Knowledge, perceptions and confidence of physicians and pharmacists towards pharmacogenetics practice in Kuwait
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Pharmacy Practice, Faculty of Pharmacy, Kuwait University, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
- Department of Pharmacy, Jahra Hospital, Ministry of Health, Jahra City, Kuwait.
- Drug Inspection Administration, Ministry of Health, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
Abstract
Background: Pharmacogenetics practice has been successfully implemented in many developed countries to enhance personalized medicine and improve clinical and economic outcomes. An understanding of healthcare providers' knowledge, perceptions, confidence towards pharmacogenetics, and their active enrollment with pharmacogenetic testing is essential for test acceptance and utilization. This study was designed to assess physicians' and pharmacists' knowledge, perceptions, and confidence towards pharmacogenetics, determine the preferred learning format for their future education in pharmacogenetics, and identify the barriers to its application in their practice settings.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted using a pretested self-administered questionnaire on a sample of 629 randomly selected physicians and pharmacists. Descriptive and comparative analyses were used in data analysis.
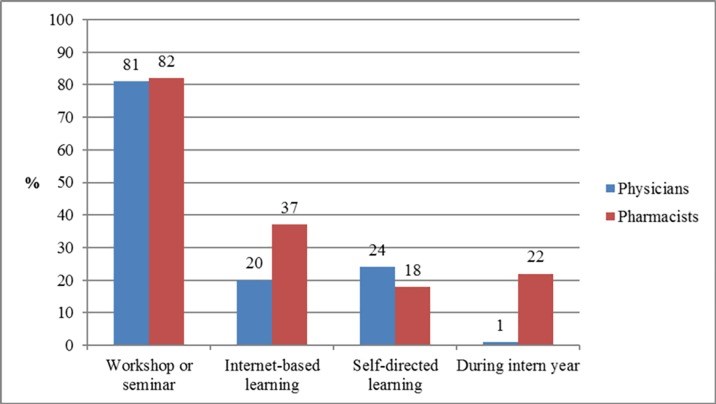
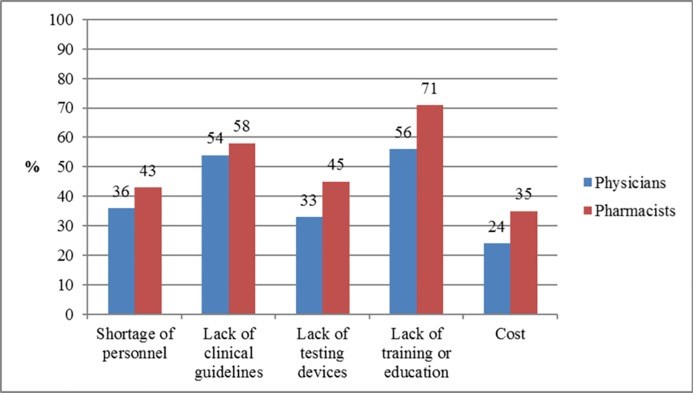
Results: The response rate was 98.1%. Less than one-tenth of respondents were exposed to pharmacogenetics education or training (8.9%), applied pharmacogenetics testing in their practice (9.4%), or provided patient counselling on the results of the pharmacogenetic testing (9.1%), and over 90% of them were physicians. The overall respondents' mean (SD) total knowledge score percentage was low [45.0% (24)] and there was no significant difference between the physicians and pharmacists scores (p>0.05). Only 16.0% of participants indicated that they felt confident in applying pharmacogenetics in their practice settings. Despite these low levels of knowledge and self-confidence, 70.2% of participants expressed overall positive perceptions towards pharmacogenetics and its clinical implications. These positive overall perceptions were found to be significantly more common among pharmacists compared to physicians (p<0.05). The top two perceived barriers facing the implementation of pharmacogenetics in Kuwait were lack of education or training and clinical guidelines.
Conclusions: These findings highlight important concerns and will aid in the assessment of current pharmacogenetics practice. Also, they will provide further insight in designing future targeted multifaceted interventions to promote the adoption and utilization of pharmacogenetics testing in Kuwait.
Figures
Similar articles
Lemay J, Bayoud T, Husain H, Sharma P.BMJ Open. 2019 Jun 16;9(6):e027395. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027395.PMID: 31209092 Free PMC article.
Pharmaceutical care in Kuwait: hospital pharmacists' perspectives.
Katoue MG, Awad AI, Schwinghammer TL, Kombian SB.Int J Clin Pharm. 2014 Dec;36(6):1170-8. doi: 10.1007/s11096-014-0013-z. Epub 2014 Sep 10.PMID: 25204259
Albassam A, Alghanem SS, Alawadhi F, Alsulaimani Z.Ther Drug Monit. 2022 Aug 1;44(4):511-519. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000966. Epub 2022 Feb 8.PMID: 35132050 Free PMC article.
