The effect of environmental chemicals on the tumor microenvironment
Stephanie C Casey 1, Monica Vaccari 2, Fahd Al-Mulla 3, Rabeah Al-Temaimi 3, Amedeo Amedei 4, Mary Helen Barcellos-Hoff 5, Dustin G Brown 6, Marion Chapellier 7, Joseph Christopher 8, Colleen S Curran 9, Stefano Forte 10, Roslida A Hamid 11, Petr Heneberg 12, Daniel C Koch 1, P K Krishnakumar 13, Ezio Laconi 14, Veronique Maguer-Satta 7, Fabio Marongiu 14, Lorenzo Memeo 15, Chiara Mondello 16, Jayadev Raju 17, Jesse Roman 18, Rabindra Roy 19, Elizabeth P Ryan 6, Sandra Ryeom 20, Hosni K Salem 21, A Ivana Scovassi 16, Neetu Singh 22, Laura Soucek 23, Louis Vermeulen 24, Jonathan R Whitfield 23, Jordan Woodrick 19, Annamaria Colacci 2, William H Bisson 25, Dean W Felsher 26
Affiliations
Affiliations
- 1Division of Oncology, Departments of Medicine and Pathology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA, Center for Environmental Carcinogenesis and Risk Assessment, Environmental Protection and Health Prevention Agency, 40126 Bologna, Italy, Department of Pathology, Kuwait University, 13110 Safat, Kuwait, Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, University of Firenze, 50134 Florence, Italy, Department of Radiation Oncology, NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY 10016, USA, Department of Environmental and Radiological Health Sciences, Colorado State University/ Colorado School of Public Health, Fort Collins, CO 80523-1680, USA, Centre De Recherche En Cancerologie De Lyon, U1052-UMR5286, Université de Lyon, 69007 Lyon, France, Cancer Research UK, Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge, Robinson Way, CB2 0RE Cambridge, UK, School of Medicine and Public Health, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53705, USA, Mediterranean Institute of Oncology, 95029 Viagrande, Italy, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, 43400 Selangor, Malaysia, Charles University in Prague, Third Faculty of Medicine, 100 00 Prague 10, Czech Republic, Center for Environment and Water, Research Institute, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran 31261, Saudi Arabia, Department of Science and Biomedical Technology, University of Cagliari, 09124 Cagliari, Italy, Pathology Unit, Mediterranean Institute of Oncology, 95029 Viagrande, Italy, Institute of Molecular Genetics, National Research Council, 27100 Pavia, Italy, Regulatory Toxicology Research Division, Bureau of Chemical Safety Food Directorate, Health Products and Food Branch Health Canada, Ottawa, Ontario K1A0K9, Canada, Department of Medicine, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY 40202, USA, Molecular Oncology Program, Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington DC 20057, USA, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine
- 2Center for Environmental Carcinogenesis and Risk Assessment, Environmental Protection and Health Prevention Agency, 40126 Bologna, Italy.
- 3Department of Pathology, Kuwait University, 13110 Safat, Kuwait.
- 4Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, University of Firenze, 50134 Florence, Italy.
- 5Department of Radiation Oncology, NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY 10016, USA.
- 6Department of Environmental and Radiological Health Sciences, Colorado State University/ Colorado School of Public Health, Fort Collins, CO 80523-1680, USA.
- 7Centre De Recherche En Cancerologie De Lyon, U1052-UMR5286, Université de Lyon, 69007 Lyon, France.
- 8Cancer Research UK, Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge, Robinson Way, CB2 0RE Cambridge, UK.
- 9School of Medicine and Public Health, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53705, USA.
- 10Mediterranean Institute of Oncology, 95029 Viagrande, Italy.
- 11Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, 43400 Selangor, Malaysia.
- 12Charles University in Prague, Third Faculty of Medicine, 100 00 Prague 10, Czech Republic.
- 13Center for Environment and Water, Research Institute, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran 31261, Saudi Arabia.
- 14Department of Science and Biomedical Technology, University of Cagliari, 09124 Cagliari, Italy.
- 15Pathology Unit, Mediterranean Institute of Oncology, 95029 Viagrande, Italy.
- 16Institute of Molecular Genetics, National Research Council, 27100 Pavia, Italy.
- 17Regulatory Toxicology Research Division, Bureau of Chemical Safety Food Directorate, Health Products and Food Branch Health Canada, Ottawa, Ontario K1A0K9, Canada.
- 18Department of Medicine, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY 40202, USA.
- 19Molecular Oncology Program, Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington DC 20057, USA.
- 20University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
- 21Urology Department, Kasr Al-Ainy School of Medicine, Cairo University, El Manial, Cairo 11562, Egypt.
