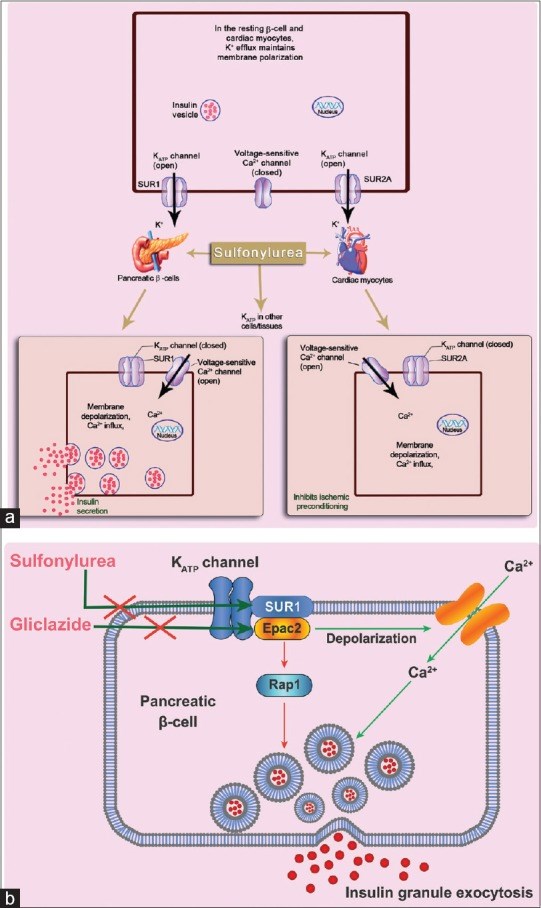
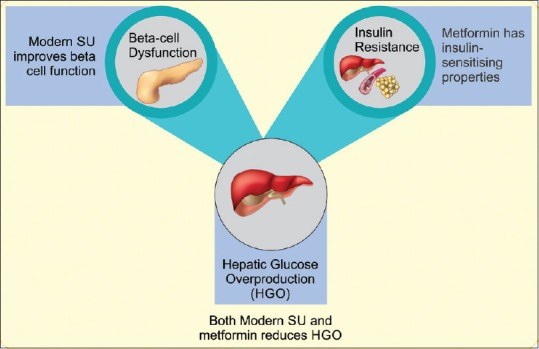
Consensus Recommendations on Sulfonylurea and Sulfonylurea Combinations in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - International Task Force
Sanjay Kalra 1, Silver Bahendeka 2, Rakesh Sahay 3, Sujoy Ghosh 4, Fariduddin Md 5, Abbas Orabi 6, Kaushik Ramaiya 7, Sameer Al Shammari 8, Dina Shrestha 9, Khalid Shaikh 10, Sachitha Abhayaratna 11, Pradeep K Shrestha 12, Aravinthan Mahalingam 13, Mazen Askheta 14, Aly Ahmed A Rahim 15, Fatimah Eliana 16, Hari K Shrestha 17, Sandeep Chaudhary 18, Nancy Ngugi 19, Jean Claude Mbanya 20, Than Than Aye 21, Tint Swe Latt 22, Zhanay A Akanov 23, Abbas Raza Syed 24, Nikhil Tandon 25, A G Unnikrishnan 26, S V Madhu 27, Ali Jawa 28, Subhankar Chowdhury 4, Sarita Bajaj 29, Ashok Kumar Das 30
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Endocrinology, Bharti Hospital, Karnal, Haryana, India.
- Department of Internal Medicine, Diabetes & Endocrinology, St. Francis Hospital, Nsambya, Kampala, Uganda.
- Department of Endocrinology, Osmania Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
- Department of Endocrinology, IPGMER and SSKM Hospital, Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
- Department of Endocrinology, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt.
- Department of Internal Medicine, Hindu Mandal Hospital, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania.
- Department of Endocrinology, Al Jahra Hospital, Al Jahra, Kuwait.
- Department of Endocrinology, Norvic International Hospital and Medical College, and Hospital for Advanced Medicine and Surgery, Maharajganj, Kathmandu, Nepal.
- Department of Diabetes, Faculty of Internal Medicine, Royal Oman Police Hospital, Muscat, Oman.
- Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, Colombo, Sri Lanka.
- Department of Medicine, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Maharajganj, Kathmandu, Nepal.
- Department of Medicine, Teaching Hospital, Jaffna, Sri Lanka.
- Department of Medicine, Tawam Hospital, Al Ain, UAE.
- Department of Internal Medicine, Diabetes & Metabolism Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt.
- Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, YARSI University, Jakarta, Indonesia.
- Department of Internal Medicine, Kathmandu University Hospital, Dhulikhel, Nepal.
- Department of Endocrinology, ADK Hospitals, Male, Maldives.
- Department of Endocrinology, Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi, Kenya.
- Department of Internal Medicine and Specialties, Faculty of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University of Yaoundé, Yaounde, Cameroon.
- Department of Endocrinology, University of Medicine 2, Yangon, Myanmar.
- Department of Medicine, University of Medicine 2, Yangon, Myanmar.
- Center of Diabetes, Clinic of Internal Diseases, Asfendiyarov Kazakh National Medical University, Almaty, Republic of Kazakhstan.
- Department of Endocrinology, Shaukat Khanum Hospital and Research Center, Lahore, Pakistan.
- Department of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
- Department of Endocrinology and Diabetes, Chellaram Diabetes Institute, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
- Department of Medicine, University of Delhi, New Delhi, India.
