Robot-assisted urological surgery in the Middle East: Where are we and how far can we go?
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Urology, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- Department of Urology, Faculty of Medicine, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt.
- Department of Surgery, Urology Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
Abstract
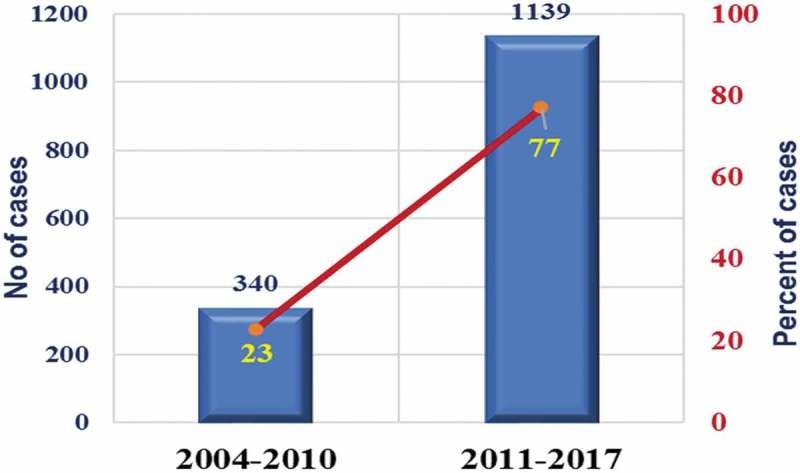
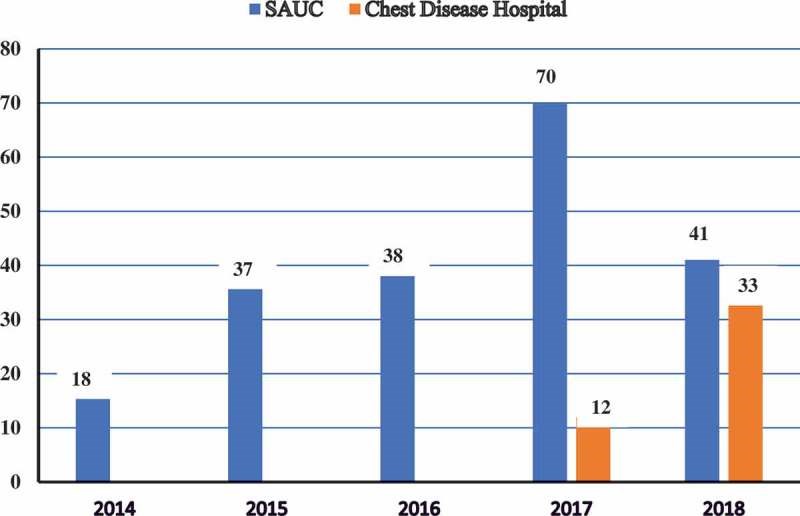
Objectives: To evaluate robot-assisted surgery (RAS) in Urology in the Middle East, and its status and future perspectives. Methods: A Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (MEDLINE) search was performed using the following keywords: 'robotics', 'robot-assisted surgery', 'laparoscopy', at first with each specific procedure name, such as radical cystectomy, followed by 'Middle East' and country names. All abstracts and articles in English that adhered to the scope of the current issue were selected, giving special consideration to relevant landmark articles and those describing trends and the future of RAS in Urology. Results: Only a few index case reports characterised RAS in the Middle East. The Middle East possess only 1% of the da Vinci® Surgical Systems (Intuitive Surgical Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) installed worldwide, including 19 in Saudi Arabia; six in Qatar; two in each of Kuwait and Lebanon; three in the United Arab Emirates; and only one in Egypt. The total number of RAS performed in the Middle East is low compared to Europe and the USA. Many countries in the Middle East still lack surgical robots despite having the expertise and appropriate caseload, whilst others seem not to utilise the surgical robot at a suitable rate, as reflected by the sparse number of operated cases and outgoing publications. There are major differences in RAS availability, usage, and perception according to the geographical place of practice and acceptance of robots by surgeons and patients. Conclusion: RAS in Urology continues to grow in the Middle East, with increasing caseloads and diversity of operated cases. Acceptance of robots by Middle East surgeons is significantly increasing. Abbreviations: 3D: three-dimensional; KSA: Kingdom Saudi Arabia;MIS: minimally invasive surgery; RAA: robot-assisted adrenalectomy; RAP: robot-assisted pyeloplasty; (O)(RA)PN: (open) (robot-assisted) partial nephrectomy; RAS: robot-assisted surgery; (O)(RA)RC: (open) (robot-assisted) radical cystectomy; (RA)RP: (robot-assisted) radical prostatectomy; SAUC: Sabah Al-Ahmad Urology Center.
Keywords: Middle East; Minimally invasive surgery; radical cystectomy; radical nephrectomy; radical prostatectomy; robot-assisted surgery.
Figures
Similar articles
Expanding the indications of robotic surgery in urology: A systematic review of the literature.
