The characterization and antibiotic resistance profiles of clinical Escherichia coli O25b-B2-ST131 isolates in Kuwait
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Kuwait University, Sulaibekhat, Sulaibekhat, 90805, Kuwait. leila@hsc.edu.kw.
Abstract
Background: Escherichia coli O25b-B2-ST131 are considered virulent extra-intestinal pathogens causing serious clinical complications such as urinary tract infection and bacteraemia. Our main objectives in this study were to characterise the multi-drug resistant (MDR) isolates of this lineage in Kuwait, and to demonstrate whether reduced susceptibility is spread clonally.
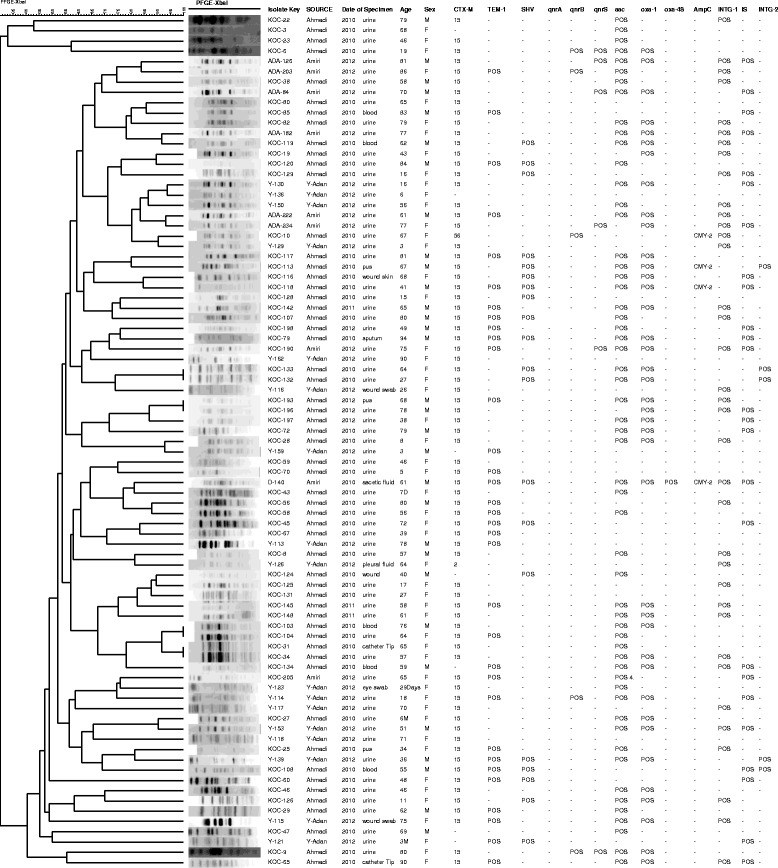
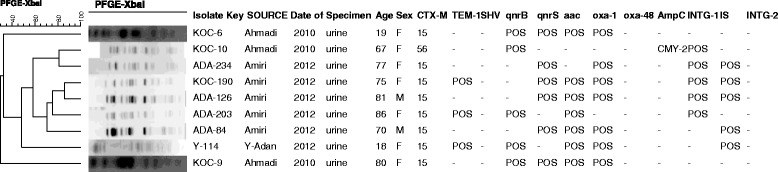
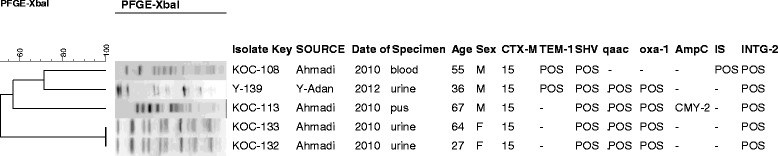
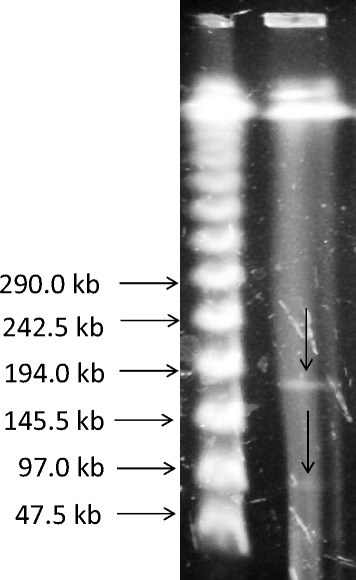
Results: A subset of 83 (10%) non-duplicate and non-selective E. coli O25b-B2-ST131 out of 832 MDR E. coli was identified and collected. Minimum inhibitory concentrations of the isolates were determined and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis was used for typing.The majority (95.2%) of the 83 E. coli O25b-B2-ST131 harboured at least one bla gene with blaCTX-M-15 being the most prevalent. blaCTX-M-2 was present in one isolate. Also one isolate harboured blaCTX-M-56, qnrB1 and blaCMY-2 genes and carried IncF1 plasmids of about 97 kb and160 kb. qnrB and qnrS were found in 8 other blaCTX-M-15 containing isolates. The blaNDM, blaIMP, blaVIM and qnrA were not detected, however, the blaOXA-48 was present in two (2.4%).