- Department of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Wilshire Cardiovascular and Endocrine Center of Excellence, Lahore, Pakistan.
- Department of Medicine, MLN Medical College, Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh, India.
- Department of General Medicine, Pondicherry Institute of Medical Sciences, Puducherry, India.
Abstract
For decades, sulfonylureas (SUs) have been important drugs in the antidiabetic therapeutic armamentarium. They have been used as monotherapy as well as combination therapy. Focus on newer drugs and concerns about the risk of severe hypoglycemia and weight gain with some SUs have led to discussion on their safety and utility. It has to be borne in mind that the adverse events associated with SUs should not be ascribed to the whole class, as many modern SUs, such as glimepiride and gliclazide modified release, are associated with better safety profiles. Furthermore, individualization of treatment, using SUs in combination with other drugs, backed with careful monitoring and patient education, ensures maximum benefits with minimal side effects. The current guidelines, developed by experts from Africa, Asia, and the Middle East, promote the safe and smart use of SUs in combination with other glucose-lowering drugs.
Keywords: Gliclazide; glimepiride; sulfonylureas; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
Kalra S, Aamir AH, Raza A, Das AK, Azad Khan AK, Shrestha D, Qureshi MF, Md Fariduddin, Pathan MF, Jawad F, Bhattarai J, Tandon N, Somasundaram N, Katulanda P, Sahay R, Dhungel S, Bajaj S, Chowdhury S, Ghosh S, Madhu SV, Ahmed T, Bulughapitiya U.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Sep-Oct;19(5):577-96. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.163171.PMID: 26425465 Free PMC article. Review.
Kalra S, A K D, Md F, K S, P S, A A R, M J, S S, A O, M R S, Selim S, M P B, Gangopadhyay KK, Y A L, T N, D D, S D T, V D, Dutta D, H K, R M, S D, A D, A B, G P, S C, Dhingra A, N P, A AA, M M.Curr Med Res Opin. 2021 Mar;37(3):403-409. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2020.1864309. Epub 2021 Jan 10.PMID: 33319626
Al-Saleh Y, Sabico S, Al-Furqani A, Jayyousi A, Alromaihi D, Ba-Essa E, Alawadi F, Alkaabi J, Hassanein M, Al-Sifri S, Saleh S, Alessa T, Al-Daghri NM.Diabetes Ther. 2021 Aug;12(8):2115-2132. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01059-1. Epub 2021 May 13.PMID: 33983614 Free PMC article.
Colagiuri S, Matthews D, Leiter LA, Chan SP, Sesti G, Marre M.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018 Sep;143:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.05.028. Epub 2018 May 24.PMID: 29802958 Review.
Is gliclazide a sulfonylurea with difference? A review in 2016.
Singh AK, Singh R.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;9(6):839-51. doi: 10.1586/17512433.2016.1159512. Epub 2016 Mar 15.PMID: 26924475 Review.
Cited by
An introduction to insulin use in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Coetzee A.S Afr Fam Pract (2004). 2023 Apr 20;65(1):e1-e5. doi: 10.4102/safp.v65i1.5702.PMID: 37132569 Free PMC article.
Mohan V, Wangnoo S, Das S, Dhediya R, Gaurav K.World J Diabetes. 2022 Dec 15;13(12):1168-1183. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1168.PMID: 36578872 Free PMC article.
Chien TY, Ting HW, Chen CF, Yang CZ, Chen CY.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Jun 13;19(6):1049-1055. doi: 10.7150/ijms.71341. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35813300 Free PMC article.
Niwaha AJ, Rodgers LR, Carr ALJ, Balungi PA, Mwebaze R, Hattersley AT, Shields BM, Nyirenda MJ, Jones AG.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022 Apr;10(2):e002714. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002714.PMID: 35450869 Free PMC article.
Position of Sulfonylureas in the Current ERA: Review of National and International Guidelines.
Mohan V, Saboo B, Khader J, Modi KD, Jindal S, Wangnoo SK, Amarnath S.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022 Feb 14;15:11795514221074663. doi: 10.1177/11795514221074663. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35185350 Free PMC article. Review.
KMEL References
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. The International Federation (IDF) Diabetes Atlas. 7th ed. Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2015. [Last accessed on 2017 Jan 25]. ISBN: 978-2-930229-81-2. Available from: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/
-
- Global Report on Diabetes – World Health Organization. 2016. [Last accessed on 2017 Jan 25]. Available from: http://www.apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/204871/1/9789241565257_eng.pdf .
-
- Truter I. An investigation into antidiabetic medication prescribing in South Africa. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1998;23:417–22. - PubMed
-
- Chiang CW, Chiu HF, Chen CY, Wu HL, Yang CY. Trends in the use of oral antidiabetic drugs by outpatients in Taiwan: 1997-2003. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2006;31:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Principal JK. A study on drug utilization of oral hypoglycemic agents in type-2 diabetic patients. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2011;4:60–4.
-
- Mandal S, Maiti T, Das AK, Das A, Mandal A, Sarkar BS, et al. Drug utilization study in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus attending diabetes clinic of a tertiary care hospital in rural Bengal. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. 2016;5:1647–54.
-
- National List of Essential Medicines. India: 2015. [Last accessed on 2017 Mar 21]. Available from: http://www.apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js23088en/
-
- Mkele G. What's the latest on sulfonylureas in the management of type 2 diabetes? South Afr Fam Pract. 2013;55:501–3.
