Opioid Antagonist in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
Affiliations
Affiliations
- 1School of Medicine, Colegio de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad San Francisco de Quito, Quito 170901, Ecuador.
- 2Neurology Department, School of Medicine, AMC MET Medical College, Ahmedabad 380008, India.
- 3Public Health Department, University of California Berkeley, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA.
- 4School of Medicine, Ternopil National Medical University, 46002 Ternopil, Ukraine.
- 5Emergency Department, Amiri Hospital, Sharq 15300, Kuwait.
- 6Department of Neurology, Larkin Community Hospital, Miami, FL 10029, USA.
- 7Public Health Department, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY 10029, USA.
Abstract
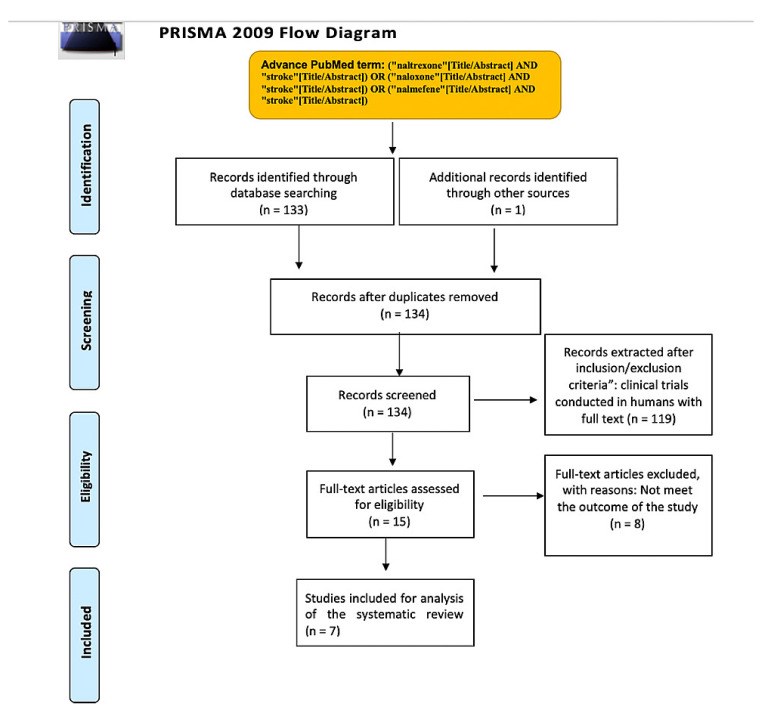
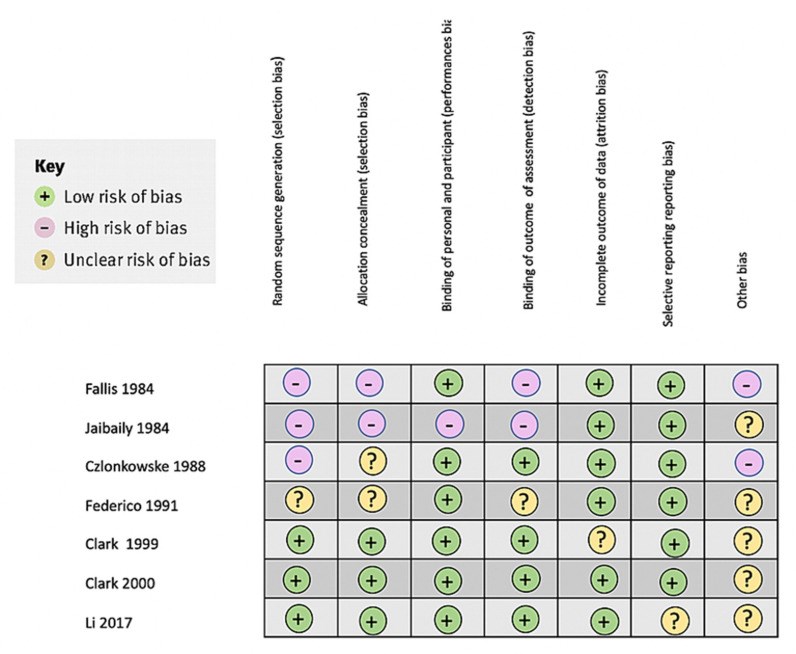
Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability, and novel treatments need to be found, particularly drugs with neuroprotective and restorative effects. Lately, there has been an increased interest in the relationship between opioids and ischemic stroke. To further appreciate this association between opioids and stroke, we conducted a systematic review to investigate anti-opioid medication's effectiveness in treating ischemic stroke. We used PubMed advanced-strategy and Google Scholar searches and only included full-text clinical trials on humans and written in the English language. After applying the inclusion/exclusion criteria, seven clinical trials were reviewed. Only one of the naloxone and nalmefene clinical trials showed statistically favorable results. Overall, the nalmefene clinical trials used more updated measures (NIHSS, GOS) to evaluate recovery and functional status in ischemic stroke patients than the naloxone clinical trials. There was less bias in the nalmefene clinical trials. Animal and in vitro studies have showed promising results. Additional research should be conducted with new clinical trials of both drugs with larger samples in patients less than 70 years old and moderate to severe infarcts.
Keywords: anti-opioids; clinical trials; nalmefene; naloxone; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
Clark WM, Raps EC, Tong DC, Kelly RE.Stroke. 2000 Jun;31(6):1234-9. doi: 10.1161/01.str.31.6.1234.PMID: 10835438 Clinical Trial.
Use of Levodopa After a Stroke: A Systematic Review.
Moncayo JA, Yepez M, Camacho M, Aguirre AS, Ojeda D, Ortiz JF, Sen M, Argudo J, Proano L, Cordova S, Kothari N.Cureus. 2022 Apr 27;14(4):e24529. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24529. eCollection 2022 Apr.PMID: 35651458 Free PMC article. Review.
Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Roberts H, Tomsick T, Connors B, Barr J, Dillon W, Warach S, Broderick J, Tilley B, Sacks D; Technology Assessment Committee of the American Society of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology; Technology Assessment Committee of the Society of Interventional Radiology.Stroke. 2003 Aug;34(8):e109-37. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000082721.62796.09. Epub 2003 Jul 17.PMID: 12869717
Opioids in Post-stroke Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Scuteri D, Mantovani E, Tamburin S, Sandrini G, Corasaniti MT, Bagetta G, Tonin P.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 27;11:587050. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.587050. eCollection 2020.PMID: 33424596 Free PMC article. Review.
Kim S, Wagner HN Jr, Villemagne VL, Kao PF, Dannals RF, Ravert HT, Joh T, Dixon RB, Civelek AC.J Nucl Med. 1997 Nov;38(11):1726-31.PMID: 9374341 Clinical Trial.
KMEL References
References
-
- Qureshi W.T., O’Neal W.T., Khodneva Y., Judd S., Safford M.M., Muntner P., Soliman E.Z. Association Between Opioid Use and Atrial Fibrillation: The Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) Study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015;175:1058–1060. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.1045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li X., Hou W.C., Song L. Nalmefene improves prognosis in patients with a large cerebral infarction: Study protocol and preliminary results of a randomized, controlled, prospective trial. Clin. Trials Degener. Dis. 2017;2:101–107.
-
- Anttila J.E., Albert K., Wires E.S., Mätlik K., Loram L.C., Watkins L.R., Rice K.C., Wang Y., Harvey B.K., Airavaara M. Post-stroke Intranasal (+)-Naloxone Delivery Reduces Microglial Activation and Improves Behavioral Recovery from Ischemic Injury. eNeuro. 2018;5 doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0395-17.2018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grace P.M., Shimizu K., Strand K.A., Rice K.C., Deng G., Watkins L.R., Herson P.S. (+)-Naltrexone is neuroprotective and promotes alternative activation in the mouse hippocampus after cardiac arrest/cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015;48:115–122. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Alebeek M.E., Arntz R.M., Ekker M.S., Synhaeve N.E., Maaijwee N.A., Schoonderwaldt H., van der Vlugt M.J., van Dijk E.J., Rutten-Jacobs L.C., de Leeuw F.E. Risk factors and mechanisms of stroke in young adults: The FUTURE study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38:1631–1634. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17707138. - DOI - PMC - PubMed