Novel Peptidomic Approach for Identification of Low and High Molecular Weight Tauopathy Peptides Following Calpain Digestion, and Primary Culture Neurotoxic Challenges
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. hamad.yadikar@ku.edu.kw.
- Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, Kuwait University, P.O. Box 5969, Safat 13060, Kuwait. hamad.yadikar@ku.edu.kw.
- Department of Chemistry, Chemistry Laboratory Building, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. hamad.yadikar@ku.edu.kw.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. connorj96@ufl.edu.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. nikop1997@ufl.edu.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. emouhawasse@ufl.edu.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. lynnng@ufl.edu.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. torresi@ufl.edu.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. milinkurup@ufl.edu.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. zhihuiyang@ufl.edu.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. firasko@gmail.com.
- Faculty of Medicine, American University of Beirut Medical Center, Beirut F32611, Lebanon. firasko@gmail.com.
- Department of Chemistry, Chemistry Laboratory Building, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. ryost@ufl.edu.
- Program for Neurotrauma, Neuroproteomics & Biomarkers Research, Departments of Emergency Medicine, Psychiatry, Neuroscience and Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA. kwang@ufl.edu.
- Brain Rehabilitation Research Center, Malcom Randall VA Medical Center, 1601 SW Archer Rd. Gainesville, FL 32608, USA. kwang@ufl.edu.
Abstract
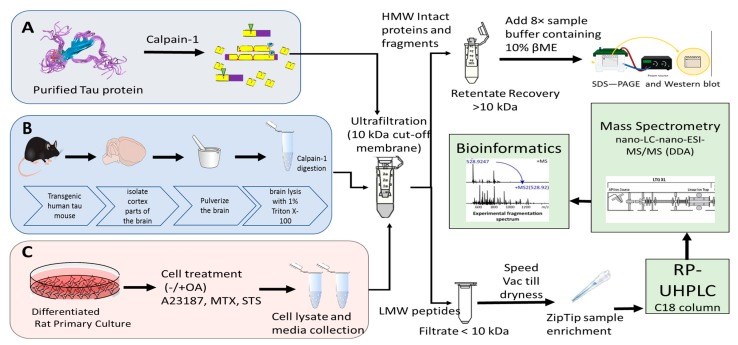
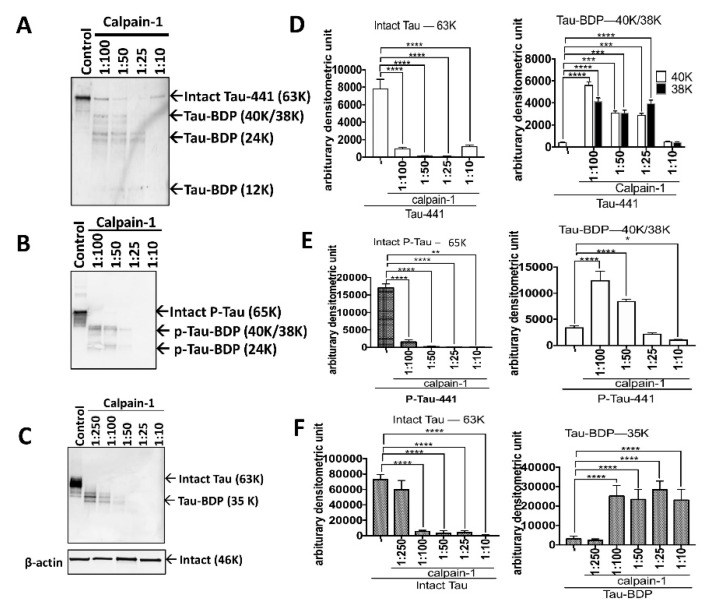
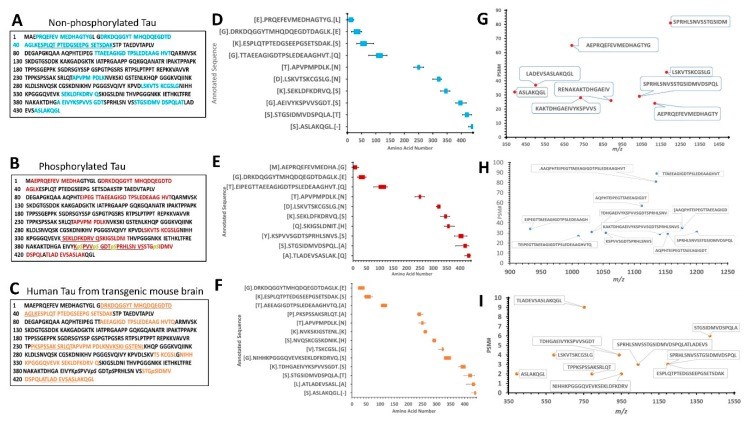
Tauopathy is a class of a neurodegenerative disorder linked with tau hyperphosphorylation, proteolysis, and aggregation. Tau can be subjected to proteolysis upon calpain activation in Alzheimer disease (AD), and traumatic brain injury (TBI). We and others have extensively researched calpain-mediated tau breakdown products (Tau-BDP; 45K, 35K, and 17K). Tau proteolysis might also generate low molecular weight (LMW ≤10K) proteolytic peptides after neurodegenerative damage. In this study, we have subjected purified tau protein (phospho and non-phospho) and mouse brain lysate to calpain-1 digestion to characterize the LMW generated by nano-liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization to tandem mass spectrometry (nano-LC-ESI-MS/MS). We have also challenged differentiated primary cerebrocortical neuronal cultures (CTX) with neurotoxic agents (calcium ionophore calcimycin (A23187), staurosporine (STS), N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), and Maitotoxin (MTX)) that mimic neurodegeneration to investigate the peptidome released into the conditioned cell media. We used a simple workflow in which we fractionate LMW calpain-mediated tau peptides by ultrafiltration (molecular weight cut-off value (MWCO) of 10K) and subject filtrate fractions to nano-LC-MS/MS analysis. The high molecular weight (HMW) peptides and intact proteins retained on the filter were analyzed separately by western blotting using total and phospho-specific tau antibodies. We have identified several novel proteolytic tau peptides (phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated) that are only present in samples treated with calpain or cell-based calpain activation model (particularly N- and C-terminal peptides). Our findings can help in developing future research strategies emphasizing on the suppression of tau proteolysis as a target.
