Causes of genome instability: the effect of low dose chemical exposures in modern society
Sabine A S Langie 1, Gudrun Koppen 1, Daniel Desaulniers 2, Fahd Al-Mulla 3, Rabeah Al-Temaimi 3, Amedeo Amedei 4, Amaya Azqueta 5, William H Bisson 6, Dustin G Brown 7, Gunnar Brunborg 8, Amelia K Charles 9, Tao Chen 10, Annamaria Colacci 11, Firouz Darroudi 12, Stefano Forte 13, Laetitia Gonzalez 14, Roslida A Hamid 15, Lisbeth E Knudsen 16, Luc Leyns 14, Adela Lopez de Cerain Salsamendi 5, Lorenzo Memeo 13, Chiara Mondello 17, Carmel Mothersill 18, Ann-Karin Olsen 8, Sofia Pavanello 19, Jayadev Raju 20, Emilio Rojas 21, Rabindra Roy 22, Elizabeth P Ryan 7, Patricia Ostrosky-Wegman 21, Hosni K Salem 23, A Ivana Scovassi 17, Neetu Singh 24, Monica Vaccari 11, Frederik J Van Schooten 25, Mahara Valverde 21, Jordan Woodrick 22, Luoping Zhang 26, Nik van Larebeke 27, Micheline Kirsch-Volders 14, Andrew R Collins 28
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Environmental Risk and Health Unit, Flemish Institute for Technological Research (VITO), Boeretang 200, 2400 Mol, Belgium, Health Canada, Environmental Health Sciences and Research Bureau, Environmental Health Centre, Ottawa, Ontario K1A0K9, Canada, Department of Pathology, Kuwait University, Safat 13110, Kuwait, Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, University of Firenze, Florence 50134, Italy, Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Navarra, Pamplona 31009, Spain, Environmental and Molecular Toxicology, Environmental Health Sciences Center, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA, Department of Environmental and Radiological Health Sciences/Food Science and Human Nutrition, College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Colorado State University/Colorado School of Public Health, Fort Collins, CO 80523-1680, USA, Department of Chemicals and Radiation, Division of Environmental Medicine, Norwegian Institute of Public Health, PO Box 4404, N-0403 Oslo, Norway, Hopkins Building, School of Biological Sciences, University of Reading, Reading, Berkshire RG6 6UB, UK, Division of Genetic and Molecular Toxicology, National Center for Toxicological Research, U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Jefferson, AR 72079, USA, Center for Environmental Carcinogenesis and Risk Assessment, Environmental Protection and Health Prevention Agency, Bologna 40126, Italy, Human and Environmental Safety Research, Department of Health Sciences, College of North Atlantic, Doha, State of Qatar, Mediterranean Institute of Oncology, 95029 Viagrande, Italy, Laboratory for Cell Genetics, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels 1050, Belgium, Department of Biomedical Science, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University Putra, Serdang 43400, Selangor, Malaysia, University of Copenhagen, Department of Public Health, Copenhagen 1353, Denmark, Institute of Molecular Genetics, National Research Council, Pavia 27100, Italy, Medical Phys
- 2Health Canada, Environmental Health Sciences and Research Bureau, Environmental Health Centre, Ottawa, Ontario K1A0K9, Canada.
- 3Department of Pathology, Kuwait University, Safat 13110, Kuwait.
- 4Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, University of Firenze, Florence 50134, Italy.
- 5Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Navarra, Pamplona 31009, Spain.
- 6Environmental and Molecular Toxicology, Environmental Health Sciences Center, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA.
- 7Department of Environmental and Radiological Health Sciences/Food Science and Human Nutrition, College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Colorado State University/Colorado School of Public Health, Fort Collins, CO 80523-1680, USA.
- 8Department of Chemicals and Radiation, Division of Environmental Medicine, Norwegian Institute of Public Health, PO Box 4404, N-0403 Oslo, Norway.
- 9Hopkins Building, School of Biological Sciences, University of Reading, Reading, Berkshire RG6 6UB, UK.
- 10Division of Genetic and Molecular Toxicology, National Center for Toxicological Research, U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Jefferson, AR 72079, USA.
- 11Center for Environmental Carcinogenesis and Risk Assessment, Environmental Protection and Health Prevention Agency, Bologna 40126, Italy.
- 12Human and Environmental Safety Research, Department of Health Sciences, College of North Atlantic, Doha, State of Qatar.
- 13Mediterranean Institute of Oncology, 95029 Viagrande, Italy.
- 14Laboratory for Cell Genetics, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels 1050, Belgium.
- 15Department of Biomedical Science, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University Putra, Serdang 43400, Selangor, Malaysia.
- 16University of Copenhagen, Department of Public Health, Copenhagen 1353, Denmark.
- 17Institute of Molecular Genetics, National Research Council, Pavia 27100, Italy.
- 18Medical Physics & Applied Radiation Sciences, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario L8S4L8, Canada.
- 19Department of Cardiac, Thoracic and Vascular Sciences, Unit of Occupational Medicine, University of Padova, Padova 35128, Italy.
- 20Toxicology Research Division, Bureau of Chemical Safety Food Directorate, Health Products and Food Branch Health Canada, Ottawa, Ontario K1A0K9, Canada.
- 21Departamento de Medicina Genomica y Toxicologia Ambiental, Instituto de Investigaciones Biomedicas, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de México, México CP 04510, México.
- 22Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC 20057, USA.
- 23Urology Department, kasr Al-Ainy School of Medicine, Cairo University, El Manial, Cairo 12515, Egypt.
- 24Centre for Advanced Research, King George's Medical University, Chowk, Lucknow 226003, Uttar Pradesh, India.
- 25Department of Toxicology, NUTRIM School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism, Maastricht University, 6200MD, PO Box 61, Maastricht, The Netherlands.
- 26Division of Environmental Health Sciences, School of Public Health, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720-7360, USA.
- 27Laboratory for Analytical and Environmental Chemistry, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels 1050, Belgium, Study Centre for Carcinogenesis and Primary Prevention of Cancer, Ghent University, Ghent 9000, Belgium;
- 28Department of Nutrition, University of Oslo, Oslo 0316, Norway.
Abstract
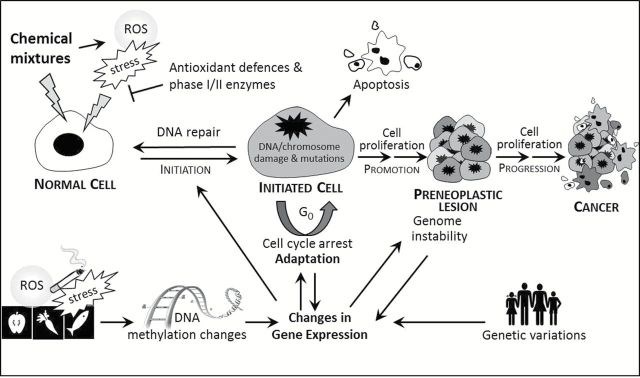
Genome instability is a prerequisite for the development of cancer. It occurs when genome maintenance systems fail to safeguard the genome's integrity, whether as a consequence of inherited defects or induced via exposure to environmental agents (chemicals, biological agents and radiation). Thus, genome instability can be defined as an enhanced tendency for the genome to acquire mutations; ranging from changes to the nucleotide sequence to chromosomal gain, rearrangements or loss. This review raises the hypothesis that in addition to known human carcinogens, exposure to low dose of other chemicals present in our modern society could contribute to carcinogenesis by indirectly affecting genome stability. The selected chemicals with their mechanisms of action proposed to indirectly contribute to genome instability are: heavy metals (DNA repair, epigenetic modification, DNA damage signaling, telomere length), acrylamide (DNA repair, chromosome segregation), bisphenol A (epigenetic modification, DNA damage signaling, mitochondrial function, chromosome segregation), benomyl (chromosome segregation), quinones (epigenetic modification) and nano-sized particles (epigenetic pathways, mitochondrial function, chromosome segregation, telomere length). The purpose of this review is to describe the crucial aspects of genome instability, to outline the ways in which environmental chemicals can affect this cancer hallmark and to identify candidate chemicals for further study. The overall aim is to make scientists aware of the increasing need to unravel the underlying mechanisms via which chemicals at low doses can induce genome instability and thus promote carcinogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
Hu Z, Brooks SA, Dormoy V, Hsu CW, Hsu HY, Lin LT, Massfelder T, Rathmell WK, Xia M, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Amedei A, Brown DG, Prudhomme KR, Colacci A, Hamid RA, Mondello C, Raju J, Ryan EP, Woodrick J, Scovassi AI, Singh N, Vaccari M, Roy R, Forte S, Memeo L, Salem HK, Lowe L, Jensen L, Bisson WH, Kleinstreuer N.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S184-202. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv036.PMID: 26106137 Free PMC article. Review.
Disruptive environmental chemicals and cellular mechanisms that confer resistance to cell death.
Narayanan KB, Ali M, Barclay BJ, Cheng QS, D'Abronzo L, Dornetshuber-Fleiss R, Ghosh PM, Gonzalez Guzman MJ, Lee TJ, Leung PS, Li L, Luanpitpong S, Ratovitski E, Rojanasakul Y, Romano MF, Romano S, Sinha RK, Yedjou C, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Amedei A, Brown DG, Ryan EP, Colacci A, Hamid RA, Mondello C, Raju J, Salem HK, Woodrick J, Scovassi AI, Singh N, Vaccari M, Roy R, Forte S, Memeo L, Kim SY, Bisson WH, Lowe L, Park HH.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S89-110. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv032.PMID: 26106145 Free PMC article. Review.