-
- Hayward RA, Reaven PD, Wiitala WL, Bahn GD, Reda DJ, Ge L, et al. Follow-up of glycemic control and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2197–206. - PubMed
-
- Phung OJ, Sobieraj DM, Engel SS, Rajpathak SN. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:410–7. - PubMed
-
- Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1577–89. - PubMed
-
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2560–72. - PubMed
-
- Del Prato S, Felton AM, Munro N, Nesto R, Zimmet P, Zinman B, et al. Improving glucose management: Ten steps to get more patients with type 2 diabetes to glycaemic goal. Int J Clin Pract. 2005;59:1345–55. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamson MJ. Should sulfonylureas remain an acceptable first-line add-on to metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes? Yes, they continue to serve us well!iabetes Care. 2015;38:166–9. - PubMed
-
- Handelsman Y, Bloomgarden ZT, Grunberger G, Umpierrez G, Zimmerman RS, Bailey TS, et al. American Association of clinical endocrinologists and American College of endocrinology – Clinical practice guidelines for developing a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan-2015. Endocr Pract. 2015;21(Suppl 1):1–87. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sarkar A, Tiwari A, Bhasin PS, Mitra M. Pharmacological and pharmaceutical profile of gliclazide: A review. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2011;1:11–9.
-
- Oderda G, Richards K, Turpin S. Sulfonylurea Agents & Combination Products Drug Class Review. University of Utah College of Pharmacy. 2013 Jul; Final Report.
-
- Lexi-Comp Inc. Drug Information Handbook. 21st ed. Hudson, OH: Lexi-Comp Inc; 2013.
-
- Ballagi-Pordány G, Németh M, Aranyi Z, Kékesi E, Koltai MZ, Papp G, et al. Effect of glimepiride on the electrical activity of isolated rabbit heart muscle. Arzneimittelforschung. 1992;42:111–3. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM, Gribble FM. Tissue-specific effects of sulfonylureas: Lessons from studies of cloned K(ATP) channels. J Diabetes Complications. 2000;14:192–6. - PubMed
-
- Gribble FM, Ashcroft FM. Sulfonylurea sensitivity of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels from beta cells and extrapancreatic tissues. Metabolism. 2000;49:3–6. - PubMed
-
- Vila-Carriles WH, Zhao G, Bryan J. Defining a binding pocket for sulfonylureas in ATP-sensitive potassium channels. FASEB J. 2007;21:18–25. - PubMed
-
- Thulé PM, Umpierrez G. Sulfonylureas: A new look at old therapy. Curr Diab Rep. 2014;14:473. - PubMed
-
- Kramer W, Müller G, Girbig F, Gutjahr U, Kowalewski S, Hartz D, et al. Differential interaction of glimepiride and glibenclamide with the beta-cell sulfonylurea receptor. II. Photoaffinity labeling of a kDa protein by [3H] glimepiride glimepiride. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1191:278–90. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe VJ, Griffith ML, Davis SN. The role of glimepiride in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010;6:225–35. - PubMed
-
- Holstein A, Plaschke A, Egberts EH. Lower incidence of severe hypoglycaemia in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with glimepiride versus glibenclamide. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001;17:467–73. - PubMed
-
- Singh AK, Singh R. Is gliclazide a sulfonylurea with difference? A review in 2016. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016;9:839–51. - PubMed
-
- Draeger KE, Wernicke-Panten K, Lomp HJ, Schüler E, Rosskamp R. Long-term treatment of type 2 diabetic patients with the new oral antidiabetic agent glimepiride (Amaryl): A double-blind comparison with glibenclamide. Horm Metab Res. 1996;28:419–25. - PubMed
-
- Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, et al. Consensus statement by the American association of clinical endocrinologists and American college of endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm-2017 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2017;23:207–38. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. 2017. [Last accessed on 2017 Feb 24]. Available from: http://www.professional.diabetes.org/sites/professional.diabetes.org/fil... .
-
- Ministry of Health, Kingdom of Bahrain. Guidelines for Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Primary Care Settings and Outpatient Clinics in the Kingdom of Bahrain. [Last accessed on 2017 Mar 08]. Available from: http://www.nhra.bh/files/files/CEO/Hypertension%20Guideline%2031052015.pdf .
-
- Chinenye S, Ofoegbu EN, Onyemelukwe GC, Uloko AE, Ogbera AO. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management in Nigeria. Diabetes Association of Nigeria (DAN) 2013
-
- Rutten GE, De Grauw WJ, Nijpels G, Houweling ST, Van de Laar FA, Bilo HJ, et al. Diabetes guideline of the Dutch College of General Practitioners (NHG-Standard Diabetes mellitus type 2 (derde herziening)) Huisarts Wet. 2013;56:512–25.
-
- Diabetes Mellitus Guidelines, WHO EMRO. 2006. [Last accessed on 2017 Apr 06]. Available from: http://www.applications.emro.who.int/dsaf/dsa664.pdf .
-
- National Clinical Guidelines for Management of Diabetes Mellitus; Republic of Kenya Ministry. 2010
-
- International Diabetes Federation Guideline Development Group. Global guideline for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;104:1–52. - PubMed
-
- Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: Management, NICE Guideline [NG28] 2015. [Last accessed on 2017 Mar 14]. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng28?unlid=739233160201610316820 .
-
- Madhu SV, Saboo B, Makkar BM, Reddy GC, Jana J, Panda JK, et al. RSSDI clinical practice recommendations for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus, 2015. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2015;35:1–71.
