Effective cleaning of endoscopic lenses to achieve visual clarity for minimally invasive abdominopelvic surgery: a systematic review
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Surgery and Cancer, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom.
- Institute of Global Health Innovation, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom.
- Department of Surgery, Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah Hospital, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
- Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Health Sciences Centre, Kuwait University, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
- Department of Surgery and Cancer, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom. h.ashrafian@imperial.ac.uk.
- Institute of Global Health Innovation, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom. h.ashrafian@imperial.ac.uk.
Abstract
Objective: To review the recently available interventions to achieve optimal visual clarity in laparoscopic abdominopelvic surgery compared to conventional cleaning alternatives. Currently, there is no consensus on the most effective method for the cleaning of endoscopic lenses used in minimally invasive abdominopelvic surgery.
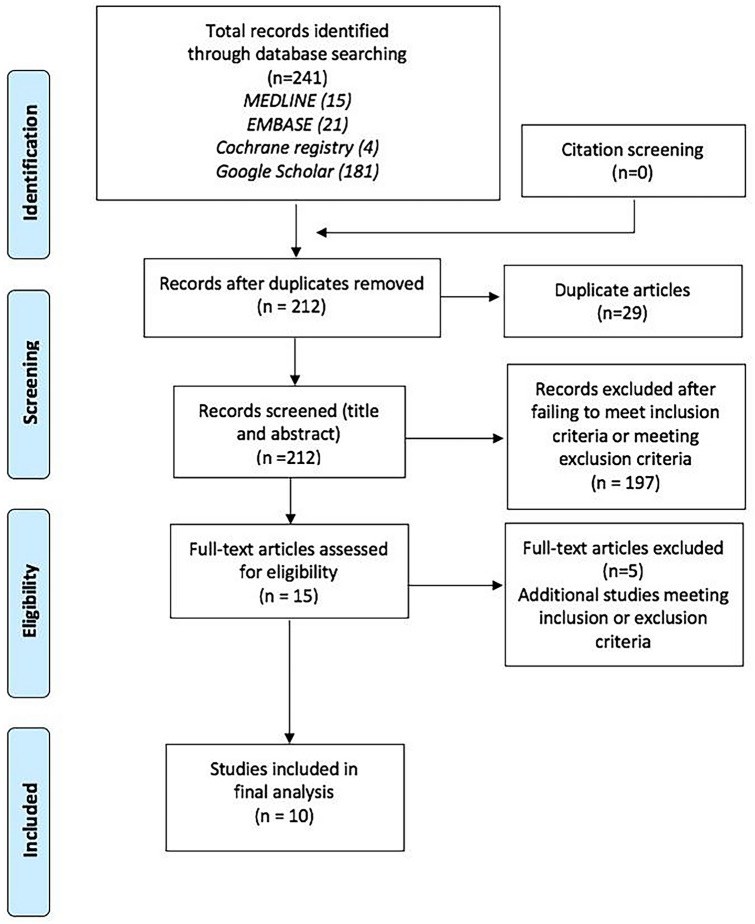
Methods: Literature searching for articles relevant to answering a predefined research question was performed in December 2019 and involved searching of the electronic databases of MEDLINE, the Cochrane Registry, and EMBASE. Basic search terms were derived using the PICO (population, intervention, comparator and outcomes) framework and through a scoping search of literature via MEDLINE. A manual search of Google Scholar and citation screening of eligible studies was also performed to ensure the identification and inclusion of all pertinent studies to address the research question.
Results: Among conventional and readily available methods, the most effective approaches involved heated sterile water, heating of laparoscope lenses, and surfactant solutions, including FRED and Ultra-Stop, while evaluations of all novel devices and methods were more effective than controls, which included lens wiping systems and air and carbon dioxide flow systems. While the former surgical techniques were consistently associated with superior lens cleaning ability and/or defogging capability and subsequent optical clarity of images within the surgical field, no methods conferred any meaningful effects upon other clinically important outcomes, such as operative time, costs, complication rates and length of stay, suggesting that decision making concerning the selection of lens cleaning method/device should suit the preferences of the instrument operator and/or the responsible surgeon.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that a range of endoscopic lens cleaning methods and devices can be used to achieve sufficient optical clarity of the laparoscopic surgical field through either preventing lenses from fogging and/or facilitating the inter-operative cleaning of fouled lenses. Despite the various methods evaluated in this review, there were no significant differences in complication rates between the intervention and control groups.
Keywords: Abdominopelvic surgery; Endoscopy; Lens cleaning; Minimally invasive surgery; Systematic review.
Figures
Similar articles
Manning TG, Perera M, Christidis D, Kinnear N, McGrath S, O'Beirne R, Zotov P, Bolton D, Lawrentschuk N.J Endourol. 2017 Apr;31(4):327-333. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0839. Epub 2017 Feb 8.PMID: 28075157 Review.
Cassera MA, Goers TA, Spaun GO, Swanström LL.Surg Innov. 2011 Jun;18(2):150-5. doi: 10.1177/1553350611399297. Epub 2011 Feb 22.PMID: 21343172 Clinical Trial.