Nagy M, Tsermpini EE, Siamoglou S, Patrinos GP.Pharmacogenomics. 2020 Nov;21(16):1179-1189. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2020-0076. Epub 2020 Oct 29.PMID: 33118449 Review.
Hansen JM, Nørgaard JDSV, Kälvemark Sporrong S.Res Social Adm Pharm. 2022 Aug;18(8):3230-3238. doi: 10.1016/j.sapharm.2021.12.002. Epub 2021 Dec 15.PMID: 34996718 Review.
Cited by
Rahma AT, Ali BR, Patrinos GP, Ahmed LA, Elbarazi I, Abdullahi AS, Elsheik M, Abbas M, Afandi F, Alnaqbi A, Al Maskari F.Hum Genomics. 2023 Jul 15;17(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s40246-023-00509-0.PMID: 37454085 Free PMC article.
Mehtar M, Hammoud SH, Amin MEK.Saudi Pharm J. 2022 Dec;30(12):1765-1772. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.10.005. Epub 2022 Oct 12.PMID: 36601506 Free PMC article.
Physicians' Knowledge, Attitude, and Experience of Pharmacogenomic Testing in China.
Jia T, Wu C, Hu X, Li S, Zhang X, Cai Y, Chen J, Shi L, Lu CY, Nie X.J Pers Med. 2022 Dec 7;12(12):2021. doi: 10.3390/jpm12122021.PMID: 36556242 Free PMC article.
Kamp M, Pain O, May A, Lewis CM, Ramsay M.J Pers Med. 2022 Aug 24;12(9):1360. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091360.PMID: 36143145 Free PMC article.
Clinical Pharmacists' Knowledge of and Attitudes toward Pharmacogenomic Testing in China.
Nie X, Jia T, Hu X, Li S, Zhang X, Wu C, Zhang Y, Chen J, Shi L, Lu CY.J Pers Med. 2022 Aug 21;12(8):1348. doi: 10.3390/jpm12081348.PMID: 36013297 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- US National Library of Medicine. Genomic Research: What is Pharmacogenetics [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2018 Mar 21]. Available from: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/primer/genomicresearch/pharmacogenetics
-
- Alrashid MH, Al-Serri A, Alshemmari SH, Koshi P, Al-Bustan SA. Association of Genetic Polymorphisms in the VKORC1 and CYP2C9 Genes with Warfarin Dosage in a Group of Kuwaiti Individuals. Mol Diagnosis Ther. 2016;20:183–90. - PubMed
-
- Sivadas A, Sharma P, Scaria V. Landscape of warfarin and clopidogrel pharmacogenetic variants in Qatari population from whole exome datasets. Pharmacogenomics. 2016;17:1891–1901. - PubMed
-
- Annis DS, Mosher DF, Roberts DD. Pharmacoginetics in clinical practice: how far have we come and where are we going? Pharmacogenomics. 2009;27: 339–351.
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Table of Pharmacogenetics Biomarkers in Drug Labeling [Internet]. [cited 2018 Mar 21]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/ScienceResearch/ResearchAreas/Pharmacogenetics...
-
- Yau A. Knowledge, attitude and practice concerning pharmacogenetics among pharmacists: A systematic Review. J Young Pharm. 2015;7: 145–154.
-
- World Health Organization. Statistics [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2018 Mar 21]. Available from: http://www.who.int/countries/kwt/en/
-
- Raosoft. Sample Size Calculator [Internet]. [cited 2018 Mar 21]. Available from: http://www.raosoft.com/samplesize.html
-
- World Health Organization. How to investigate drug use in health facilities: Selected drug use indicators. 1993.
-
- Bannur Z, Bahaman S, Salleh M, Kek T. Pharmacogenetics based practice in Malaysia: The attitude, knowledge and adoption by the healthcare professionals. Int Med J Malaysia. 2014;13: 41–50.
-
- Katoue M, Awad A, Schwinghammer T, Kombian S. Pharmaeutical care in Kuwait: hospital pharmacists’ perspectives. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2014;36: 1170–1178. - PubMed
-
- Stanford University & St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2018 May 25]. Available from: https://cpicpgx.org/
-
- Williams M. Genomic medicine implementation: learning by example. Am J Med Genet. 2014;166: 8–14. - PubMed
-
- Patrinos G, Katsila T. Pharmacogenomics education and research at the Department of Pharmacy, University of Patras, Greece. Pharmacogenomics. 2016;17: 1865–1872.