Pal RP, Koupparis AJ.Arab J Urol. 2018 Aug 7;16(3):270-284. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2018.05.005. eCollection 2018 Sep.PMID: 30147957 Free PMC article. Review.
Comparative analysis of global practice patterns in urologic robot-assisted surgery.
Yuh BE, Hussain A, Chandrasekhar R, Bienko M, Piacente P, Wilding G, Menon M, Peabody J, Guru KA.J Endourol. 2010 Oct;24(10):1637-44. doi: 10.1089/end.2010.0024.PMID: 20818990
The development of robotic surgery in the Middle East.
Rabah DM, Al-Abdin OZ.Arab J Urol. 2012 Mar;10(1):10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2011.12.001. Epub 2012 Jan 26.PMID: 26557999 Free PMC article. Review.
The age of robotic surgery - Is laparoscopy dead?
Schwaibold H, Wiesend F, Bach C.Arab J Urol. 2018 Jul 30;16(3):262-269. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2018.07.003. eCollection 2018 Sep.PMID: 30140462 Free PMC article. Review.
From Leonardo to da Vinci: the history of robot-assisted surgery in urology.
Yates DR, Vaessen C, Roupret M.BJU Int. 2011 Dec;108(11):1708-13; discussion 1714. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10576.x. Epub 2011 Sep 27.PMID: 21951677
Cited by
Saudi Urological Association consensus guidelines on the use of robotic surgery in urology.
Azhar RA, Rabah D, Alenizi AM, Alammari A, Alasker A, Alqahtani AA, Alsaikhan BH, Alyami FA, Alzahrani HM, Alothman KI, Moazin MS, Alhgbani M, Baghdadi M, Alotaibi MF.Urol Ann. 2022 Jul-Sep;14(3):199-204. doi: 10.4103/ua.ua_46_22. Epub 2022 Jul 18.PMID: 36117790 Free PMC article. Review.
Al-Thani H, Al-Thani N, Al-Sulaiti M, Tabeb A, Asim M, El-Menyar A.Front Surg. 2022 Mar 3;9:848565. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.848565. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35310427 Free PMC article.
Market potentials of robotic systems in medical science: analysis of the Avatera robotic system.
Liatsikos E, Tsaturyan A, Kyriazis I, Kallidonis P, Manolopoulos D, Magoutas A.World J Urol. 2022 Jan;40(1):283-289. doi: 10.1007/s00345-021-03809-z. Epub 2021 Aug 23.PMID: 34424374 Free PMC article.
Labban M, Bulbul M, Wazzan W, Khauli R, El Hajj A.Arab J Urol. 2020 Aug 26;19(2):152-158. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2020.1814184.PMID: 34104490 Free PMC article.
Aldousari S, Yaiesh S, Alkandari O.Can Urol Assoc J. 2021 Sep;15(9):E458-E464. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.6880.PMID: 33591897 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Khan MS, Elhage O, Challacombe B, et al. Long-term outcomes of robot-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2013;64:219–224. - PubMed
-
- Yuh B, Artibani W, Heidenreich A, et al. The role of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection in the management of high-risk prostate cancer: a systematic review. Eur Urol. 2014;65:918–927. - PubMed
-
- Novara G, Catto JW, Wilson T, et al. Systematic review and cumulative analysis of perioperative outcomes and complications after robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Eur Urol. 2015;67:376–401. - PubMed
-
- Bentas W, Wolfram M, Bräutigam R, et al. Vinci robot assisted Anderson-Hynes dismembered pyeloplasty: technique and 1-year follow-up. World J Urol. 2003;21:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Gettman MT, Peschel R, Neururer R, et al. A comparison of laparoscopic pyeloplasty performed with the daVinci robotic system versus standard laparoscopic techniques: initial clinical results. Eur Urol. 2002;42:453–457. - PubMed
-
- Mettler L, Schollmeyer T, Boggess JF, et al. Robotic assistance in gynecological oncology. Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20:581–589. - PubMed
-
- Nezhat C, Lavie O, Lemyre M, et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery in gynecology: scientific dream or reality? Fertil Steril. 2009;91:2620–2622. - PubMed
-
- Yuh BE, Hussain A, Chandrasekhar R, et al. Comparative Analysis of global practice patterns in urologic robot-assisted surgery. J Endourol. 2010;24(10):1637–1644. - PubMed
-
- Intuitive Surgical da Vinci’s manufacturer [cited 2018 June] Available from: https://www.scribd.com/document/290566330/Intuitive-Surgical-Investor-Pr...
-
- Hemal AK, Abol-Enein H, Tewari A, et al. Robotic radical cystectomy and urinary diversion in the management of bladder cancer. Urol Clin North Am. 2004;31:719–729. - PubMed
-
- El-Tabey NA, Shoma AM. Port site metastases after robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy. Urology. 2005;66:1110.e1–1110.e3. - PubMed
-
- Atallah MM, Othman MM. Robotic laparoscopic radical cystectomy inhalational versus total intravenous anesthesia: a pilot study. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2009;20:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Al-Alao O, Peyrat J, Abinahed J, et al. Development of robot-assisted surgery in Qatar - Camera Ready Copy. 6th Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics; 2013: 89–90. DOI:10.13140/RG.2.1.3060.9685 - DOI
-
- Aldousari S, Almarzouq A, Al-Yousef RJ, et al. Robotic surgery in Kuwait: the first experience. Can Urol Assoc J. 2015;9(Suppl. 2):S77.