-
- The Society for Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes of South Africa Type 2 Diabetes Guidelines Expert Committee. The 2017 SEMDSA Guideline for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Guideline Committee. JEMDSA. 2017;21(Supplement 1):S1–S196.
-
- The United Republic of Tanzania, Standard Treatment Guidelines and Essential Medicines List; Ministry of Health and Social Welfare. (4th ed) 2013 May;
-
- National Diabetes Guidelines, United Arab Emirates. 2009. [Last accessed on 2017 Mar 08]. Available from: cms.wounds-uk.com/media/NationalDiabetesGuidelinesUAE.pdf .
-
- The Republic of Uganda, Ministry of Health, National Guidelines for Management of Common Conditions; Uganda Clinical Guidelines. 2016
-
- Del Prato S, Vigili de Kreutzenberg S, Riccio A, Tiengo A. Hepatic sensitivity to insulin: Effects of sulfonylurea drugs. Am J Med. 1991:29S–36S. - PubMed
-
- Bolen S, Tseng E, Hutfless S, Segal JB, Suarez-Cuervo C, Berger Z, et al. Diabetes Medications for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: An Update. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016. [Last accessed on 2017 Jan 12]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK362863/
-
- Ahrén B, Johnson SL, Stewart M, Cirkel DT, Yang F, Perry C, et al. HARMONY 3: 104-week randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled trial assessing the efficacy and safety of albiglutide compared with placebo, sitagliptin, and glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes taking metformin. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2141–8. - PubMed
-
- Kim HS, Kim DM, Cha BS, Park TS, Kim KA, Kim DL, et al. Efficacy of glimepiride/metformin fixed-dose combination vs. metformin uptitration in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled on low-dose metformin monotherapy: A randomized, open label, parallel group, multicenter study in Korea. J Diabetes Investig. 2014;5:701–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kalra S, Das AK. Epidemiologic surveillance of glycemic response to a scored, breakable, extended release, fixed dose combination of gliclazide and metformin in persons with type 2 diabetes. J Assoc Physicians India. 2017;65:38–41. - PubMed
-
- Charpentier G, Fleury F, Kabir M, Vaur L, Halimi S. Improved glycaemic control by addition of glimepiride to metformin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 2001;18:828–34. - PubMed
-
- González-Ortiz M, Martínez-Abundis E. Grupo para el Tratamiento de la Diabetes Mellitus con Combinaciones. Efficacy and safety of glimepiride plus metformin in a single presentation, as combined therapy, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and secondary failure to glibenclamide, as monotherapy. Rev Invest Clin. 2004;56:327–33. - PubMed
-
- Ristic S, Collober-Maugeais C, Cressier F, Tang P, Pecher E. Nateglinide or gliclazide in combination with metformin for treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on maximum doses of metformin alone: 1-year trial results. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007;9:506–11. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein BJ, Pans M, Rubin CJ. Multicenter, randomized, double-masked, parallel-group assessment of simultaneous glipizide/metformin as second-line pharmacologic treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus that is inadequately controlled by a sulfonylurea. Clin Ther. 2003;25:890–903. - PubMed
-
- Feinglos M, Dailey G, Cefalu W, Osei K, Tayek J, Canovatchel W, et al. Effect on glycemic control of the addition of 2.5 mg glipizide GITS to metformin in patients with T2DM. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005;68:167–75. - PubMed
-
- Marre M, Howlett H, Lehert P, Allavoine T. Improved glycaemic control with metformin-glibenclamide combined tablet therapy (Glucovance) in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabet Med. 2002;19:673–80. - PubMed
-
- Chien HH, Chang CT, Chu NF, Hsieh SH, Huang YY, Lee IT, et al. Effect of glyburide-metformin combination tablet in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Chin Med Assoc. 2007;70:473–80. - PubMed
-
- Ray JA, Huet D, Valentine WJ, Palmer AJ, Cugnardey N, Renaudin C, et al. Long-term costs and clinical outcomes associated with metformin-glibenclamide combination tablets (Glucovance®) in patients with type 2 diabetes sub-optimally controlled by metformin: A modelling study in the French setting. Br J Diabetes Vasc Dis. 2008;8:39–44.
