CHD2 variants are a risk factor for photosensitivity in epilepsy
Elizabeth C Galizia 1, Candace T Myers 2, Costin Leu 3, Carolien G F de Kovel 4, Tatiana Afrikanova 5, Maria Lorena Cordero-Maldonado 5, Teresa G Martins 5, Maxime Jacmin 5, Suzanne Drury 6, V Krishna Chinthapalli 3, Hiltrud Muhle 7, Manuela Pendziwiat 7, Thomas Sander 8, Ann-Kathrin Ruppert 8, Rikke S Møller 9, Holger Thiele 8, Roland Krause 5, Julian Schubert 10, Anna-Elina Lehesjoki 11, Peter Nürnberg 8, Holger Lerche 10; EuroEPINOMICS CoGIE Consortium; Aarno Palotie 12, Antonietta Coppola 13, Salvatore Striano 14, Luigi Del Gaudio 14, Christopher Boustred 6, Amy L Schneider 15, Nicholas Lench 6, Bosanka Jocic-Jakubi 16, Athanasios Covanis 17, Giuseppe Capovilla 18, Pierangelo Veggiotti 19, Marta Piccioli 20, Pasquale Parisi 21, Laura Cantonetti 22, Lynette G Sadleir 23, Saul A Mullen 24, Samuel F Berkovic 15, Ulrich Stephani 7, Ingo Helbig 7, Alexander D Crawford 5, Camila V Esguerra 25, Dorothee G A Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité 4, Bobby P C Koeleman 26, Heather C Mefford 27, Ingrid E Scheffer 28, Sanjay M Sisodiya 1
Affiliations
Affiliations
- NIHR Biomedical Research Centre Department of Clinical and Experimental Epilepsy, UCL Institute of Neurology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square, London, UK 2 Epilepsy Society, Bucks, UK s.sisodiya@ucl.ac.uk scheffer@unimelb.edu.au hmefford@uw.edu b.p.c.koeleman@umcutrecht.nl.
- Department of Paediatrics, University of Washington, USA.
- NIHR Biomedical Research Centre Department of Clinical and Experimental Epilepsy, UCL Institute of Neurology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square, London, UK 2 Epilepsy Society, Bucks, UK.
- Department of Medical Genetics Research, University Medical Centre Utrecht, The Netherlands.
- Luxembourg Centre for Systems Biomedicine, University of Luxembourg, Esch-sur-Alzette, Luxembourg.
- North East Thames Regional Genetics Laboratories, Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK.
- Department of Neuropaediatrics, University Medical Centre Schleswig-Holstein and Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel, Kiel, Germany.
- Cologne Centre for Genomics, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany.
- Danish Epilepsy Centre, Dianalund, Denmark 10 Institute for Regional Health Services, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark.
- Deptartment of Neurology and Epileptology, Hertie Institut for Clinical Brain Research, Tübingen, Germany.
- Folkhälsan Institute of Genetics and Neuroscience Centre, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland 13 Research Programs Unit, Molecular Neurology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland.
- Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Wellcome Trust Genome Campus, Hinxton, Cambridgeshire, UK 15 Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland 16 Program in Medical and Population Genetics and Genetic Analysis Platform, The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, USA.
- NIHR Biomedical Research Centre Department of Clinical and Experimental Epilepsy, UCL Institute of Neurology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square, London, UK 2 Epilepsy Society, Bucks, UK 17 Epilepsy Centre, Neurology Department, Federico II University of Naples, Naples, Italy.
- Epilepsy Centre, Neurology Department, Federico II University of Naples, Naples, Italy.
- Department of Medicine, University of Melbourne, Austin Health, Melbourne, Australia.
- Department of Child Neurology, Paediatric Clinic, Clinical Centre Nis, Serbia 20 Department of Paediatric Neurology, Paediatric Clinic, Al Sabah Hospital, Kuwait.
- Neurology Department, The Children's Hospital Agia Sophia, Athens, Greece.
- Epilepsy Centre 'C. Poma Hospital', Mantova, Italy.
- Department of Child Neurology and Psychiatry C. Mondino National Neurological Institute, Via Mondino, 2, 27100, Pavia, Italy 24 Brain and Behaviour Department, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy.