Goodson WH 3rd, Lowe L, Carpenter DO, Gilbertson M, Manaf Ali A, Lopez de Cerain Salsamendi A, Lasfar A, Carnero A, Azqueta A, Amedei A, Charles AK, Collins AR, Ward A, Salzberg AC, Colacci A, Olsen AK, Berg A, Barclay BJ, Zhou BP, Blanco-Aparicio C, Baglole CJ, Dong C, Mondello C, Hsu CW, Naus CC, Yedjou C, Curran CS, Laird DW, Koch DC, Carlin DJ, Felsher DW, Roy D, Brown DG, Ratovitski E, Ryan EP, Corsini E, Rojas E, Moon EY, Laconi E, Marongiu F, Al-Mulla F, Chiaradonna F, Darroudi F, Martin FL, Van Schooten FJ, Goldberg GS, Wagemaker G, Nangami GN, Calaf GM, Williams G, Wolf GT, Koppen G, Brunborg G, Lyerly HK, Krishnan H, Ab Hamid H, Yasaei H, Sone H, Kondoh H, Salem HK, Hsu HY, Park HH, Koturbash I, Miousse IR, Scovassi AI, Klaunig JE, Vondráček J, Raju J, Roman J, Wise JP Sr, Whitfield JR, Woodrick J, Christopher JA, Ochieng J, Martinez-Leal JF, Weisz J, Kravchenko J, Sun J, Prudhomme KR, Narayanan KB, Cohen-Solal KA, Moorwood K, Gonzalez L, Soucek L, Jian L, D'Abronzo LS, Lin LT, Li L, Gulliver L, McCawley LJ, Memeo L, Vermeulen L, Leyns L, Zhang L, Valverde M, Khatami M, Romano MF, Chapellier M, Williams MA, Wade M, Manjili MH, Lleonart ME, Xia M, Gonzalez MJ, Karamouzis …See abstract for full author list ➔Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S254-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv039.PMID: 26106142 Free PMC article. Review.
Engström W, Darbre P, Eriksson S, Gulliver L, Hultman T, Karamouzis MV, Klaunig JE, Mehta R, Moorwood K, Sanderson T, Sone H, Vadgama P, Wagemaker G, Ward A, Singh N, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Amedei A, Colacci AM, Vaccari M, Mondello C, Scovassi AI, Raju J, Hamid RA, Memeo L, Forte S, Roy R, Woodrick J, Salem HK, Ryan EP, Brown DG, Bisson WH.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S38-60. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv030.PMID: 26106143 Free PMC article. Review.
Robey RB, Weisz J, Kuemmerle NB, Salzberg AC, Berg A, Brown DG, Kubik L, Palorini R, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Colacci A, Mondello C, Raju J, Woodrick J, Scovassi AI, Singh N, Vaccari M, Roy R, Forte S, Memeo L, Salem HK, Amedei A, Hamid RA, Williams GP, Lowe L, Meyer J, Martin FL, Bisson WH, Chiaradonna F, Ryan EP.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S203-31. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv037.PMID: 26106140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
Histone Demethylase Modulation: Epigenetic Strategy to Combat Cancer Progression.
Srivastava R, Singh R, Jauhari S, Lodhi N, Srivastava R.Epigenomes. 2023 May 17;7(2):10. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes7020010.PMID: 37218871 Free PMC article. Review.
Epigenome-wide association study of serum folate in maternal peripheral blood leukocytes.
Fragoso-Bargas N, Page CM, Joubert BR, London SJ, Lee-Ødegård S, Opsahl JO, Sletner L, Jenum AK, Qvigstad E, Prasad RB, Moen GH, Birkeland KI, Sommer C.Epigenomics. 2023 Jan;15(1):39-52. doi: 10.2217/epi-2022-0427. Epub 2023 Mar 28.PMID: 36974632
HIV Infection, Chromosome Instability, and Micronucleus Formation.
Ellwanger JH, Kulmann-Leal B, Ziliotto M, Chies JAB.Viruses. 2023 Jan 4;15(1):155. doi: 10.3390/v15010155.PMID: 36680195 Free PMC article. Review.
Muciño-Hernández G, Acevo-Rodríguez PS, Cabrera-Benitez S, Guerrero AO, Merchant-Larios H, Castro-Obregón S.J Cell Sci. 2023 Jan 1;136(1):jcs260563. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260563. Epub 2023 Jan 12.PMID: 36633090 Free PMC article.
A CRISPR/Cas9-based method for targeted DNA methylation enables cancer initiation in B lymphocytes.
Katayama S, Shiraishi K, Gorai N, Andou M.Adv Genet (Hoboken). 2021 Mar 11;2(1):e10040. doi: 10.1002/ggn2.10040. eCollection 2021 Mar.PMID: 36618443 Free PMC article.