-
- Umpierrez G, Issa M, Vlajnic A. Glimepiride versus pioglitazone combination therapy in subjects with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy: Results of a randomized clinical trial. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006;22:751–9. - PubMed
-
- Matthews DR, Charbonnel BH, Hanefeld M, Brunetti P, Schernthaner G. Long-term therapy with addition of pioglitazone to metformin compared with the addition of gliclazide to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, comparative study. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2005;21:167–74. - PubMed
-
- Mishriky BM, Cummings DM, Tanenberg RJ. The efficacy and safety of DPP4 inhibitors compared to sulfonylureas as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;109:378–88. - PubMed
-
- Zhou JB, Bai L, Wang Y, Yang JK. The benefits and risks of DPP4-inhibitors vs. sulfonylureas for patients with type 2 diabetes: Accumulated evidence from randomised controlled trial. Int J Clin Pract. 2016;70:132–41. - PubMed
-
- Amate JM, Lopez-Cuadrado T, Almendro N, Bouza C, Saz-Parkinson Z, Rivas-Ruiz R, et al. Effectiveness and safety of glimepiride and iDPP4, associated with metformin in second line pharmacotherapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2015;69:292–304. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Filozof C, Gautier JF. A comparison of efficacy and safety of vildagliptin and gliclazide in combination with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone: A 52-week, randomized study. Diabet Med. 2010;27:318–26. - PubMed
-
- Göke B, Gallwitz B, Eriksson J, Hellqvist A, Gause-Nilsson I D1680C00001 Investigators. Saxagliptin is non-inferior to glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin alone: A 52-week randomised controlled trial. Int J Clin Pract. 2010;64:1619–31. - PubMed
-
- Thomsen RW, Baggesen LM, Søgaard M, Pedersen L, Nørrelund H, Buhl ES, et al. Early glycaemic control in metformin users receiving their first add-on therapy: A population-based study of 4,734 people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2015;58:2247–53. - PubMed
-
- Ridderstråle M, Andersen KR, Zeller C, Kim G, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, et al. Comparison of empagliflozin and glimepiride as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 104-week randomised, active-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:691–700. - PubMed
-
- Cefalu WT, Leiter LA, Yoon KH, Arias P, Niskanen L, Xie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (CANTATA-SU): 52 week results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2013;382:941–50. - PubMed
-
- Nauck MA, Del Prato S, Meier JJ, Durán-García S, Rohwedder K, Elze M, et al. Dapagliflozin versus glipizide as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycemic control with metformin: A randomized, 52-week, double-blind, active-controlled noninferiority trial. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:2015–22. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nauck M, Frid A, Hermansen K, Thomsen AB, During M, Shah N, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety comparison of liraglutide, glimepiride and placebo, all in combination with metformin in type 2 diabetes: 2-year results from the LEAD-2 study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:204–12. - PubMed
-
- Yang W, Chen L, Ji Q, Liu X, Ma J, Tandon N, et al. Liraglutide provides similar glycaemic control as glimepiride (both in combination with metformin) and reduces body weight and systolic blood pressure in Asian population with type 2 diabetes from China, South Korea and India: A 16-week, randomized, double-blind, active control trial(*) Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13:81–8. - PubMed
-
- Massi-Benedetti M. Glimepiride in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of the worldwide therapeutic experience. Clin Ther. 2003;25:799–816. - PubMed
-
- Green JB, Feinglos MN. Are sulfonylureas passé? Curr Diab Rep. 2006;6:373–7. - PubMed
-
- Charbonnel B, Schernthaner G, Brunetti P, Matthews DR, Urquhart R, Tan MH, et al. Long-term efficacy and tolerability of add-on pioglitazone therapy to failing monotherapy compared with addition of gliclazide or metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2005;48:1093–104. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Hong J, Chi J, Gu W, Ning G, Wang W, et al. Head-to-head comparison of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors and sulfonylureas – A meta-analysis from randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014;30:241–56. - PubMed
-
- Hissa MR, Cavalcante LL, Guimarães SB, Hissa MN. A 16-week study to compare the effect of vildagliptin versus gliclazide on postprandial lipoprotein concentrations and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015;7:62. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leiter LA, Yoon KH, Arias P, Langslet G, Xie J, Balis DA, et al. Canagliflozin provides durable glycemic improvements and body weight reduction over 104 weeks versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes on metformin: A randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:355–64. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Putignano P, Bossi AC, Bonaventura A, Querci F, Franzetti IG, et al. Exenatide or glimepiride added to metformin on metabolic control and on insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;666:251–6. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Maffioli P, Salvadeo SA, Ferrari I, Ragonesi PD, Querci F, et al. Exenatide versus glibenclamide in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2010;12:233–40. - PubMed
-
- Moon JS, Ha KS, Yoon JS, Lee HW, Lee HC, Won KC, et al. The effect of glargine versus glimepiride on pancreatic β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on metformin monotherapy: Open-label, randomized, controlled study. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51:277–85. - PubMed
-
- Chan SP, Colagiuri S. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and hypoglycemic safety of gliclazide versus other insulinotropic agents. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;110:75–81. - PubMed
-
- Schernthaner G, Grimaldi A, Di Mario U, Drzewoski J, Kempler P, Kvapil M, et al. GUIDE study: Double-blind comparison of once-daily gliclazide MR and glimepiride in type 2 diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34:535–42. - PubMed
-
- Del Prato S, Nauck M, Durán-Garcia S, Maffei L, Rohwedder K, Theuerkauf A, et al. Long-term glycaemic response and tolerability of dapagliflozin versus a sulphonylurea as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: 4-year data. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:581–90. - PubMed