- 22Centre for Advanced Research, King George's Medical University, Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh 226003, India.
- 23Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO) and Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA), 08035 Barcelona, Spain.
- 24Center for Experimental Molecular Medicine (CEMM), Academic Medical Center (AMC), Meibergdreef 9, 1105 AZ, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 25Department of Environmental and Molecular Toxicology, Environmental Health Sciences Center, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA, and.
- 26Division of Oncology, Departments of Medicine and Pathology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA dfelsher@stanford.edu.
Abstract
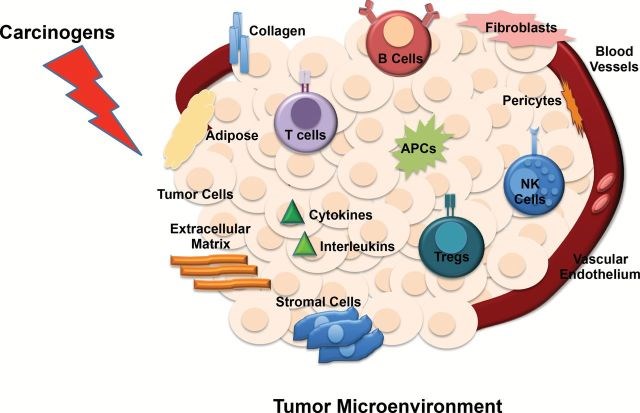
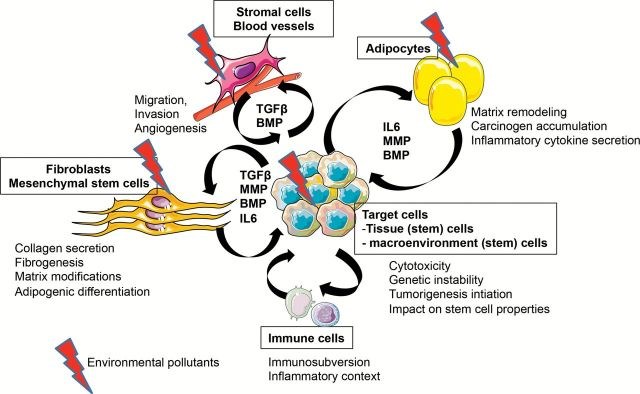
Potentially carcinogenic compounds may cause cancer through direct DNA damage or through indirect cellular or physiological effects. To study possible carcinogens, the fields of endocrinology, genetics, epigenetics, medicine, environmental health, toxicology, pharmacology and oncology must be considered. Disruptive chemicals may also contribute to multiple stages of tumor development through effects on the tumor microenvironment. In turn, the tumor microenvironment consists of a complex interaction among blood vessels that feed the tumor, the extracellular matrix that provides structural and biochemical support, signaling molecules that send messages and soluble factors such as cytokines. The tumor microenvironment also consists of many host cellular effectors including multipotent stromal cells/mesenchymal stem cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cell precursors, antigen-presenting cells, lymphocytes and innate immune cells. Carcinogens can influence the tumor microenvironment through effects on epithelial cells, the most common origin of cancer, as well as on stromal cells, extracellular matrix components and immune cells. Here, we review how environmental exposures can perturb the tumor microenvironment. We suggest a role for disrupting chemicals such as nickel chloride, Bisphenol A, butyltins, methylmercury and paraquat as well as more traditional carcinogens, such as radiation, and pharmaceuticals, such as diabetes medications, in the disruption of the tumor microenvironment. Further studies interrogating the role of chemicals and their mixtures in dose-dependent effects on the tumor microenvironment could have important general mechanistic implications for the etiology and prevention of tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
Hu Z, Brooks SA, Dormoy V, Hsu CW, Hsu HY, Lin LT, Massfelder T, Rathmell WK, Xia M, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Amedei A, Brown DG, Prudhomme KR, Colacci A, Hamid RA, Mondello C, Raju J, Ryan EP, Woodrick J, Scovassi AI, Singh N, Vaccari M, Roy R, Forte S, Memeo L, Salem HK, Lowe L, Jensen L, Bisson WH, Kleinstreuer N.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S184-202. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv036.PMID: 26106137 Free PMC article. Review.
Disruptive environmental chemicals and cellular mechanisms that confer resistance to cell death.
Narayanan KB, Ali M, Barclay BJ, Cheng QS, D'Abronzo L, Dornetshuber-Fleiss R, Ghosh PM, Gonzalez Guzman MJ, Lee TJ, Leung PS, Li L, Luanpitpong S, Ratovitski E, Rojanasakul Y, Romano MF, Romano S, Sinha RK, Yedjou C, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Amedei A, Brown DG, Ryan EP, Colacci A, Hamid RA, Mondello C, Raju J, Salem HK, Woodrick J, Scovassi AI, Singh N, Vaccari M, Roy R, Forte S, Memeo L, Kim SY, Bisson WH, Lowe L, Park HH.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S89-110. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv032.PMID: 26106145 Free PMC article. Review.