Conclusions: The majority of isolates harbouring qnr genes demonstrated relatedness (≥85%) by PFGE. However, the diversity in PFGE profiles for the other MDR isolates reflected the changes in population genetics of E. coli O25b-B2-ST131. We identified for the first time the appearance of blaCTX-M-2 in the Middle East and blaCTX-M-56 outside the Latin American countries. The isolate harbouring blaCTX-M-56 also contained qnrB1 and blaCMY-2 genes and carried IncF1 plasmids. The appearance of a highly virulent E. coli O25b-ST131 that is resistant to penicillins, most cephalosproins, β-lactamase inhibitors as well as fluoroquinolones is a cause for concern.
Figures
Similar articles
Hirai I, Fukui N, Taguchi M, Yamauchi K, Nakamura T, Okano S, Yamamoto Y.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013 Dec;42(6):500-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Sep 10.PMID: 24091130
Dziri O, Dziri R, Maraoub A, Chouchani C.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Jul;26(7):741-746. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2019.0076. Epub 2020 Jan 9.PMID: 31916915
Colomer-Lluch M, Mora A, López C, Mamani R, Dahbi G, Marzoa J, Herrera A, Viso S, Blanco JE, Blanco M, Alonso MP, Jofre J, Muniesa M, Blanco J.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Apr;68(4):758-65. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks477. Epub 2012 Dec 7.PMID: 23221627
Non-ST131 Escherichia coli from cattle harbouring human-like bla(CTX-M-15)-carrying plasmids.
Madec JY, Poirel L, Saras E, Gourguechon A, Girlich D, Nordmann P, Haenni M.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012 Mar;67(3):578-81. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr542. Epub 2011 Dec 29.PMID: 22210752
Escherichia coli ST1193: Following in the Footsteps of E. coli ST131.
Pitout JDD, Peirano G, Chen L, DeVinney R, Matsumura Y.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Jul 19;66(7):e0051122. doi: 10.1128/aac.00511-22. Epub 2022 Jun 6.PMID: 35658504 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
Antibiotic-Resistance Genes in E. coli strains in GCC Countries: A Meta-Analysis.
Bindayna KM, Joji RM, Ezzat H, Jahrami HA.Saudi J Med Med Sci. 2022 Jan-Apr;10(1):1-11. doi: 10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_638_21. Epub 2022 Jan 17.PMID: 35283714 Free PMC article.
Contreras-Alvarado LM, Zavala-Vega S, Cruz-Córdova A, Reyes-Grajeda JP, Escalona-Venegas G, Flores V, Alcázar-López V, Arellano-Galindo J, Hernández-Castro R, Castro-Escarpulli G, Xicohtencatl-Cortes J, Ochoa SA.Microorganisms. 2021 Nov 5;9(11):2299. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112299.PMID: 34835425 Free PMC article.
Emerging Status of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Fungi in the Arabian Peninsula.
Borgio JF, Rasdan AS, Sonbol B, Alhamid G, Almandil NB, AbdulAzeez S.Biology (Basel). 2021 Nov 6;10(11):1144. doi: 10.3390/biology10111144.PMID: 34827138 Free PMC article. Review.
Marchisio ML, Liebrenz KI, Méndez ELA, Di Conza JA.Braz J Microbiol. 2021 Dec;52(4):1853-1863. doi: 10.1007/s42770-021-00574-4. Epub 2021 Jul 16.PMID: 34269999 Free PMC article.
Dandachi I, Chaddad A, Hanna J, Matta J, Daoud Z.Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 23;10:1941. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01941. eCollection 2019.PMID: 31507558 Free PMC article. Review.