-
- Gallwitz B, Guzman J, Dotta F, Guerci B, Simó R, Basson BR, et al. Exenatide twice daily versus glimepiride for prevention of glycaemic deterioration in patients with type 2 diabetes with metformin failure (EUREXA): An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;379:2270–8. - PubMed
-
- Mamza J, Mehta R, Donnelly R, Idris I. Important differences in the durability of glycaemic response among second-line treatment options when added to metformin in type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Med. 2016;48:224–34. - PubMed
-
- Schramm TK, Gislason GH, Vaag A, Rasmussen JN, Folke F, Hansen ML, et al. Mortality and cardiovascular risk associated with different insulin secretagogues compared with metformin in type 2 diabetes, with or without a previous myocardial infarction: A nationwide study. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1900–8. - PubMed
-
- Mogensen UM, Andersson C, Fosbøl EL, Schramm TK, Vaag A, Scheller NM, et al. Cardiovascular safety of combination therapies with incretin-based drugs and metformin compared with a combination of metformin and sulphonylurea in type 2 diabetes mellitus – A retrospective nationwide study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:1001–8. - PubMed
-
- Pfützner A, Schöndorf T, Tschöpe D, Lobmann R, Merke J, Müller J, et al. PIOfix-study: Effects of pioglitazone/metformin fixed combination in comparison with a combination of metformin with glimepiride on diabetic dyslipidemia. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011;13:637–43. - PubMed
-
- Prentice JC, Conlin PR, Gellad WF, Edelman D, Lee TA, Pizer SD, et al. Capitalizing on prescribing pattern variation to compare medications for type 2 diabetes. Value Health. 2014;17:854–62. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Zhang X, Hu C, Lu W. Exenatide reduces urinary transforming growth factor-β1 and type IV collagen excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012;35:483–8. - PubMed
-
- Palmer SC, Mavridis D, Nicolucci A, Johnson DW, Tonelli M, Craig JC, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes and adverse events associated with glucose-lowering drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: A Meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016;316:313–24. - PubMed
-
- Comaschi M, Demicheli A, Di Pietro C, Bellatreccia A, Mariz S COM06 Study Investigators. Effects of pioglitazone in combination with metformin or a sulfonylurea compared to a fixed-dose combination of metformin and glibenclamide in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2007;9:387–98. - PubMed
-
- Schernthaner G, Durán-Garcia S, Hanefeld M, Langslet G, Niskanen L, Östgren CJ, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of saxagliptin compared with glimepiride in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, controlled study (GENERATION) Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:630–8. - PubMed
-
- McCluskey D, Touger MS, Melis R, Schleusener DS, McCluskey D. Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study administering glimepiride to patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with rosiglitazone monotherapy. Clin Ther. 2004;26:1783–90. - PubMed
-
- Chou HS, Palmer JP, Jones AR, Waterhouse B, Ferreira-Cornwell C, Krebs J, et al. Initial treatment with fixed-dose combination rosiglitazone/glimepiride in patients with previously untreated type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10:626–37. - PubMed
-
- Hanefeld M, Brunetti P, Schernthaner GH, Matthews DR, Charbonnel BH QUARTET Study Group. One-year glycemic control with a sulfonylurea plus pioglitazone versus a sulfonylurea plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:141–7. - PubMed
-
- Harashima SI, Ogura M, Tanaka D, Fukushima T, Wang Y, Koizumi T, et al. Sitagliptin add-on to low dosage sulphonylureas: Efficacy and safety of combination therapy on glycaemic control and insulin secretion capacity in type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66:465–76. - PubMed
-
- Roberts VL, Stewart J, Issa M, Lake B, Melis R. Triple therapy with glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled by metformin and a thiazolidinedione: Results of a 30-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Clin Ther. 2005;27:1535–47. - PubMed
-
- Arai K, Maeda H, Sirabe S, Yamamoto R, Yamauchi M, Hirao T, et al. Glimepiride strongly enhances the glucose-lowering effect in triple oral antidiabetes therapy with sitagliptin and metformin for Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013;15:335–41. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Cicero AF, D’Angelo A, Gaddi A, Ciccarelli L, Piccinni MN, et al. Effects of 1 year of treatment with pioglitazone or rosiglitazone added to glimepiride on lipoprotein (a) and homocysteine concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. Clin Ther. 2006;28:679–88. - PubMed
-
- Davidson JA, McMorn SO, Waterhouse BR, Cobitz AR. A 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of the efficacy and tolerability of combination therapy with rosiglitazone and sulfonylurea in African American and Hispanic American patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with sulfonylurea monotherapy. Clin Ther. 2007;29:1900–14. - PubMed
-
- Umayahara R, Yonemoto T, Kyou C, Morishita K, Ogawa T, Taguchi Y, et al. Low-dose glimepiride with sitagliptin improves glycemic control without dose-dependency in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on high-dose glimepiride. Endocr J. 2014;61:1163–70. - PubMed
-
- Schernthaner G, Rosas-Guzmán J, Dotta F, Guerci B, Simó R, Festa A, et al. Treatment escalation options for patients with type 2 diabetes after failure of exenatide twice daily or glimepiride added to metformin: Results from the prospective European Exenatide (EUREXA) study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:689–98. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Cicero AF, Gaddi A, Ragonesi PD, Fogari E, Bertone G, et al. Metabolic effects of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in patients with diabetes and metabolic syndrome treated with glimepiride: A twelve-month, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled, parallel-group trial. Clin Ther. 2004;26:744–54. - PubMed
-
- Meshram DM, Langade DG, Kinagi SB, Naikwadi AA, Morye V, Chopra D, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of fixed dose combination of glimepiride 2 mg plus pioglitazone 15 mg plus metformin SR 500 mg in the management of patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. J Indian Med Assoc. 2005;103:447–50. - PubMed
-
- Lebovitz HE, Pasmantier R. Combination insulin-sulfonylurea therapy. Diabetes Care. 1990;13:667–75. - PubMed
-
- Groop LC, Groop PH, Stenman S. Combined insulin-sulfonylurea therapy in treatment of NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1990;13(Suppl 3):47–52. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Zheng F, Guo X, Yang H, Zhang M, Tian H, et al. Glargine insulin/gliclazide MR combination therapy is more effective than premixed insulin monotherapy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on oral antidiabetic drugs. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015;31:725–33. - PubMed
-
- Schiel R, Müller UA. Efficacy and treatment satisfaction of once-daily insulin glargine plus one or two oral antidiabetic agents versus continuing premixed human insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes previously on long-term conventional insulin therapy: The SWITCH pilot study. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2008;116:58–64. - PubMed
-
- Janka HU, Plewe G, Busch K. Combination of oral antidiabetic agents with basal insulin versus premixed insulin alone in randomized elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007;55:182–8. - PubMed
-
- Standl E, Maxeiner S, Raptis S, Karimi-Anderesi Z, Schweitzer MA HOE901/4009 Study Group. Good glycemic control with flexibility in timing of basal insulin supply: A 24-week comparison of insulin glargine given once daily in the morning or at bedtime in combination with morning glimepiride. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:419–20. - PubMed
-
- Olsson PO, Lindström T. Combination-therapy with bedtime nph insulin and sulphonylureas gives similar glycaemic control but lower weight gain than insulin twice daily in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2002;28:272–7. - PubMed
-
- Vos RC, van Avendonk MJ, Jansen H, Goudswaard AN, van den Donk M, Gorter K, et al. Insulin monotherapy compared with the addition of oral glucose-lowering agents to insulin for people with type 2 diabetes already on insulin therapy and inadequate glycaemic control. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;9:CD006992. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pugh JA, Wagner ML, Sawyer J, Ramirez G, Tuley M, Friedberg SJ, et al. Is combination sulfonylurea and insulin therapy useful in NIDDM patients? A metaanalysis. Diabetes Care. 1992;15:953–9. - PubMed
-
- Esposito K, Ciotola M, Maiorino MI, Gualdiero R, Schisano B, Ceriello A, et al. Addition of neutral protamine lispro insulin or insulin glargine to oral type 2 diabetes regimens for patients with suboptimal glycemic control: A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:531–9. - PubMed
-
- Janka HU, Plewe G, Riddle MC, Kliebe-Frisch C, Schweitzer MA, Yki-Järvinen H, et al. Comparison of basal insulin added to oral agents versus twice-daily premixed insulin as initial insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:254–9. - PubMed
-
- Wright A, Burden AC, Paisey RB, Cull CA, Holman RR U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Sulfonylurea inadequacy: Efficacy of addition of insulin over 6 years in patients with type 2 diabetes in the U.K. Prospective diabetes study (UKPDS 57) Diabetes Care. 2002;25:330–6. - PubMed
-
- Yki-Järvinen H, Ryysy L, Nikkilä K, Tulokas T, Vanamo R, Heikkilä M, et al. Comparison of bedtime insulin regimens in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:389–96. - PubMed
-
- Holman RR, Thorne KI, Farmer AJ, Davies MJ, Keenan JF, Paul S, et al. Addition of biphasic, prandial, or basal insulin to oral therapy in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1716–30. - PubMed
-
- Holman RR, Farmer AJ, Davies MJ, Levy JC, Darbyshire JL, Keenan JF, et al. Three-year efficacy of complex insulin regimens in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1736–47. - PubMed
-
- Stuart CA, Gilkison CR, Carlson RF, Stuart CA, Gilkison CR, Carlson RF, et al. Effect of adding a sulfonylurea in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus previously well controlled with insulin. Endocr Pract. 1997;3:344–8. - PubMed
-
- Riddle M, Hart J, Bingham P, Garrison C, McDaniel P. Combined therapy for obese type 2 diabetes: Suppertime mixed insulin with daytime sulfonylurea. Am J Med Sci. 1992;303:151–6. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, McCoy RG, Mason JE, Smith SA, Shah ND, Denton BT, et al. Second-line agents for glycemic control for type 2 diabetes: Are newer agents better? Diabetes Care. 2014;37:1338–45. - PubMed
-
- Saini SD, Schoenfeld P, Kaulback K, Dubinsky MC. Effect of medication dosing frequency on adherence in chronic diseases. Am J Manag Care. 2009;15:e22–33. - PubMed
-
- Meece J. Improving medication adherence among patients with type 2 diabetes. J Pharm Pract. 2014;27:187–94. - PubMed
-
- Bangalore S, Kamalakkannan G, Parkar S, Messerli FH. Fixed-dose combinations improve medication compliance: A meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2007;120:713–9. - PubMed
-
- Blonde L, San Juan ZT. Fixed-dose combinations for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adv Ther. 2012;29:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Riddle M. Combining sulfonylureas and other oral agents. Am J Med. 2000;108(Suppl 6a):15S–22S. - PubMed
-
- Kalra S. Aggressive treatment in newly diagnosed diabetes with fixed dose combinations. Medicine. 2012;22:249–53.
-
- Han S, Iglay K, Davies MJ, Zhang Q, Radican L. Glycemic effectiveness and medication adherence with fixed-dose combination or coadministered dual therapy of antihyperglycemic regimens: A meta-analysis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2012;28:969–77. - PubMed
-
- Hutchins V, Zhang B, Fleurence RL, Krishnarajah G, Graham J. A systematic review of adherence, treatment satisfaction and costs, in fixed-dose combination regimens in type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011;27:1157–68. - PubMed
-
- Drouin P, Standl E Diamicron MR Study Group. Gliclazide modified release: Results of a 2-year study in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2004;6:414–21. - PubMed
-
- Chanal H. Should elderly patients with type 2 diabetes be treated with glibenclamide (glyburide) or different sulphonylurea? Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- International Diabetes Federation, Managing Older People with Type 2 Diabetes. Global Guideline. 2013. [Last accessed on 2017 Apr 27]. Available from: https://www.idf.org/e-library/guidelines/78-global-guideline-for-managin... .
-
- Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Meneilly GS, Knip A, Tessier D. Diabetes in the elderly. [Last accessed on 2015 Aug 11];Can J Diabetes. 2013 37(Suppl 1):S184–90. Available from: http://www.canadianjournalofdiabetes.com/article/S1499-2671(13)00046-4/pdf . - PubMed
-
- Gottschalk M, Danne T, Vlajnic A, Cara JF. Glimepiride versus metformin as monotherapy in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, single-blind comparative study. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:790–4. - PubMed
-
- Fajans SS, Brown MB. Administration of sulfonylureas can increase glucose-induced insulin secretion for decades in patients with maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:1254–61. - PubMed
-
- Raile K, Schober E, Konrad K, Thon A, Grulich-Henn J, Meissner T, et al. Treatment of young patients with HNF1A mutations (HNF1A-MODY) Diabet Med. 2015;32:526–30. - PubMed
-
- Thanabalasingham G, Owen KR. Diagnosis and management of maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY) BMJ. 2011;343:d6044. - PubMed
-
- Hanas R, Donaghue K, Klingensmith G, Swift P, Colagiuri S. Global IDF/ISPAD Guideline for Diabetes in Childhood and Adolescence. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2011.
-
- Oztekin O, Durmaz E, Kalay S, Flanagan SE, Ellard S, Bircan I, et al. Successful sulfonylurea treatment of a neonate with neonatal diabetes mellitus due to a novel missense mutation, p.P1199L, in the ABCC8 gene. J Perinatol. 2012;32:645–7. - PubMed
-
- Pearson ER, Flechtner I, Njølstad PR, Malecki MT, Flanagan SE, Larkin B, et al. Switching from insulin to oral sulfonylureas in patients with diabetes due to kir6.2 mutations. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:467–77. - PubMed
-
- Babenko AP, Polak M, Cavé H, Busiah K, Czernichow P, Scharfmann R, et al. Activating mutations in the ABCC8 gene in neonatal diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:456–66. - PubMed
-
- Sagen JV, Raeder H, Hathout E, Shehadeh N, Gudmundsson K, Baevre H, et al. Permanent neonatal diabetes due to mutations in KCNJ11 encoding kir6.2: Patient characteristics and initial response to sulfonylurea therapy. Diabetes. 2004;53:2713–8. - PubMed
-
- Codner E, Flanagan SE, Ugarte F, García H, Vidal T, Ellard S, et al. Sulfonylurea treatment in young children with neonatal diabetes: Dealing with hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and sick days. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:e28–9. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson W, Bolen S, Witkop CT, Neale D, Wilson L, Bass E, et al. Benefits and risks of oral diabetes agents compared with insulin in women with gestational diabetes: A systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:193–205. - PubMed
-
- Dhulkotia JS, Ola B, Fraser R, Farrell T. Oral hypoglycemic agents vs. insulin in management of gestational diabetes: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;203:457. e1-9. - PubMed
-
- Gutzin SJ, Kozer E, Magee LA, Feig DS, Koren G. The safety of oral hypoglycemic agents in the first trimester of pregnancy: A meta-analysis. Can J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;10:179–83. - PubMed
-
- Rosenkranz B, Profozic V, Metelko Z, Mrzljak V, Lange C, Malerczyk V, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of glimepiride at clinically effective doses in diabetic patients with renal impairment. Diabetologia. 1996;39:1617–24. - PubMed
-
- Saini JS. Management guidelines for use of oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA) in complex clinical situations and important drug interactions with OHA's. Acta Endocrinol. 1991;108:85–90.
-
- Tolman KG, Fonseca V, Dalpiaz A, Tan MH. Spectrum of liver disease in type 2 diabetes and management of patients with diabetes and liver disease. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:734–43. - PubMed
-
- Hassanein M, Al-Arouj M, Hamdy O, Bebakar WM, Jabbar A, Al-Madani A, et al. Diabetes and Ramadan: Practical guidelines. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;126:303–16. - PubMed
-
- Glimepiride in Ramadan (GLIRA) Study Group. The efficacy and safety of glimepiride in the management of type 2 diabetes in Muslim patients during Ramadan. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:421–2. - PubMed
-
- Hassanein M, Abdallah K, Schweizer A. A double-blind, randomized trial, including frequent patient-physician contacts and Ramadan-focused advice, assessing vildagliptin and gliclazide in patients with type 2 diabetes fasting during Ramadan: The STEADFAST study. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014;10:319–26. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brady EM, Davies MJ, Gray LJ, Saeed MA, Smith D, Hanif W, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing the GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide to a sulphonylurea as add on to metformin in patients with established type 2 diabetes during Ramadan: The treat 4 Ramadan trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:527–36. - PubMed
-
- Latt TS, Kalra S. Managing diabetes during fasting – A focus on Buddhist lent. Diabetes Voice. 2012;57:42–5.
-
- Glyade: Gliclazide Tablets: Label Information of TGA. Diabeta. [Last accessed on 2015 Mar 25]. Available from: http://www.medicines.org.au/files/afpglyad.pdf .
-
- Glyburide Tablets. Label Information of FDA. [Last accessed on 2015 Mar 25]. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/017532Orig1s034... .
-
- Amaryl: Glimepiride Tablets. Label Information of FDA. [Last accessed on 2015 Mar 25]. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/020496s027lbl.pdf .
-
- Powers MA, Bardsley J, Cypress M, Duker P, Funnell MM, Fischl AH, et al. Diabetes self-management education and support in type 2 diabetes: A joint position statement of the American Diabetes Association, the American association of diabetes educators, and the academy of nutrition and dietetics. Diabetes Educ. 2015;41:417–30. - PubMed