Causes of genome instability: the effect of low dose chemical exposures in modern society.
Langie SA, Koppen G, Desaulniers D, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Amedei A, Azqueta A, Bisson WH, Brown DG, Brunborg G, Charles AK, Chen T, Colacci A, Darroudi F, Forte S, Gonzalez L, Hamid RA, Knudsen LE, Leyns L, Lopez de Cerain Salsamendi A, Memeo L, Mondello C, Mothersill C, Olsen AK, Pavanello S, Raju J, Rojas E, Roy R, Ryan EP, Ostrosky-Wegman P, Salem HK, Scovassi AI, Singh N, Vaccari M, Van Schooten FJ, Valverde M, Woodrick J, Zhang L, van Larebeke N, Kirsch-Volders M, Collins AR.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S61-88. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv031.PMID: 26106144 Free PMC article. Review.
Goodson WH 3rd, Lowe L, Carpenter DO, Gilbertson M, Manaf Ali A, Lopez de Cerain Salsamendi A, Lasfar A, Carnero A, Azqueta A, Amedei A, Charles AK, Collins AR, Ward A, Salzberg AC, Colacci A, Olsen AK, Berg A, Barclay BJ, Zhou BP, Blanco-Aparicio C, Baglole CJ, Dong C, Mondello C, Hsu CW, Naus CC, Yedjou C, Curran CS, Laird DW, Koch DC, Carlin DJ, Felsher DW, Roy D, Brown DG, Ratovitski E, Ryan EP, Corsini E, Rojas E, Moon EY, Laconi E, Marongiu F, Al-Mulla F, Chiaradonna F, Darroudi F, Martin FL, Van Schooten FJ, Goldberg GS, Wagemaker G, Nangami GN, Calaf GM, Williams G, Wolf GT, Koppen G, Brunborg G, Lyerly HK, Krishnan H, Ab Hamid H, Yasaei H, Sone H, Kondoh H, Salem HK, Hsu HY, Park HH, Koturbash I, Miousse IR, Scovassi AI, Klaunig JE, Vondráček J, Raju J, Roman J, Wise JP Sr, Whitfield JR, Woodrick J, Christopher JA, Ochieng J, Martinez-Leal JF, Weisz J, Kravchenko J, Sun J, Prudhomme KR, Narayanan KB, Cohen-Solal KA, Moorwood K, Gonzalez L, Soucek L, Jian L, D'Abronzo LS, Lin LT, Li L, Gulliver L, McCawley LJ, Memeo L, Vermeulen L, Leyns L, Zhang L, Valverde M, Khatami M, Romano MF, Chapellier M, Williams MA, Wade M, Manjili MH, Lleonart ME, Xia M, Gonzalez MJ, Karamouzis …See abstract for full author list ➔Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S254-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv039.PMID: 26106142 Free PMC article. Review.
Environmental immune disruptors, inflammation and cancer risk.
Thompson PA, Khatami M, Baglole CJ, Sun J, Harris SA, Moon EY, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Brown DG, Colacci A, Mondello C, Raju J, Ryan EP, Woodrick J, Scovassi AI, Singh N, Vaccari M, Roy R, Forte S, Memeo L, Salem HK, Amedei A, Hamid RA, Lowe L, Guarnieri T, Bisson WH.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S232-53. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv038.PMID: 26106141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
Della Rocca Y, Traini EM, Diomede F, Fonticoli L, Trubiani O, Paganelli A, Pizzicannella J, Marconi GD.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 10;15(3):908. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030908.PMID: 36986769 Free PMC article. Review.
Colacci A, Corvi R, Ohmori K, Paparella M, Serra S, Da Rocha Carrico I, Vasseur P, Jacobs MN.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 16;24(6):5659. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065659.PMID: 36982734 Free PMC article. Review.
Role of tumor microenvironment in cancer progression and therapeutic strategy.
Wang Q, Shao X, Zhang Y, Zhu M, Wang FXC, Mu J, Li J, Yao H, Chen K.Cancer Med. 2023 May;12(10):11149-11165. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5698. Epub 2023 Feb 21.PMID: 36807772 Free PMC article. Review.
Almansour NM.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jan 25;9:836417. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.836417. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35145999 Free PMC article. Review.
Guyot B, Lefort S, Voeltzel T, Pécheur EI, Maguer-Satta V.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 3;9:787989. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.787989. eCollection 2021.PMID: 35047500 Free PMC article. Review.