- Neurophysiopathology Unit, San Filippo Neri Hospital, Rome, Italy.
- Child Neurology, NESMOS Department, Faculty of Medicine and Psychology, Sapienza University, Rome, Italy.
- Neurorehabilitation Unit, Department of Neuroscience and Neurorehabilitation, IRCCS, Bambino Gesu' Children's Hospital, Rome, Italy.
- Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Otago, Wellington, New Zealand.
- Florey Institute of Neurosciences and Mental Health, and Department of Paediatrics, University of Melbourne, Royal Children's Hospital, Melbourne, Australia.
- Chemical Neuroscience Group, Biotechnology Centre of Oslo, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway 31 Laboratory for Molecular Biodiscovery, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
- Department of Medical Genetics Research, University Medical Centre Utrecht, The Netherlands s.sisodiya@ucl.ac.uk scheffer@unimelb.edu.au hmefford@uw.edu b.p.c.koeleman@umcutrecht.nl.
- Department of Paediatrics, University of Washington, USA s.sisodiya@ucl.ac.uk scheffer@unimelb.edu.au hmefford@uw.edu b.p.c.koeleman@umcutrecht.nl.
- Department of Medicine, University of Melbourne, Austin Health, Melbourne, Australia 29 Florey Institute of Neurosciences and Mental Health, and Department of Paediatrics, University of Melbourne, Royal Children's Hospital, Melbourne, Australia s.sisodiya@ucl.ac.uk scheffer@unimelb.edu.au hmefford@uw.edu b.p.c.koeleman@umcutrecht.nl.
Collaborators
- EuroEPINOMICS CoGIE Consortium:
Anna-Elina Lehesjoki Folkhälsan, Ann-Kathrin Ruppert, Bobby Koeleman, Dennis Lal, Federico Zara, Felicitas Becker, Caglayan Hande, Helle Hjalgrim, Hiltrud Muhle, Holger Lerche, Holger Thiele, Ingo Helbig, Janine Altmüller, Julian Schubert, Kamel Jabbari, Kate Everett, Pasquale Striano, Patrick May, Peter Nürnberg, Rikke Møller, Rima Nabbout, Roland Krause, Rudi Balling, Stephanie Baulac, Thomas Sander, Wolfram Kunz, Yvonne Weber
Abstract
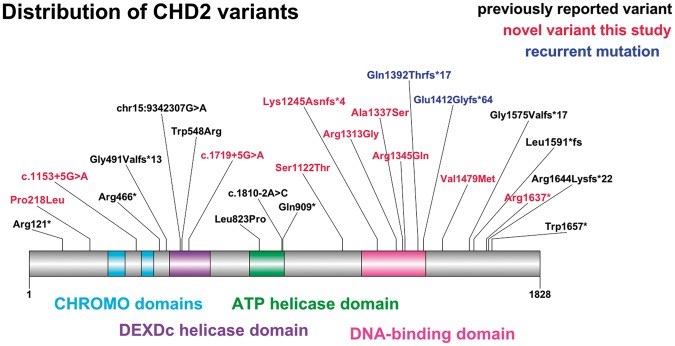
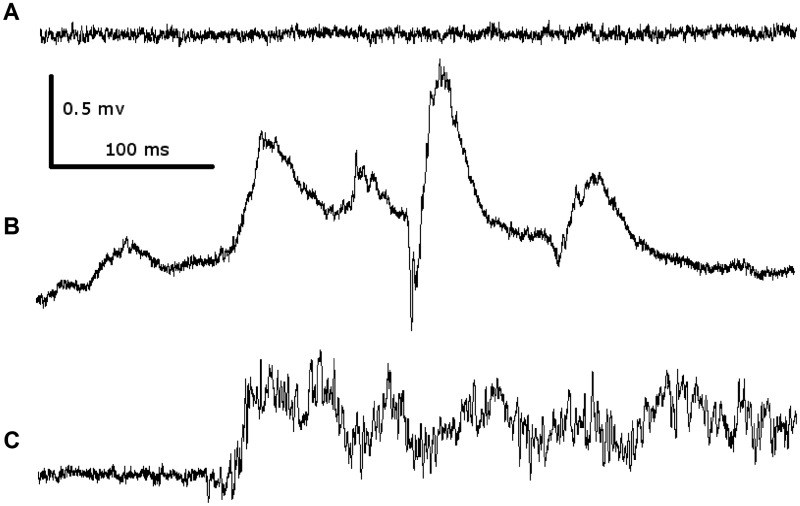
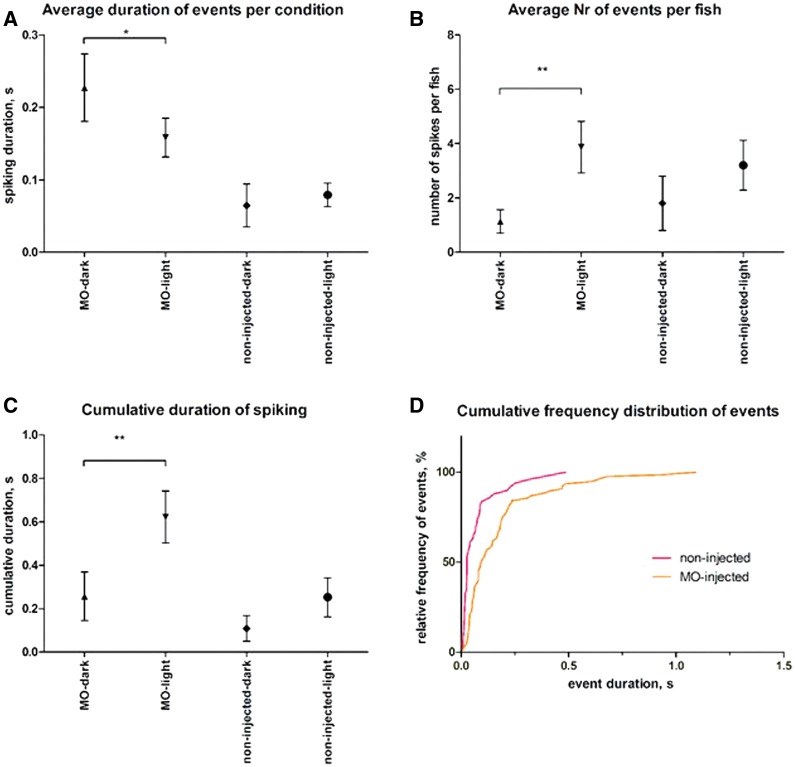
Photosensitivity is a heritable abnormal cortical response to flickering light, manifesting as particular electroencephalographic changes, with or without seizures. Photosensitivity is prominent in a very rare epileptic encephalopathy due to de novo CHD2 mutations, but is also seen in epileptic encephalopathies due to other gene mutations. We determined whether CHD2 variation underlies photosensitivity in common epilepsies, specific photosensitive epilepsies and individuals with photosensitivity without seizures. We studied 580 individuals with epilepsy and either photosensitive seizures or abnormal photoparoxysmal response on electroencephalography, or both, and 55 individuals with photoparoxysmal response but no seizures. We compared CHD2 sequence data to publicly available data from 34 427 individuals, not enriched for epilepsy. We investigated the role of unique variants seen only once in the entire data set. We sought CHD2 variants in 238 exomes from familial genetic generalized epilepsies, and in other public exome data sets. We identified 11 unique variants in the 580 individuals with photosensitive epilepsies and 128 unique variants in the 34 427 controls: unique CHD2 variation is over-represented in cases overall (P = 2.17 × 10(-5)). Among epilepsy syndromes, there was over-representation of unique CHD2 variants (3/36 cases) in the archetypal photosensitive epilepsy syndrome, eyelid myoclonia with absences (P = 3.50 × 10(-4)). CHD2 variation was not over-represented in photoparoxysmal response without seizures. Zebrafish larvae with chd2 knockdown were tested for photosensitivity. Chd2 knockdown markedly enhanced mild innate zebrafish larval photosensitivity. CHD2 mutation is the first identified cause of the archetypal generalized photosensitive epilepsy syndrome, eyelid myoclonia with absences. Unique CHD2 variants are also associated with photosensitivity in common epilepsies. CHD2 does not encode an ion channel, opening new avenues for research into human cortical excitability.
Keywords: eyelid myoclonia with absences; photosensitive; seizure.
