Impact of National Economy and Policies on End-Stage Kidney Care in South Asia and Southeast Asia
Suceena Alexander 1, Sanjiv Jasuja 2, Maurizio Gallieni 3, Manisha Sahay 4, Devender S Rana 5, Vivekanand Jha 6, Shalini Verma 7, Raja Ramachandran 8, Vinant Bhargava 5, Gaurav Sagar 2, Anupam Bahl 2, Mamun Mostafi 9, Jayakrishnan K Pisharam 10, Sydney C W Tang 11, Chakko Jacob 12, Atma Gunawan 13, Goh B Leong 14, Khin T Thwin 15, Rajendra K Agrawal 16, Kriengsak Vareesangthip 17, Roberto Tanchanco 18, Lina H L Choong 19, Chula Herath 20, Chih C Lin 21, Nguyen T Cuong 22, Ha P Haian 23, Syed F Akhtar 24, Ali Alsahow 25, Mohan M Rajapurkar 26, Vijay Kher 27, Hemant Mehta 28, Anil K Bhalla 5, Umesh B Khanna 29, Deepak S Ray 30, Sonika Puri 31, Himanshu Jain 7, Aida Lydia 32, Tushar Vachharajani 33
Affiliations
Affiliations
Department of Nephrology, Christian Medical College, Vellore 632004, India.- 2Department of Nephrology, Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, Delhi 110020, India.
- 3Department of Nephrology, "L. Sacco" Department of Biomedical and Clinical Sciences, University of Milano, Milan 20157, Italy.
- 4Department of Nephrology, Osmania General Hospital, Hyderabad 500012, India.
- 5Department of Nephrology, Sir Gangaram Hospital, Delhi 110060, India.
- 6Department of Nephrology, George Institute of Global Health, Delhi 110025, India.
- 7Clinical Research, AVATAR Foundation, New Delhi 110025, India.
- 8Department of Nephrology, PGIMER, Chandigarh 160012, India.
- 9Department of Nephrology, Armed Forces Medical College, Dhaka Cantonment, Dhaka 1206, Bangladesh.
- 10Department of Nephrology, Ministry of Health, Brunei Darussalam Medical Services, BB3910, Brunei Darussalam.
- 11Department of Nephrology, Queen Mary Hospital, Pok Fu Lam Road DD3LM 1969, Pok Fu Lam, Hong Kong.
- 12Department of Nephrology, Bangalore Baptist Hospital, Bengaluru 560024, India.
- 13Department of Nephrology, Brawijaya University, Malang 65145, Indonesia.
- 14Department of Nephrology, Serdang Hospital, Selangor 43000, Malaysia.
- 15Department of Nephrology, University of Medicine, North Okkalapa 11031, Yangon, Myanmar.
- 16Department of Nephrology, Bir Hospital, Kathmandu 44600, Nepal.
- 17Department of Nephrology, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10700, Thailand.
- 18Department of Nephrology, The Medical City, Pasig City 1605, Philippines.
- 19Department of Nephrology, Singapore General Hospital 169608, Singapore.
- 20Department of Nephrology, Sri Jayewardenepura General Hospital, Nugegoda 10100, Sri Lanka.
- 21Department of Nephrology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei City 11217, Taiwan.
- 22Department of Kidney Disease and Dialysis, Vietduc University Hospital, No 40, Trangathi Street, Hanoi, Vietnam.
- 23Department of Nephrology, Viet Duc University Hospital, Hanoi 40, Vietnam.
- 24Department of Nephrology, Sindh Institute of Urology and Transplantation, Karachi 74200, Pakistan.
- 25Department of Nephrology, Jahra Hospital, Al Jahra, Kuwait.
- 26Department of Nephrology, Muljibhai Patel Urological Hospital, Nadiad 387001, India.
- 27Department of Nephrology, Medanta Hospital, Gurugram 122006, India.
- 28Department of Nephrology, Lilawati Hospital, Mumbai 400050, India.
- 29Department of Nephrology, Lancelot Kidney & GI Centre in Borivali West, Mumbai 400092, India.