-
- Aldousari S, Almarzouq A, Al-Yousef RJ, et al. Robotic surgery in Kuwait: the first experience. Conference: Canadian Urological Association 2015, Ottawa [cited 2018 June] Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280133601_UP0511
-
- Aldousari S, Abul F, Khajah M, et al. Does a standardized algorithm for managing patients post-robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy improve recovery? Experience with the optimized surgical journey. Eur Urol Suppl. 2016;15:293 [Abstract PE78].
-
- Park SY, Jeong W, Ham WS, et al. Initial experience of robotic nephron-ureterectomy: a hybrid-port technique. BJU Int. 2009;104:1718–1721. - PubMed
-
- Montorsi F, Wilson TG, Rosen RC, et al. Best practices in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: recommendations of the Pasadena consensus panel. Eur Urol. 2012;62:368–381. - PubMed
-
- Tewari A, Sooriakumaran P, Bloch DA, et al. Wiklund P Surgical margin and perioperative complication rates of primary surgical treatments for prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing retropubic, laparoscopic, and robotic prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Diaz M, Peabody JO, Kapoor V, et al. Oncologic outcomes at 10 years following robotic radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2015;67:1168–1176. - PubMed
-
- Ficarra V, Novara G, Ahlering TE, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting potency rates after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:418–430. - PubMed
-
- Ficarra V, Rossanese M, Gnech M, et al. Outcomes and limitations of laparoscopic and robotic partial nephrectomy. Curr Opin Urol. 2014;24:441–447. - PubMed
-
- Tanagho YS, Kaouk JH, Allaf ME, et al. Perioperative complications of robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: analysis of 886 patients at 5 United States centers. Urology. 2013;81:573–579. - PubMed
-
- Khalifeh A, Kaouk JH, Bhayani S, et al. Positive surgical margins in robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: a multi-institutional analysis of oncologic outcomes (leave no tumor behind). J Urol. 2013;190:1674–1679. - PubMed
-
- Khalifeh A, Autorino R, Eyraud R, et al. Three-year oncologic and renal functional outcomes after robot-assisted partial nephrectomy. Eur Urol. 2013;64:744–750. - PubMed
-
- Masson-Lecomte A, Bensalah K, Seringe E, et al. A prospective comparison of surgical and pathological outcomes obtained after robot-assisted or pure laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in moderate to complex renal tumors: results from a French multicenter collaborative study. BJU Int. 2013;111:256–263. - PubMed
-
- Parekh DJ, Reis IM, Castle EP, et al. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy in patients with bladder cancer (RAZOR): an open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391:2525–2536. - PubMed
-
- Hayn MH, Hussain A, Mansour AM, et al. The learning curve of robot-assisted radical cystectomy: results from the international robotic cystectomy consortium. Eur Urol. 2010;58:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Johar RS, Hayn MH, Stegemann AP, et al. Complications after robot-assisted radical cystectomy: results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. Eur Urol. 2013;64:52–57. - PubMed
-
- Dasgupta P, Rimington P, Murphy D, et al. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder cancer and 2-year follow-up. BJU Int. 2007;99(Suppl. 4):P35.
-
- Brunaud L, Ayav A, Zarnegar R, et al. Prospective evaluation of 100 robotic-assisted unilateral adrenalectomies. Surgery. 2008;144:995–1001. - PubMed
-
- Giulianotti PC, Buchs NC, Addeo P, et al. Robot-assisted adrenalectomy: a technical option for the surgeon? Int J Med Robot. 2011;7:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Brunaud L, Bresler L, Ayav A, et al. Robotic-assisted adrenalectomy: what advantages compared to lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy? Am J Surg. 2008;195:433–438. - PubMed
-
- Menon M, Hemal AK, Tewari A, et al. Nerve-sparing robot-assisted radical cystoprostatectomy and urinary diversion. BJU Int. 2003;92:232–236. - PubMed
-
- Hilal L, Shahait M, Mukherji D, et al. Prostate cancer in the Arab world: a view from the inside. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015;13:505–511. - PubMed
-
- Shahait M, Khauli R, Saoud R, et al. Impact of introducing robotic assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) on surgical volume at a major Middle Eastern institution. Eur Urol Suppl. 2015;14:e1364.
-
- Gupta NP, Nayyar R, Hemal AK, et al. Outcome analysis of robotic pyeloplasty: a large single-center experience. BJU Int. 2010;105:980–983. - PubMed
-
- Nayyar R, Gupta NP, Hemal AK. Robotic management of complicated ureteropelvic junction obstruction. World J Urol. 2010;28:599–602. - PubMed