Knowledge, attitudes and practices of caregivers in relation to oral health of preschool children
Affiliations
Affiliations
Faculty of Dentistry, Kuwait University, Jabriya, Kuwait.
Abstract
Objective: To assess the knowledge, attitudes and practices of caregivers in Kuwait in relation to the oral health of preschool children.
Subjects and methods: Questionnaires with multiple-choice questions were distributed to 334 caregivers of children under the age of 6 years attending vaccination centers in Kuwait. For each question, one of the multiple-choice answers was consistent with the consensus in the pediatric dental literature in relation to early childhood caries prevention, and was considered to be correct. The χ2 test, independent t test, ANOVA, and stepwise linear regression were used to assess the associations between the variables in question and p ≤ 0.05 was accepted as statistically significant.
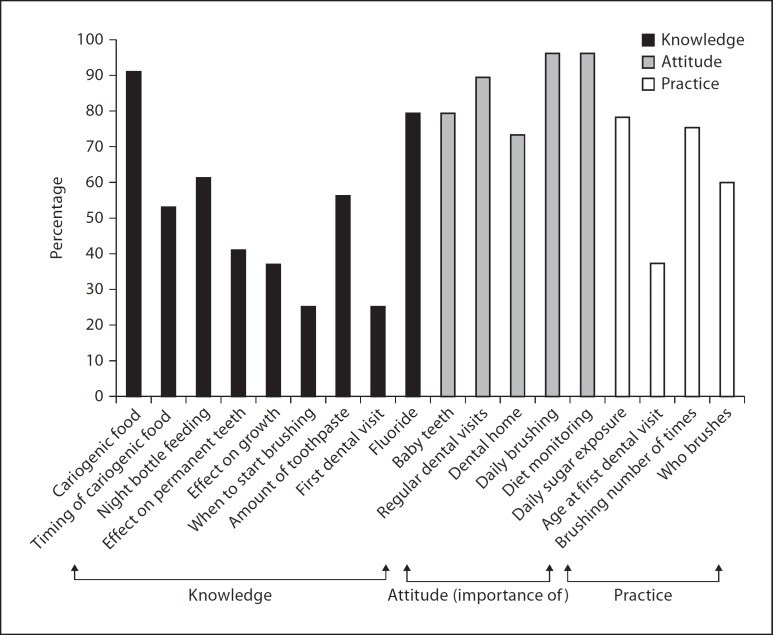
Results: Of the 334 participants, 234 (70%) were between 20 and 40 years of age with a high school diploma or higher degree and had between 2 and 5 children. The mean knowledge score was 4.68 ± 1.87, the mean attitude score was 4.34 ± 0.88 and the mean practice score was 2.45 ± 0.99. Major weaknesses were reported in infant oral health-related concepts. Mothers had better knowledge than other caregivers (p < 0.001). Higher education was significantly associated with better knowledge (p = 0.003) and better practices (p = 0.017). In addition, knowledge, attitude and level of education were positively and significantly associated with practices (p < 0.005).
Conclusions: Our study showed that caregivers had weak knowledge and practice in relation to the oral health of preschool children. Mothers and caregivers with higher education had better knowledge and practices. Education and attitude appeared to be favorable indicators of the caregivers' practices with regard to the oral health of their preschool children.
Figures
Similar articles
Oral health practices and knowledge among parents and hired caregivers.
Alkhubaizi Q, Moule A, Al-Sane M, Sorkin JD.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2018 Dec;19(6):403-410. doi: 10.1007/s40368-018-0372-6. Epub 2018 Oct 12.PMID: 30315536
Parental knowledge and practices regarding their children's oral health in Kuwait.
Alyahya L.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2016 Dec;17(4):267-273.PMID: 28045313
Chan SC, Tsai JS, King NM.Int J Paediatr Dent. 2002 Sep;12(5):322-31. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-263x.2002.00389.x.PMID: 12199891
Impact evaluation of a school-based oral health program: Kuwait National Program.
Alsumait A, ElSalhy M, Behzadi S, Raine KD, Gokiert R, Cor K, Almutawa S, Amin M.BMC Oral Health. 2019 Sep 2;19(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12903-019-0895-1.PMID: 31477082 Free PMC article.
Naidu R, Nunn J, Irwin JD.BMC Oral Health. 2015 Sep 2;15:101. doi: 10.1186/s12903-015-0068-9.PMID: 26328785 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.Rural-urban disparities in knowledge, attitude, and practice toward child oral health among mothers of 9-36-month-old children.
Mishra A, Sharma D, Tripathi GM, Khan TA.J Rural Med. 2023 Jul;18(3):175-181. doi: 10.2185/jrm.2022-043. Epub 2023 Jul 7.PMID: 37448700 Free PMC article.
Balwanth S, Singh S.Health SA. 2023 Mar 3;28:2147. doi: 10.4102/hsag.v28i0.2147. eCollection 2023.PMID: 37064651 Free PMC article.
Alkhtib AO, Mohamed HG.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2023 Jan 12;3(1):e0001228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0001228. eCollection 2023.PMID: 36962836 Free PMC article.
Al Mejmaj DI, Nimbeni SB, Alrashidi RM.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022 Jul-Aug;15(4):407-411. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2409.PMID: 36875969 Free PMC article.
Level of Awareness and Attitude Toward Cerebral Palsy Among Parents in Al-Baha City, Saudi Arabia.
Salih EM, Alghamdi SA, Alghamdi RA, Alghamdi MS, Alzahrani TA.Cureus. 2022 Nov 22;14(11):e31791. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31791. eCollection 2022 Nov.PMID: 36569676 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Ripa LW. Nursing caries: a comprehensive review. Pediatr Dent. 1988;10:268–282. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Policy on early childhood caries (ECC): classifications, consequences, and preventive strategies. Pediatr Dent 2008/ 2009;30:40–43. - PubMed
-
- Williams NJ, Whittle JG, Gatrell AC. The relationship between socio-demographic characteristics and dental health knowledge and attitudes of parents with young children. Br Dent J. 2002;193:651–654. - PubMed
-
- Borssen E, Stecksen-Blicks C. Risk factors for dental caries in 2-year-old children. Swed Dent J. 1998;22:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Stroebe W, Stroebe M. Social Psychology and Health. ed 1. Buckingham: Open University Press; 1995.
-
- Szatko F, Wierzbicka M, Dybizbanska E, Struzycka I, Iwanicka-Frankowska E. Oral health of Polish three-year-olds and mothers’ oral health-related knowledge. Community Dent Health. 2004;21:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Pattussi MP, Marcenes W, Croucher R, Sheiham A. Social deprivation, income inequality, social cohesions and dental caries in Brazilian schoolchildren. Soc Sci Med. 2001;53:915–925. - PubMed
-
- Watt RG. Emerging theories into the social determinants of health: implications for oral health promotion. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2002;30:241–247. - PubMed
-
- Akpata ES, Al-Attar A, Sharma PN. Factors associated with severe caries among adults in Kuwait. Med Princ Pract. 2009;18:93–99. - PubMed
-
- Dye BA, Tan S, Smith V, Lewis BJ, Barker LK, Thornton-Evans G, Eke PI, Beltran-Aguilar ED, Horowitz AM, Li CH. Trends in oral health status: United States, 1988–1994 and 1999–2004. Vital Health Stat 11. 2007;248:1–92. - PubMed
-
- Behbehani JM, Scheutz F. Oral health in Kuwait. Int Dent J. 2004;54(suppl 1):401–408. - PubMed
-
- Behbehani JM, Shah NM. Oral health in Kuwait before the Gulf War. Med Princ Prac. 2002;11(suppl 1):36–43. - PubMed
-
- Vigild M, Skougaard M, Hadi RA, Al-Zaabi F, Al-Yasseen I. Dental caries and dental fluorosis among 4-, 6-, 12- and 15-year-old children in kindergartens and public schools in Kuwait. Community Dent Health. 1996;13:47–50. - PubMed
-
- Glass RL. Kuwait national dental health survey. Part I. The oral health of school children 6–16 years of age in Kuwait 1982. Kuwait Ministry of Health; 1982.
-
- Al-Mutawa SA, Shyama M, Al-Duwairi Y, Soparkar P. Dental caries experience of Kuwaiti schoolchildren. Community Dent Health. 2006;23:31–36. - PubMed
-
- Blinkhorn AS, Wainwright-Stringer YM, Holloway PJ. Dental health knowledge and attitudes of regularly attending mothers of high-risk, pre-school children. Int Dent J. 2001;51:435–438. - PubMed
-
- Schroth RJ, Brothwell DJ, Moffatt M. Caregiver knowledge and attitudes of preschool oral health and early childhood caries (ECC) Int J Circumpolar Health. 2007;66:153–167. - PubMed
-
- Saied-Moallemi Z, Virtanen JI, Ghofranipour F, Murtomaa H. Influence of mothers’ oral health knowledge and attitudes on their children's dental health. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2008;9:79–83. - PubMed
-
- Chan SC, Tsai JS, King NM. Feeding and oral hygiene habits of preschool children in Hong Kong and their caregivers’ dental knowledge and attitudes. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2002;12:322–331. - PubMed
-
- Kay E, Locker D. A systematic review of the effectiveness of health promotion aimed at improving oral health. Community Dent Health. 1998;15:132–144. - PubMed
-
- Kay E, Locker D. Is dental health education effective? A systematic review of current evidence. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1996;24:231–235. - PubMed
-
- Ammari JB, Baqain ZH, Ashley PF. Effects of programs for prevention of early childhood caries. A systematic review. Med Princ Pract. 2007;16:437–442. - PubMed