Use of Midodrine in Heart Failure: Two Case Reports and a Review of the Literature
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Clinical Pharmacy Department, Ahmadi Hospital - Kuwait Oil Company, Al Ahmadi, Kuwait.
- Internal Medicine Department, Ahmadi Hospital - Kuwait Oil Company, Al Ahmadi, Kuwait.
Abstract
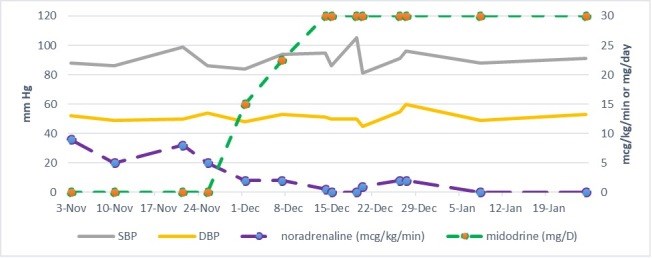
Hypotension in patients with heart failure is much more frequent in daily clinical practice than the 10-15% reported in clinical trials. In patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), hypotension frequently limits the initiation and up-titration of guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). Midodrine is a peripheral alpha-1 agonist and a vasopressor anti-hypotensive agent approved for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension. We describe two cases where midodrine was prescribed in patients with HFrEF and hypotension.
Learning points: Hypotension in patients with systolic heart failure is a frequent presentation and can limit the initiation and optimization of guideline-directed medical therapy.Midodrine is a peripheral alpha-1 agonist and anti-hypotensive agent approved for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension.Midodrine may be used off-label in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and symptomatic hypotension to allow optimization of medical therapy.
Keywords: Midodrine; heart failure; noradrenaline.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
Midodrine to optimize heart failure therapy in patients with concurrent hypotension.
Shiu P, Grewal GS, Kozik TM.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2022 May 18;10:2050313X221100400. doi: 10.1177/2050313X221100400. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35601610 Free PMC article.
Asai Y, Sato T, Kito D, Yamamoto T, Hioki I, Urata Y, Abe Y.J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2021 Mar 3;7(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40780-021-00193-z.PMID: 33653416 Free PMC article.
Hurst GC, Somerville KT, Alloway RR, Gaber AO, Stratta RJ.Clin Transplant. 2000 Feb;14(1):42-7. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0012.2000.140108.x.PMID: 10693634
McTavish D, Goa KL.Drugs. 1989 Nov;38(5):757-77. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198938050-00004.PMID: 2480881 Review.
Cruz DN.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000 May;1(4):835-40. doi: 10.1517/14656566.1.4.835.PMID: 11249519 Review.
KMEL References
References
-
- CONSENSUS Trial Study Group. Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. Results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS) N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1429–1435. - PubMed
-
- Komajda M, Schope J, Wagenpfeil S, Tavazzi L, Bohm M, Ponikowski P, et al. QUALIFY Investigators. Physicians’ guideline adherence is associated with long-term heart failure mortality in outpatients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: the QUALIFY international registry. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21:921–929. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosy AP, Vaduganathan M, Mentz RJ, Greene SJ, Subacius H, Konstam MA, et al. Clinical profile and prognostic value of low systolic blood pressure in patients hospitalized for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: insights from the Efficacy of Vasopressin Antagonism in Heart Failure: Outcome Study with Tolvaptan (EVEREST) trial. Am Heart J. 2013;165:216–225. - PubMed
-
- Tartiere JM, Logeart D, Safar ME, Cohen-Solal A. Interaction between pulse wave velocity, augmentation index, pulse pressure and left ventricular function in chronic heart failure. J Hum Hypertens. 2006;20:213–219. - PubMed
-
- National Library of Medicine- PubChem. Midodrine hydrochloride. Available from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Midodrine-hydrochloride.
-
- Scoma C, Dae-Hyun L, Cohen A, Fernandez J. Prevalence of midodrine use in patients admitted with systolic congestive heart. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(18):678. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(21)02037-4.. - DOI
-
- Folefack A, Zakir RM, Saric M, Berkowitz RL. Midodrine increases blood pressure in hypotensive heart failure patients facilitating optimization of heart failure therapy leading to improved outcomes. J Cardiac Fail. 2006;12(6):S129. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2006.06.448. doi: - DOI
-
- Vijayaraghavan K, Little D, Mercer T, Querrey T, Wilmowski S, Win A, et al. Midodrine as a bridge to enable use of life enhancing therapies in chronic heart failure. J Cardiac Fail. 2020;26(10):S59. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.09.175. - DOI