- 30Department of Nephrology, Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, Kolkata 700026, India.
- 31Department of Nephrology, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ 08901, USA.
- 32Department of Nephrology and Hypertension, Universitas Indonesia-Dr Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Salemba 10430, Jakarta, Indonesia.
- 33Department of Nephrology, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH 44195, USA.
Abstract
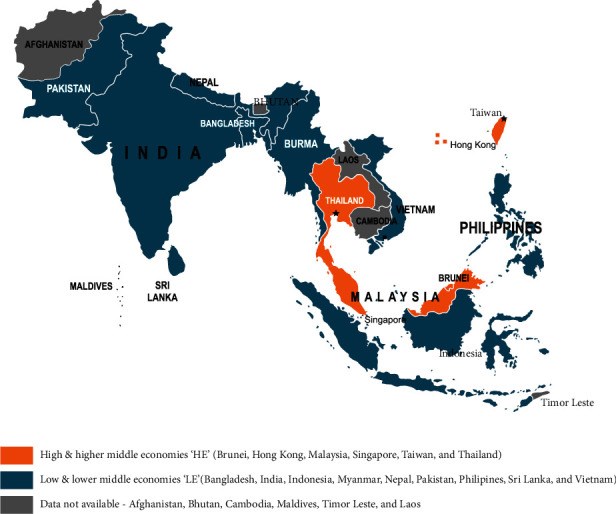
Background: The association between economic status and kidney disease is incompletely explored even in countries with higher economy (HE); the situation is complex in lower economies (LE) of South Asia and Southeast Asia (SA and SEA).
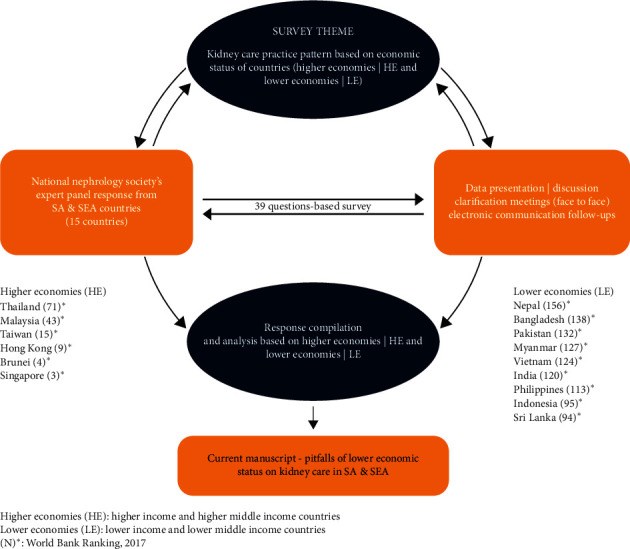
Methods: Fifteen countries of SA and SEA categorized as HE and LE, represented by the representatives of the national nephrology societies, participated in this questionnaire and interview-based assessment of the impact of economic status on renal care.
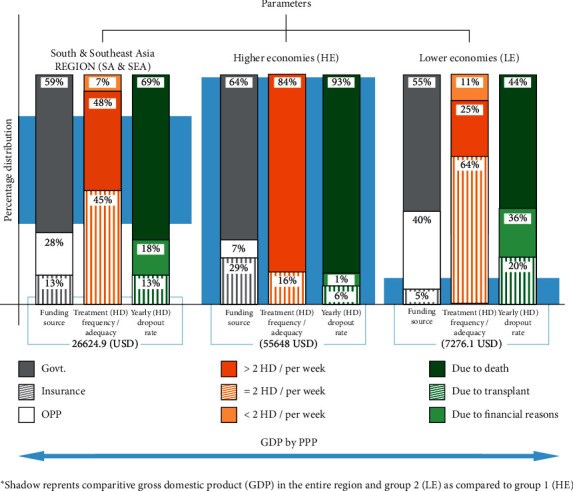
Results: Average incidence and prevalence of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) per million population (pmp) are 1.8 times and 3.3 times higher in HE. Hemodialysis is the main renal replacement therapy (RRT) (HE-68%, LE-63%). Funding of dialysis in HE is mainly by state (65%) or insurance bodies (30%); out of pocket expenses (OOPE) are high in LE (41%). Highest cost for hemodialysis is in Brunei and Singapore, and lowest in Myanmar and Nepal. Median number of dialysis machines/1000 ESKD population is 110 in HE and 53 in LE. Average number of machines/dialysis units in HE is 2.7 times higher than LE. The HE countries have 9 times more dialysis centers pmp (median HE-17, LE-02) and 16 times more nephrologist density (median HE-14.8 ppm, LE-0.94 ppm). Dialysis sessions >2/week is frequently followed in HE (84%) and <2/week in LE (64%). "On-demand" hemodialysis (<2 sessions/week) is prevalent in LE. Hemodialysis dropout rates at one year are lower in HE (12.3%; LE 53.4%), death being the major cause (HE-93.6%; LE-43.8%); renal transplants constitute 4% (Brunei) to 39% (Hong Kong) of the RRT in HE. ESKD burden is expected to increase >10% in all the HE countries except Taiwan, 10%-20% in the majority of LE countries.
Conclusion: Economic disparity in SA and SEA is reflected by poor dialysis infrastructure and penetration, inadequate manpower, higher OOPE, higher dialysis dropout rates, and lesser renal transplantations in LE countries. Utility of RRT can be improved by state funding and better insurance coverage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
Sahay M, Jasuja S, Tang SCW, Alexander S, Jha V, Vachharajani T, Mostafi M, Pisharam JK, Jacob C, Gunawan A, Bak Leong G, Thwin KT, Agrawal RK, Vareesangthip K, Tanchanco R, Choong L, Herath C, Lin CC, Cuong NT, Haian HP, Akhtar SF, Alsahow A, Rana DS, Rajapurkar MM, Kher V, Verma S, Ramachandran R, Bhargava V, Puri S, Sagar G, Bahl A, Mandal S, Gupta A, Gallieni M.Nephrology (Carlton). 2021 Feb;26(2):142-152. doi: 10.1111/nep.13825. Epub 2020 Dec 28.PMID: 33169890
Dialysis Care and Dialysis Funding in Asia.
Tang SCW, Yu X, Chen HC, Kashihara N, Park HC, Liew A, Goh BL, Nazareth MGC, Bunnag S, Tan J, Lun V, Lydia A, Sharma SK, Hoque E, Togtokh A, Ghnaimet M, Jha V.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 May;75(5):772-781. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.08.005. Epub 2019 Nov 5.PMID: 31699518
Couchoud C, Lassalle M, Jacquelinet C.Nephrol Ther. 2013 Sep;9 Suppl 1:S3-6. doi: 10.1016/S1769-7255(13)70036-1.PMID: 24119584 French.
Prasad N, Jha V.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2015 Dec;1(3):165-77. doi: 10.1159/000441816. Epub 2015 Nov 18.PMID: 27536677 Free PMC article. Review.
Kwong VW, Li PK.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2015 Dec;1(3):147-56. doi: 10.1159/000439193. Epub 2015 Sep 11.PMID: 27536675 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
Zafar MN, Rizvi SAH.Transpl Int. 2023 Jul 11;36:11290. doi: 10.3389/ti.2023.11290. eCollection 2023.PMID: 37497280 Free PMC article.
Risk factors of recurrent secondary hyperparathyroidism after adequate primary surgical treatment.
Kuo YC, Wang SY, Hung YL, Hsu CC, Kou HW, Chen MY, Tsai CY, Chang CH, Wang YC, Hsu JT, Yeh TS, Lee WC, Yeh CN.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 3;14:1063837. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1063837. eCollection 2023.PMID: 36817581
KMEL References
References
-
- Maheswaran R., Payne N., Meechan D., Burden R. P., Fryers P. R., Hutchinson A. Socioeconomic deprivation, travel distance, and renal replacement therapy in the Trent region, United Kingdom 2000: an ecological study. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health. 2003;57(7):523–524. doi: 10.1136/jech.57.7.523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- The ASEAN Post Team. Southeast Asia’s Widening Inequalities, 2018, https://theaseanpost.com/article/southeast-asias-widening-inequalities%2....