Figures
Similar articles
CHD2 mutations are a rare cause of generalized epilepsy with myoclonic-atonic seizures.
Trivisano M, Striano P, Sartorelli J, Giordano L, Traverso M, Accorsi P, Cappelletti S, Claps DJ, Vigevano F, Zara F, Specchio N.Epilepsy Behav. 2015 Oct;51:53-6. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.06.029. Epub 2015 Aug 7.PMID: 26262932
Koutroumanidis M, Tsirka V, Panayiotopoulos C.Epileptic Disord. 2015 Sep;17(3):275-86. doi: 10.1684/epd.2015.0765.PMID: 26293003
Suls A, Jaehn JA, Kecskés A, Weber Y, Weckhuysen S, Craiu DC, Siekierska A, Djémié T, Afrikanova T, Gormley P, von Spiczak S, Kluger G, Iliescu CM, Talvik T, Talvik I, Meral C, Caglayan HS, Giraldez BG, Serratosa J, Lemke JR, Hoffman-Zacharska D, Szczepanik E, Barisic N, Komarek V, Hjalgrim H, Møller RS, Linnankivi T, Dimova P, Striano P, Zara F, Marini C, Guerrini R, Depienne C, Baulac S, Kuhlenbäumer G, Crawford AD, Lehesjoki AE, de Witte PA, Palotie A, Lerche H, Esguerra CV, De Jonghe P, Helbig I; EuroEPINOMICS RES Consortium.Am J Hum Genet. 2013 Nov 7;93(5):967-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.09.017. Epub 2013 Oct 24.PMID: 24207121 Free PMC article.
[Photosensitive epilepsies of children].
Rodríguez-Barrionuevo AC, Bauzano-Poley E, Rodríguez Vives MA.Rev Neurol. 2001 Apr 16-30;32(8):768-72.PMID: 11391515 Review. Spanish.
Photosensitivity in idiopathic generalized epilepsies.
Covanis A.Epilepsia. 2005;46 Suppl 9:67-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.00315.x.PMID: 16302877 Review.
Cited by
D'Amora M, Galgani A, Marchese M, Tantussi F, Faraguna U, De Angelis F, Giorgi FS.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 22;24(9):7702. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097702.PMID: 37175408 Free PMC article. Review.
Genetic and phenotypic spectrum of Chinese patients with epilepsy and photosensitivity.
Niu Y, Gong P, Jiao X, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Yang Z.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 2;13:907228. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.907228. eCollection 2022.PMID: 36034301 Free PMC article.
Zebrafish Is a Powerful Tool for Precision Medicine Approaches to Neurological Disorders.
Ochenkowska K, Herold A, Samarut É.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jul 6;15:944693. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.944693. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35875659 Free PMC article. Review.
Photo-Dependent Reflex Seizures-A Scoping Review with Proposal of Classification.
Strzelecka J, Mazurkiewicz DW, Skadorwa T, Gąsior JS, Jóźwiak S.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 29;11(13):3766. doi: 10.3390/jcm11133766.PMID: 35807051 Free PMC article. Review.
Clinical analysis of CHD2 gene mutations in pediatric patients with epilepsy.