KMEL References
References
-
- Dahbi G, Mora A, López C, Alonso MP, Mamani R, Marzoa J, Coira A, García-Garrote F, Pita JM, Velasco D, Herrera A, Viso S, Blanco JE, Blanco M, Blanco J. Emergence of new variants of ST131 clonal group among extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli producing extended-spectrum β-lactamases. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013;42:347–351. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.06.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lau SH, Kaufmann MK, Livermore DM, Woodford N, Willshaw GA, Cheasty T, Stamper K, Reddy S, Cheesbrough J, Bolton FJ, Fox AJ, Upton M. UK epidemic Escherichia coli strains A E, with CTX-M-15 β-lactamase, all belong to the international O25:H4-ST131 clone. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;62:1241–1244. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn380. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pitout JDD, Gregson DB, Campbell L, Laupland KB. Molecular characteristics of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolates causing bacteremia in the Calgary health region from 2000 to 2007: Emergence of clone ST131 as a cause of community-acquired infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;2009(53):2846–2851. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johnson JR, Johnson B, Clabots C, Kuskowski MA, Pendyala S, DebRoy C, Nowicki B, Rice J. Escherichia coli sequence type ST131 as an emerging fluoroquinolone-resistant uropathogen among renal transplant recipients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:546–550. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01089-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blanco M, Alonso MP, Nicolas-Chanoine MH, Dahbi G, Mora A, Blanco JE, López C, Cortés P, Llagostera M, Leflon-Guibout V, Puentes B, Mamani R, Herrera A, Coira MA, García-Garrote F, Pita JM, Blanco J. Molecular epidemiology of Escherichia coli producing extended-spectrum β-lactamases in Lugo (Spain): dissemination of clone O25b:H4-ST131 producing CTX-M-15. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;63:1135–1141. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp122. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mora A, Herrera A, Mamani R, López C, Alonso MP, Blanco JE, Blanco M, Dahbi G, García-Garrote F, Pita JM, Coira A, Bernárdez MI, Blanco J. Recent emergence of clonal group O25b:K1:H4-B2-ST131 ibeA strains among Escherichia coli poultry isolates, including CTX-M-9-producing strains, and comparison with clinical human isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76:6991–6997. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01112-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jamal W, Rotimi VO, Albert MJ, Khodakhast F, Udo EE, Poirel L. Emergence of nosocomial New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in patients admitted to a tertiary care hospital in Kuwait. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;39:183–184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.10.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clermont O, Dhanji H, Upton M, Gibreel T, Fox A, Boyd D, Mulvey MR, Nordmann P, Ruppé E, Sarthou JL, Frank T, Vimont S, Arlet G, Branger C, Woodford N, Denamur E. Rapid detection of the O25b-ST131 clone of Escherichia coli encompassing the CTX-M-15 producing strains. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;64:274–277. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp194. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . Document M100-S21. Wayne, PA: CLSI; 2012. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-first informational supplement.
-
- Giraud E, Brisabois A, Martel JL, Chaslus-Dancla EP. Comparative study of mutations in animal isolates and experimental in-vitro and in-vivo mutation of Salmonella spp. suggests a counter selection of highly fluoroquinolone resistant strains in the field. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43:2131–2137. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kiratisin P, Apisarnthanarak A, Saifon P, Laesripa C, Kitphati R, Mundy LM. The emergence of a novel ceftazidime-resistant CTX-M extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, CTX-M-55, in both community-onset and hospital-acquired infections in Thailand. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007;58:349–355. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.02.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ribot FM, Fair NA, Gautom R, Carmeron DN, Hunter SB, Swaminathan B, Barrett TJ. Standardization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for the subtyping of Escherichia coli O157, Salmonella and Shigella for pulsenet. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2006;3:59–67. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2006.3.59. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khan MA, Lemmens N, Riera E, Blonk T, Goedhart J, Van Belkum A, Goessens W, Hays JP, Van Westreenen M. Dominance of CTX-M-2 and CTX-M-56 among extended-spectrum β-lactamases produced by Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli isolated in hospitals in Paraguay. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;64:1330–1332. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp382. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pallecchi L, Bartoloni A, Fiorelli C, Mantella A, Di Maggio T, Gamboa H, Gotuzzo E, Kronvall G, Paradisi F, Rossolini GM. Rapid dissemination and diversity of CTX-M Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase genes in commensal Escherichia coli isolates from healthy children from low-resource settings in Latin America. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51:2720–2725. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00026-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Woodford N, Carattoli A, Karisik E, Underwood A, Ellington MJ, Livermore DM. Complete nucleotide sequences of plasmids pEK204, pEK499, and pEK516, encoding CTX-M Enzymes in Three Major Escherichia coli Lineages from the United Kingdom, All Belonging to the International O25:H4-ST131 Clone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:4472–4482. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00688-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed