M., Mayet A., Aljadhey H. Medication error reporting in a university teaching hospital in Saudi Arabia. J. Patient. Saf. 2013;9:145–149. - PubMed
-
- Al-Tajir G., Kelly W. Epidemiology, comparative methods of detection and preventability of adverse drug events. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005;39:1169–1174. - PubMed
-
- Altebenaui A., Alrashedi M., Alshammari T. Completeness of medications prescriptions: prescription errors study in hail region (PeSHR) Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2015;24:101.
-
- Arabi Y., Alamry A., Al Owais S., Al-Dorzi H. Incident reporting at a tertiary care hospital in Saudi Arabia. J. Patient Saf. 2012;8:81–87. - PubMed
-
- ASHP, 1982. Standard definition of a medication error. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1982; 39 321. 120 - PubMed
-
- ASHP ASHP guidelines on preventing medication errors in hospitals. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1993;50(2):305–314. - PubMed
-
- Bates D.W., Cullen D., Laird N. Incidence of adverse drug events and potential adverse drug events: implications for prevention. JAMA. 1995;274(1):29–34. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960;20:37–46.
-
- Dean B.S., Barber N.D. A validated, reliable method of scoring the severity of medication errors. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 1999;56:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Dean B., Schachter M., Vincent C., Barber N. Causes of prescribing errors in hospital inpatients: a prospective study. Lancet. 2002;359:1373–1378. - PubMed
-
- Dibbi H., Al-Abrashy H., Hussein W. Causes and outcome of medication errors in hospitalised patients. Saudi Med J. 2006;27(10):1489–1492. - PubMed
-
- Elnour A., Ellahham N., Qassas H. Implementation of medication error reporting through med safe tool: the clinical pharmacists and the inpatient nursing staff collaborative approach. J. Patient Saf. 2007;3(4):177–183.
-
- Ferner R.E., Aronson J.K. Clarification of terminology in medication errors. Drug Saf. 2006;29:1011–1022. - PubMed
-
- Fick D., Cooper J., Wade W., Waller J., MacLean R., Beers M. Updating the Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication use in older adults. Results of a US Consensus Panel of Experts. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:2716–2724. - PubMed
-
- Franklin and Tully, preface In Tully, M., Franklin, B.D. (Eds.) Safety in Medication Use. Boca Ranton, United States, Taylor and Francis Group, pp xiii.
-
- Flynn E.A., Barker K.N. Medication error research. In: Cohen M.R., editor. Medication Errors. American Pharmaceutical Association; Washington DC: 1999.
-
- Flynn E.A., Barker K.N., Pepper G.A. Comparison of methods for detecting medication errors in 36 hospitals and skilled-nursing facilities. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2002;59:436–446. - PubMed
-
- Ghaleb M., Barber N., Franklin B., Yeung V. Systematic review of medication errors in pediatric patients. Ann. Pharmacother. 2006;40:1766–1776. - PubMed
-
- Ghaleb M.A., Barber N., Dean Franklin B., Wong I.C.K. The incidence and nature of prescribing and medication administration errors in paediatric inpatients. Arch. Dis. Child. 2010;95:113–118. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi T.K., Seger D.L., Bates D.W. Identifying drug safety issues: from research to practice. Int J Qual Health Care. 2000;12:69–76. - PubMed
-
- Hemida AlHawawi, Alawwad, Medication errors in a neonatal intensive care unit, Saudi ArabiaA retrospective study. Pediatr. Res. 2011;70:604. 101038/pr.2011.829.
-
- Hepler C.D., Strand L.M. Opportunities and responsibilities in pharmaceutical care. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1990;47(3):533–543. - PubMed
-
- Insley J. 13th Edition. Arnold; London: 1996. Prescribing. A pediatric vade-mecum.
-
- Irshaid Y.M., Al Homrany M., Hamdi A.A., Adjepon-Yamoah K.K., Mahfouz A.A. Compliance with good practice in prescription writing at outpatient clinics in Saudi Arabia. East Mediterr Health J. 2005;11(5–6):922–928. - PubMed
-
- Jha A.K., Prasopa-Plaizier N., Larizgoita I., Bates D.W. On behalf of the research priority setting working group of the world alliance for patient safety (2010). Patient safety research an overview of the global evidence. Qual. Saf. Health Care. 2010;19:42–47. - PubMed
-
- Kaushal R., Bates D.W., Landrigan C., McKenna K.J., Clapp M.D. Medication errors and adverse drug events in pediatric inpatients. JAMA. 2001;285(16):2114–2120. - PubMed
-
- Kheir N., Awaisu A., Sharfi A. Drug-related problems identified by pharmacists conducting medication use reviews at a primary health centre in Qatar. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2014;36:702–706. - PubMed
-
- Khoja T., Neyaz Y., Qureshi N., Magzoub M. Medication errors in primary care in Riyadh City. Saudi Arabia. East Mediterr. Health J. 2011;17(2):156–159. - PubMed
-
- Kohn L.T., Corrigan J.M., Donalson M.S., editors. To err is human: building a safer health system. National Academy Press; Washington, DC: 2000. (Vol. 627)
-
- Landis J.R., Koch G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–174. - PubMed
-
- Lisby M., Nielsen L.P., Brock B., Mainz J. How are medication errors defined? A systematic literature review of definitions and characteristics. Int. J. Qual. Health Care. 2010;22(507–518):126. - PubMed
-
- Mahmoud M.A., Aljadhey H., Hassali M.A. Incidence of prescribing errors in hospitalized patients in Saudi Arabia. Value In Health. 2016;1(9):A1–A318.
-
- McLeod M. Measuring medication errors. In: Tully M., Franklin B.D., editors. Safety in Medication Use. Boca Ranton; United States, Talor and Francis Group: 2016. pp. 61–72.
-
- McPhillips H.A., Stille C.J., Smith D., Hecht J., Pearson J. Potential medication dosing errors in outpatient pediatrics. J Pediatr. 2005;147(6):761–767. - PubMed
-
- Mendonca J.M., Lyra D.P., Jr, Rabelo J.S. Analysis and detection of dental prescribing errors at primary health care units in Brazil. Pharm World Sci. 2010;32(1):30–35. - PubMed
-
- Mitwally H., Ibrahim T., Fayez A. (2015) Impact of physicians education on prescribing errors within an inpatient setting. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35(11) e183.
-
- Naranjo C.A., Busto U., Sellers E.M., Sandor P., Ruiz I., Roberts E.A. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981;30:239–245. - PubMed
-
- National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. NCC MERP (2008). National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. Available at http://www.nccmerp.org.
-
- NCCMERP (2012). National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention, About Medication Errors: What is a Medication Error? Available from: <http://www.nccmerp.org/aboutMedErrors.html>. (Last accessed on 2012 Jan 19).
-
- Nebeker J.R., Barach P., Samore M.H. Clarifying adverse drug events: a clinician’s guide to terminology, documentation, and reporting. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004;140(10):795–801. - PubMed
-
- Ninno S.D., Ninno M.A., editors. Pharmacotherapy Self-assessment Program. Kansas City (MO); American College Clinical Pharmacy: 2000. pp. 113–148.
-
- Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe (PCNE), 2008 http:// www.pcne.org/ (accessed January 2012).
-
- Rahman, S, Farooki, M.Q., Alsalamah S., 1994 Pharmacist intervention in preventing prescribing error in a tertiary care hospital in Saudi Arabia. IPA 51 (Jun) MCS-14.
-
- Rashed A., Neubert A., Tomlin S., Jackman J. Epidemiology and potential associated risk factors of drug-related problems in hospitalised children in the United Kingdom and Saudi Arabia. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012;68:1657–1666. - PubMed
-
- Rashed A., Neubert A., Alhamdan H., Tomlin S., Alazmi A. Drug related problems found in children attending an emergency department in Saudi Arabia and the United Kingdom. Int J Clin Pharm. 2013;35:327–331. - PubMed
-
- Rehmani R. Medication history taking in emergency department is unreliable. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2011;58(4S):S251.
-
- Sadat-Ali M., Al-Shafei B., Al-Turki R., Ahmed S., Al-Abbas S., Al-Omran A. Medication administration errors in Eastern Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2010;31(11):1257–1259. - PubMed
-
- Shaughnessy A., Nickel R. Prescription-writing patterns and errors in a family medicine residency program. 1989;29(3):290–295. - PubMed
-
- Sonallah H., Ibrahim T., Izham M. Evaluation of medication reconciliation conducted by clinical pharmacists at a newly established hospital in Qatar. Pharmacotherapy. 2014;34(10):e249.
-
- Strand, L.M., Morley, P.C., Cipolle, R.J., Ramsey, R, Lamsam, G.D., Drug-related problems: their structure and function. DICP.1990;24:1093–1097. - PubMed
-
- Szeinbach, S., Seoane-Vazquez, E., Parekh, A., Herderick, M., 2007. Dispensing errors in community pharmacy: perceived influence of sociotechnical factors. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 19 (4) 203–209. 130. - PubMed
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva: 1999. Reporting adverse drug reactions.
-
- WHO. 2014. WHO definitions (cited 2014). <http://www.who.int/medicines/areas/quality_safety_efficacy/trainingcours....
-
- WHO Collaborating Centre for International Drug Monitoring., 2017. UMC WHO Programme Members. [ONLINE] Available at: http;//www.who-umc.org/global-pharmacovigilance/members/who-programme-members/. (accessed 9 October 2017).
-
- World Bank . World Bank; Washington, DC: 2017. The World Bank Annual Report 2017. (c) World Bank. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/27986 License: CC BY-NC-ND.
-
- World Health Organisation. 2014. http://www.who.int/gho/health_financing/total_expenditure/en/. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/health_financing/total_expenditure/en/. (accessed 4 October 2017).
-
- Youssef, A, Almubarak, A, Aljohnai, M et al., 2015. Contraindicated medications administered to inpatients with renal insufficiency in a Saudi Arabian hospital that has a computerized clinical decision support system. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 10 (3) 320–26. 132.