Feng W, Fang F, Wang X, Chen C, Lu J, Deng J.Pediatr Investig. 2022 Apr 26;6(2):93-99. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12321. eCollection 2022 Jun.PMID: 35774528 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Capelli LP, Krepischi ACV, Gurgel-Giannetti J, Mendes MF, Rodrigues T, Varela MC, et al. Deletion of the RMGA and CHD2 genes in a child with epilepsy and mental deficiency. Eur J Med Genet. 2012;55:132–4. - PubMed
-
- De Kovel CGF, Pinto D, Tauer U, Lorenz S, Muhle H, Leu C, et al. Whole-genome linkage scan for epilepsy-related photosensitivity: a mega-analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2010;89:286–94. - PubMed
-
- Dhamija R, Breningstall G, Wong-Kisiel L, Dolan M, Hirsch B, Wirrell E. Microdeletion of chromosome 15q26.1 in a child with intractable generalized epilepsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2011;45:60–2. - PubMed
-
- Gregory RP, Oates T, Merry RT. Electroencephalogram epileptiform abnormalities in candidates for aircrew training. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1993;86:75–7. - PubMed
-
- Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité D, Rubboli G, Hirsch E, Martins da Silva A, Seri S, Wilkins A, et al. Methodology of photic stimulation revisited: updated European algorithm for visual stimulation in the EEG laboratory. Epilepsia. 2012;53:16–24. - PubMed
-
- Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenite D, Silva L, Maureza M. Prevelance of photoparoxysmal EEG responses in normal children and adolescents in Teofile Otoni, Brazil; 2001-2002. Epilepsia. 2003;44(Suppl 8):48. - PubMed
-
- Koeleman BPC, de Kovel CGF, Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité DGA. Photoparoxysmal EEG response and genetic dissection of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2013;28(Suppl 1):S69–71. - PubMed
-
- Lu Y, Waltz S, Stenzel K, Muhle H, Stephani U. Photosensitivity in epileptic syndromes of childhood and adolescence. Epileptic Disord. 2008;10:136–43. - PubMed
-
- Lund C, Brodtkorb E, Oye A-M, Røsby O, Selmer KK. CHD2 mutations in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Epilepsy Behav. 2014;33:18–21. - PubMed
-
- Lund C, Brodtkorb E, Røsby O, Rødningen OK, Selmer KK. Copy number variants in adult patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome features. Epilepsy Res. 2013;105:110–17. - PubMed
-
- Marfella CGA, Ohkawa Y, Coles AH, Garlick DS, Jones SN, Imbalzano AN. Mutation of the SNF2 family member Chd2 affects mouse development and survival. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:162–71. - PubMed
-
- Newmark ME, Penry JK. Photosensitivity and epilepsy: a review. New York: Raven Press; 1979.
-
- Oguni H, Hayashi K, Awaya Y, Fukuyama Y, Osawa M. Severe myoclonic epilepsy in infants–a review based on the Tokyo Women’s Medical University series of 84 cases. Brain Dev. 2001;23:736–48. - PubMed
-
- Quirk JA, Fish DR, Smith SJ, Sander JW, Shorvon SD, Allen PJ. Incidence of photosensitive epilepsy: a prospective national study. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995;95:260–7. - PubMed
-
- Sadleir LG, Vears D, Regan B, Redshaw N, Bleasel A, Scheffer IE. Family studies of individuals with eyelid myoclonia with absences. Epilepsia. 2012;53:2141–8. - PubMed
-
- Schuster EF, Stöger R. CHD5 defines a new subfamily of chromodomain-SWI2/SNF2-like helicases. Mamm Genome. 2002;13:117–19. - PubMed
-
- So EL, Ruggles KH, Ahmann PA, Olson KA. Prognosis of photoparoxysmal response in nonepileptic patients. Neurology. 1993;43:1719–22. - PubMed
-
- Tauer U, Lorenz S, Lenzen KP, Heils A, Muhle H, Gresch M, et al. Genetic dissection of photosensitivity and its relation to idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:866–73. - PubMed
-
- Taylor I, Berkovic SF, Scheffer IE. Genetics of epilepsy syndromes in families with photosensitivity. Neurology. 2013;80:1322–9. - PubMed
-
- Taylor I, Marini C, Johnson MR, Turner S, Berkovic SF, Scheffer IE. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy and idiopathic photosensitive occipital lobe epilepsy: is there overlap? Brain J Neurol. 2004;127:1878–86. - PubMed
-
- Veredice C, Bianco F, Contaldo I, Orteschi D, Stefanini MC, Battaglia D, et al. Early onset myoclonic epilepsy and 15q26 microdeletion: observation of the first case. Epilepsia. 2009;50:1810–15. - PubMed
-
- Verrotti A, Beccaria F, Fiori F, Montagnini A, Capovilla G. Photosensitivity: epidemiology, genetics, clinical manifestations, assessment, and management. Epileptic Disord Int Epilepsy J Videotape. 2012;14:349–62. - PubMed
-
- Walter WG, Dovey VJ, Shipton H. Analysis of the electrical response of the human cortex to photic stimulation. Nature. 1946;158:540. - PubMed
-
- Waltz S, Stephani U. Inheritance of photosensitivity. Neuropediatrics. 2000;31:82–5. - PubMed