Merkx R, Muselaers C, d'Ancona F, Warlé M, van der Jagt M, Kusters A, Poyck P, Schulte R, Langenhuijsen J.J Endourol. 2018 Jan;32(1):54-58. doi: 10.1089/end.2017.0683. Epub 2018 Jan 3.PMID: 29186976 Clinical Trial.
Quantifying Intraoperative Laparoscopic Visual Field Opacity.
Abbitt D, Khallouq BB, Redan J.JSLS. 2017 Apr-Jun;21(2):e2017.00004. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2017.00004.PMID: 28584499 Free PMC article.
Ahmed K, Wang TT, Patel VM, Nagpal K, Clark J, Ali M, Deeba S, Ashrafian H, Darzi A, Athanasiou T, Paraskeva P.Surg Endosc. 2011 Feb;25(2):378-96. doi: 10.1007/s00464-010-1208-6. Epub 2010 Jul 10.PMID: 20623239 Review.
References
-
- Levy B, Mobasheri M. Principles of safe laparoscopic surgery. Surgery. 2017;35(4):216–219.
-
- Higgins J, Thomas J (2018) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Available from https://training.cochrane.org/handbook - PubMed
-
- Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):65–94. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00136. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cochrane Collaboration (2019) Data extraction forms. Available from https://dplp.cochrane.org/data-extraction-forms
-
- CASP (2020) CASP Checklists. Available from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
-
- Bendifallah S, Salakos E, Naoura I, Aristizabal P, Furet E, Zilberman S, et al. Prospective, randomized comparison of the use of FloShield Air System ® versus the reference technique (water + povidone-iodine solution) during gynecologic endoscopic surgery to evaluate the operative lens vision quality. SurgEndosc. 2018;32(3):1593–1599. - PubMed
-
- Cassera MA, Goers TA, Spaun GO, Swanstrom LL. Efficacy of using a novel endoscopic lens cleaning device: a prospective randomized controlled trial. SurgInnov. 2011;18(2):150–155. - PubMed
-
- Song T, Lee DH. A randomized Comparison of laparoscopic LEns defogging using Anti-fog solution, waRm saline, and chlorhexidine solution (CLEAR) SurgEndosc. 2019;2(1):1–12. - PubMed
-
- Manning TG, Papa N, Perera M, McGrath S, Christidis D, Khan M, et al. Laparoscopic lens fogging: solving a common surgical problem in standard and robotic laparoscopes via a scientific model. SurgEndosc. 2018;32(3):1600–1606. - PubMed
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J ClinEpidemiol. 2011;64(4):383–94. - PubMed
-
- Jategaonkar PA, Jategaonkar SP, Yadav SP. Simple, rapid and effective technique for intracorporeal defogging of laparoscopic lens. Hell J Surg. 2016;88(3):214–216. doi: 10.1007/s13126-016-0320-z. - DOI
-
- Bessell JR, Flemming E, Kunert W, Buess G. Maintenance of clear vision during laparoscopic surgery. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 1996;5(5):450–455. doi: 10.3109/13645709609153708. - DOI
-
- Ohdaira T, Nagai H, Kayano S, Kazuhito H. Antifogging effects of a socket-type device with the superhydrophilic, titanium dioxide-coated glass for the laparoscope. SurgEndosc. 2007;21(2):333–338. - PubMed
-
- Flemming E, Bessell JR, Kunert W, Eibl H, Buess G. Principles determining optical clarity in endoscopic surgery. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 1996;5(5):440–444. doi: 10.3109/13645709609153706. - DOI
-
- Rosen MJ, Kunjappu JT. Surfactants and interfacial phenomena. 4. New York: Wiley; 2012.
-
- McCain LA, Jones G. Endoscopic techniques in aesthetic plastic surgery. PlastSurgNurs. 1995;15(3):145–148. - PubMed
-
- Manning TG, Perera M, Christidis D, Kinnear N, McGrath S, O'Beirne R, et al. Visual occlusion during minimally invasive surgery: a contemporary review of methods to reduce laparoscopic and robotic lens fogging and other sources of optical loss. J Endourol. 2017;31(4):327–333. doi: 10.1089/end.2016.0839. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schurr MO, Bablich H, Wurster H, Melzer A, Roth K, Wiest FM, et al. A new optic cleaning and visualization stabilizing system for endoscopic surgery. Minim Invasive Ther. 1994;3(3):131–134. doi: 10.1080/0961625X.1994.11665539. - DOI
-
- Farley DR, Greenlee SM, Larson DR, Harrington JR. Double-blind, prospective, randomized study of warmed, humidified carbon dioxide insufflation vs standard carbon dioxide for patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Arch Surg. 2004;139(7):739–44. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.139.7.739. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yong N, Grange P, Eldred-Evans D. Impact of laparoscopic lens contamination in operating theaters: a study on the frequency and duration of lens contamination and commonly utilized techniques to maintain clear vision. SurgLaparoscEndoscPercutan Tech. 2016;26(4):286–289. - PubMed