-
- South Asia Forum on Sustainable Development Goals. Subregional Preparatory Meeting for the Asia-Pacific Forum on Sustainable Development (APFSD) New Delhi, India: ESCAP; 2018. https://www.unescap.org/sites/default/files/South%20Asia%20SDG%20Forum%2....
-
- Hyodo T., Hirawa N., Hayashi M., et al. Present status of renal replacement therapy at 2015 in Asian countries (Myanmar, Vietnam, Thailand, China, and Japan) Renal Replacement Therapy. 2017;3:p. 11. doi: 10.1186/s41100-016-0082-7. - DOI
-
- Harsha Kumar H. N. Rise in Haemodialysis cases- peritoneal dialysis could be a solution. Medical Dialogues. 2019
-
- Hussain R., Tufail M., Naqvi A. A. J. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) as a model of renal replacement therapy (RRT) in children and adults-Pakistan experience. Indian Journal of Peritoneal Dialysis. 2006;11:10–13.
-
- Ur H., Rashid H. Management of end stage renal disease-Bangladesh perspective. The Open Urology & Nephrology Journal. 2014;71:108–112.
-
- Lin Y. C., Hsu C. Y., Kao C. C., et al. Incidence and prevalence of ESRD in taiwan renal registry data system (TWRDS): 2005-2012. Acta Nephrologica. 2014;28(2):65–68.
-
- Hada R., Khakurel S., Agrawal R. K., Kafle R. K., Bajracharya S. B., Raut K. B. Incidence of end stage renal disease on renal replacement therapy in Nepal. Kathmandu University Medical Journal (KUMJ) 2009;7(27):301–305. - PubMed
-
- Mazhar F., Nizam N., Fatima N., Siraj S., Rizvi S. A. Problems associated with access to renal replacement therapy: experience of the Sindh Institute of Urology and transplantation. Experimental and Clinical Transplantation. 2017;15(suppl 1):46–49. - PubMed
-
- The Kidney Foundation. Dialysis Registry of Pakistan 2014. Karachi, Pakistan: The University of Karachi; 2020.
-
- Naqvi S. A. J. Nephrology services in Pakistan. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2000;15(6):769–771. - PubMed
-
- Stankuvienė A., Ziginskienė E., Kuzminskis V., Bumblytė I. A. Impact of hemodialysis dose and frequency on survival of patients on chronic hemodialysis in Lithuania during 1998-2005. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) 2010;46(8):516–521. - PubMed
-
- Thapa N., Sharma B., Jnawali K. Expenditure for hemodialysis: a study among patient Attending at hospitals of Pokhara metropolitan city, Nepal. JHAS. 2019;9(1):46–50.
-
- Adithyan G. S., Mariappan M. Factors that determine deceased organ transplantation in India. Indian Journal of Transplant. 2017;11(2):26–30.
-
- Nizam N., Mazhar F., Abbas K., et al. Kidney swap in Pakistan: experience at the Sindh Institute of Urology and transplantation. Experimental and Clinical Transplant. 2017;15(Suppl 1):76–78. - PubMed
-
- Grady D., O’Connor A. The kidney swap: adventures in saving lives. New York Times on the Web. 2004;F1:F6–F7. - PubMed
-
- Jha P., Nandwani A., Kher A., et al. ABO-incompatible renal transplantation: the journey so far on a road less traveled. Indian Journal of Transplantation. 2018;12(3):177–181. doi: 10.4103/ijot.ijot_23_18. - DOI
-
- Harris D., Davies S. J., Finkelstein F. O., et al. The second Global Kidney Health Summit outputs: developing a strategic plan to increase access to integrated end-stage kidney disease care worldwide. Kidney International Supplements. 2020;10(1):e1–e2. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2019.09.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed