Cardiac Sodium Channel Blockade Due to Antiepileptic Drug Combination
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Internal Medicine Department, Ahmadi Hospital, Kuwait Oil Company, Al Ahmadi, Kuwait.
- Nursing Department, Ahmadi Hospital, Kuwait Oil Company, Al Ahmadi, Kuwait.
- Internal Medicine Department, Al Salam Hospital, Kuwait.
- Department of Cardiology, Chest Diseases Hospital, Kuwait.
Abstract
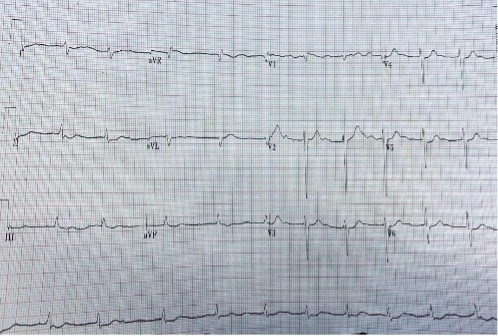
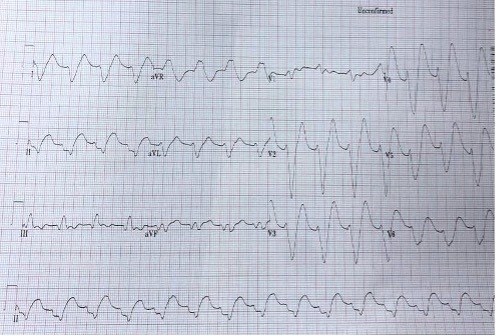
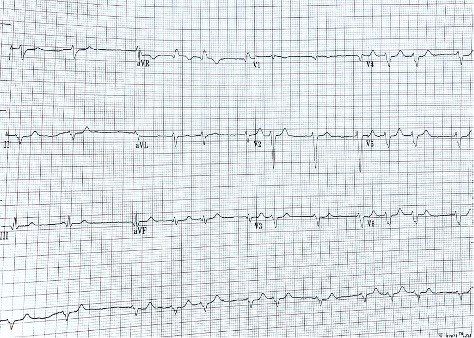
Drugs that inhibit voltage-dependent sodium channels are commonly used to treat epilepsy. Old and novel antiepileptic drugs are used either as monotherapy or in combination to control epilepsy. For a long time, carbamazepine has been used as the first choice for the treatment of simple and complex partial seizures. In the USA, lacosamide was approved in October 2008 as an adjunctive treatment for partial-onset seizures. We describe the effect of two sodium channel blockers on the heart of a patient with epilepsy.
Learning points: Approximately 30% of patients with epilepsy require combination therapy with antiepileptic drugs for seizure reduction.Lacosamide and carbamazepine are both sodium channel blockers but exert their effects through different mechanisms.Electrocardiogram monitoring is necessary when lacosamide and carbamazepine are used together as this combination may predispose to seizures, conduction abnormalities and dysrhythmia.
Keywords: Sodium channel blockers; electrocardiogram; lacosamide.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
Sake JK, Hebert D, Isojärvi J, Doty P, De Backer M, Davies K, Eggert-Formella A, Zackheim J.CNS Drugs. 2010 Dec;24(12):1055-68. doi: 10.2165/11587550-000000000-00000.PMID: 21090839
Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data.
Nevitt SJ, Sudell M, Weston J, Tudur Smith C, Marson AG.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 29;6(6):CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub2.PMID: 28661008 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Barcs Gábor, Szűcs A, Horváth A, Kamondi A.Ideggyogy Sz. 2015 Jan 30;68(1-2):23-9.PMID: 25842913 Hungarian.
Chua-Tuan JL, Cao D, Iwanicki JL, Hoyte CO.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2015 Jul;53(6):565-8. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1040157. Epub 2015 May 8.PMID: 25951877
Current understanding of the mechanism of action of the antiepileptic drug lacosamide.
Rogawski MA, Tofighy A, White HS, Matagne A, Wolff C.Epilepsy Res. 2015 Feb;110:189-205. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.11.021. Epub 2014 Dec 3.PMID: 25616473 Review.
KMEL References
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/