Keywords: calpain; neurodegeneration; peptidomics; tau proteolysis; tauopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
Liu MC, Kobeissy F, Zheng W, Zhang Z, Hayes RL, Wang KK.ASN Neuro. 2011 Feb 16;3(1):e00051. doi: 10.1042/AN20100012.PMID: 21359008 Free PMC article.
Yadikar H, Johnson C, Pafundi N, Nguyen L, Kurup M, Torres I, Al-Enezy A, Yang Z, Yost R, Kobeissy FH, Wang KKW.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Apr;60(4):2295-2319. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03165-y. Epub 2023 Jan 13.PMID: 36635478
Zhang Z, Ottens AK, Sadasivan S, Kobeissy FH, Fang T, Hayes RL, Wang KK.J Neurotrauma. 2007 Mar;24(3):460-72. doi: 10.1089/neu.2006.0078.PMID: 17402852
Hajimohammadreza I, Raser KJ, Nath R, Nadimpalli R, Scott M, Wang KK.J Neurochem. 1997 Sep;69(3):1006-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.69031006.x.PMID: 9282922
Peptidomics: LC-MS operational parameters do matter.
Descamps A, Van der Borght K, De Spiegeleer A, Wynendaele E, De Spiegeleer B.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023 May 30;229:115348. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115348. Epub 2023 Mar 20.PMID: 36963248 Review.
Cited by
Yang Z, Arja RD, Zhu T, Sarkis GA, Patterson RL, Romo P, Rathore DS, Moghieb A, Abbatiello S, Robertson CS, Haskins WE, Kobeissy F, Wang KKW.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 11;23(16):8960. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168960.PMID: 36012232 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Kovacs G.G. Tauopathies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017;145:355–368. - PubMed
-
- Mondello S., Robicsek S.A., Gabrielli A., Brophy G.M., Papa L., Tepas J., III, Robertson C., Buki A., Scharf D., Jixiang M., et al. αII-Spectrin Breakdown Products (SBDPs): Diagnosis and Outcome in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients. J. Neurotrauma. 2010;27:1203–1213. doi: 10.1089/neu.2010.1278. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kurbatskaya K., Phillips E.C., Croft C.L., Dentoni G., Hughes M.M., Wade M.A., Al-Sarraj S., Troakes C., O’Neill M.J., Perez-Nievas B.G., et al. Upregulation of calpain activity precedes tau phosphorylation and loss of synaptic proteins in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016;4:34. doi: 10.1186/s40478-016-0299-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ozaki H., Ishihara H., Kohama K., Nonomura Y., Shibata S., Karaki H. Calcium-independent phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chain by okadaic acid isolated from black sponge (Halichondria okadai) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987;243:1167–1173. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y.P., Biernat J., Pickhardt M., Mandelkow E., Mandelkow E.M. Stepwise proteolysis liberates tau fragments that nucleate the Alzheimer-like aggregation of full-length tau in a neuronal cell model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:10252–10257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703676104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed