A biomarker based severity progression indicator for COVID-19: the Kuwait prognosis indicator score
Affiliations
Affiliations
- COVID-19 Research Group, Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah Hospital, Ministry of Health of Kuwait, Safat,Kuwait.
- Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Health Sciences Center, Kuwait University, Kuwait.
- Department of Population Medicine, College of Medicine, QU Health, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar.
- Clinical Epidemiology, Research School of Population Health, College of Health and Medicine, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia.
- Public Health Administration, Ministry of Health of Kuwait, Safat,Kuwait.
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering, College of Engineering, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar.
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 is a worldwide pandemic that is mild in most patients but can result in a pneumonia like illness with progression to acute respiratory distress syndrome and death. Predicting the disease severity at time of diagnosis can be helpful in prioritizing hospital admission and resources.
Methods: We prospectively recruited 1096 consecutive patients of whom 643 met the inclusion criterion with COVID-19 from Jaber Hospital, a COVID-19 facility in Kuwait, between 24 February and 20 April 2020. The primary endpoint of interest was disease severity defined algorithmically. Predefined risk variables were collected at the time of PCR based diagnosis of the infection. Prognostic model development used 5-fold cross-validated regularized logit regression. The model was externally validated against data from Wuhan, China.
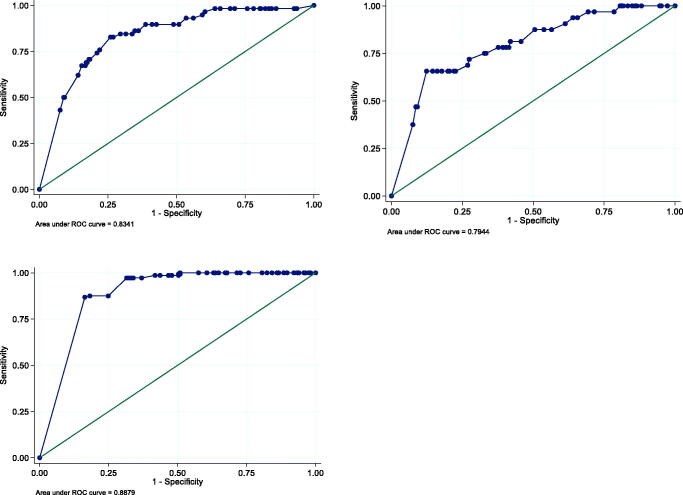
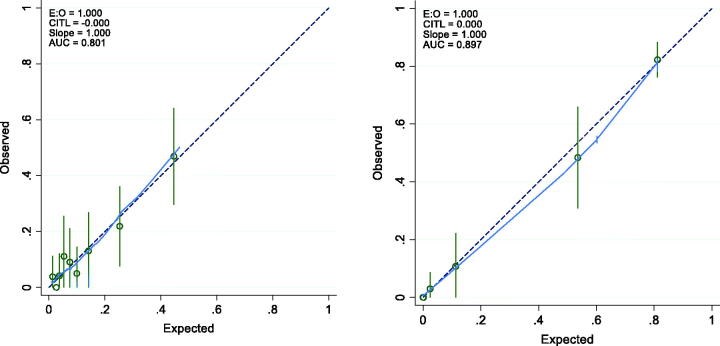
Results: There were 643 patients with clinical course data of whom 94 developed severe COVID-19. In the final model, age, CRP, procalcitonin, lymphocyte percentage, monocyte percentages and serum albumin were independent predictors of a more severe illness course. The final prognostic model demonstrated good discrimination, and both discrimination and calibration were confirmed with an external dataset.
Conclusion: We developed and validated a simple score calculated at time of diagnosis that can predict patients with severe COVID-19 disease reliably and that has been validated externally. The KPI score calculator is now available online at covidkscore.com.
Keywords: COVID-19; adverse outcome; health policy; mortality; procalcitonin; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
Kaal A, Snel L, Dane M, van Burgel N, Ottens T, Broekman W, El Bouazzaoui L, Kolfschoten N, Schippers E, Steyerberg E, Meziyerh S, van Nieuwkoop C.Emerg Med J. 2021 Sep;38(9):685-691. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2020-211027. Epub 2021 Jul 21.PMID: 34289966 Free PMC article.
Sayah W, Berkane I, Guermache I, Sabri M, Lakhal FZ, Yasmine Rahali S, Djidjeli A, Lamara Mahammed L, Merah F, Belaid B, Berkani L, Lazli NZ, Kheddouci L, Kadi A, Ouali M, Khellafi R, Mekideche D, Kheliouen A, Hamidi RM, Ayoub S, Raaf NB, Derrar F, Gharnaout M, Allam I, Djidjik R.Cytokine. 2021 May;141:155428. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155428. Epub 2021 Jan 15.PMID: 33550165 Free PMC article.
Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Severe Pneumonia Caused by the SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China.
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Yang Z, Xia D, Hu Y, Geng S.Respiration. 2020;99(8):649-657. doi: 10.1159/000507940. Epub 2020 Aug 25.PMID: 32841948 Free PMC article.
Henry BM, Benoit SW, de Oliveira MHS, Hsieh WC, Benoit J, Ballout RA, Plebani M, Lippi G.Clin Biochem. 2020 Jul;81:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 May 27.PMID: 32473151 Free PMC article. Review.
Association of elevated inflammatory markers and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis.
Ji P, Zhu J, Zhong Z, Li H, Pang J, Li B, Zhang J.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 20;99(47):e23315. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023315.PMID: 33217868 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahrens, A., Hansen, C.B., and Schaffer, M.E., 2020. Lassopack: model selection and prediction with regularized regression in Stata. The stata journal: promoting communications on statistics and stata, 20 (1), 176–235.
-
- Ensor, J., Snell, K.I.E., and Martin, E.C., 2018. “PMCALPLOT: Stata module to produce calibration plot of prediction model performance,” Statistical Software Components S458486, Boston College Department of Economics, revised 04 Jan 2020.
-
- Yan, L., et al. , 2020. An interpretable mortality prediction model for COVID-19 patients. Nature machine intelligence, 1–6.doi:10.1038/s42256-020-0180-7 - DOI