Quality of life of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes in Kuwait
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Health Sciences Center, Kuwait University, Kuwait, Kuwait. majdah.a@hsc.edu.kw
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) in Kuwait using the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL) 4.0 Generic Core Scale and PedsQL 3.0 Diabetes Module, and to identify the risk factors associated with unsatisfactory QoL and their effects on metabolic control.
Subjects and methods: A total of 436 patients (2-18 years) with T1DM (>6 months) and 389 healthy controls, with the parents of both groups, completed the Arabic Generic Core Scale. Those with T1DM also completed the Arabic Diabetes Module.
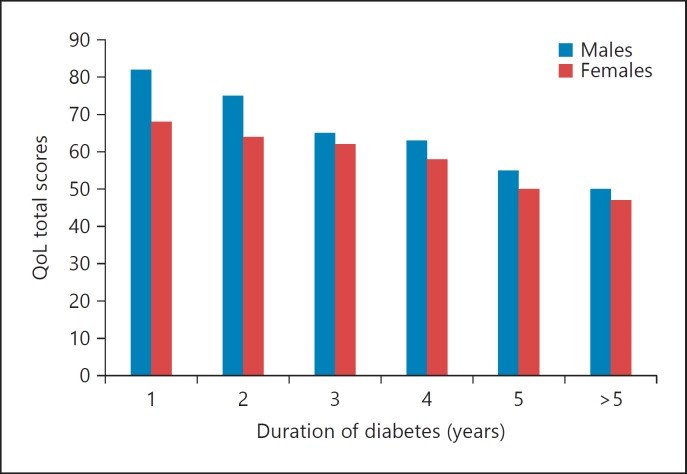
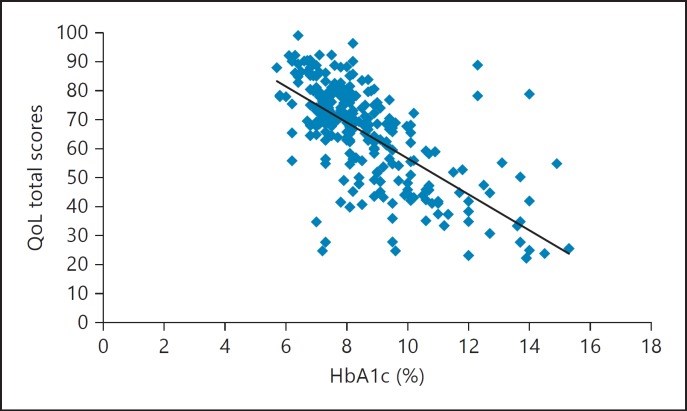
Results: The mean total score of the PedsQL Diabetes Module was 70.2 ± 9.8 reported by children and 59.9 ± 11.1 reported by parents (higher scores indicate better QoL). Young age and long duration of diabetes were associated with poor QoL (p < 0.001). Boys had better total scores than girls in most age groups (70.3 ± 9.3 vs. 52.3 ± 7.2, p < 0.001); however, girls did better than boys regarding treatment barriers and adherence (71.3 ± 7.8 vs. 68.1 ± 6.2, p < 0.005). Higher HbA1c values were associated with lower QoL scores (31.1 ± 5.1 at HbA1c of 15% vs. 82.5 ± 6.1 at HbA1c of 6%, p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: HRQoL of children and adolescents with T1DM was consistently poorer than controls. Parents consistently reported poorer QoL scores than their children. We recommend that more support should be provided for the care of children with diabetes in Kuwait.
Figures
Similar articles
Samardzic M, Tahirovic H, Popovic N, Popovic-Samardzic M.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jun 1;29(6):663-8. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2015-0420.PMID: 27054599
Health related quality of life in pediatric onset Type 1 diabetes mellitus in Kerala, India.
Bhavani N, Prince S, Menon AS, Abraham N, Pavithran PV, Menon UV, Nair V, Kumar H.Pediatr Diabetes. 2021 Mar;22(2):369-373. doi: 10.1111/pedi.13151. Epub 2020 Nov 25.PMID: 33180987
Kalyva E, Malakonaki E, Eiser C, Mamoulakis D.Pediatr Diabetes. 2011 Feb;12(1):34-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2010.00653.x.PMID: 20546163
Quality of life of children with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review.
Nieuwesteeg A, Pouwer F, van der Kamp R, van Bakel H, Aanstoot HJ, Hartman E.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2012 Nov;8(6):434-43. doi: 10.2174/157339912803529850.PMID: 22934548 Review.
[Impact on the quality of life of adolescents with diabetes mellitus type 1].
Lizama Fuentes F, Ormeño Rojas S, Mourguiart Liberona F, Fuentes Cammell J, López-Alegría F.Rev Chil Pediatr. 2020 Dec;91(6):968-981. doi: 10.32641/rchped.vi91i6.2457. Epub 2020 Nov 16.PMID: 33861836 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
Health-related quality of life of Kuwaiti adults living with diabetes.
Alowayesh MS, Aljunid SM, Aladsani A, Alessa T, Alattar A, Alroudhan D.Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 23;11:1085928. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1085928. eCollection 2023.PMID: 37033039 Free PMC article.
Al-Abdulrazzaq D, Khalifa D, Alqaisi T, Al-Juailla F, Othman F, Qabazard S, Al-Kandari H.Front Public Health. 2022 Dec 23;10:1056967. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1056967. eCollection 2022.PMID: 36620301 Free PMC article.
Raicevic M, Obradovic A, Samardzic M, Raicevic M, Curovic Popovic N, Panic Zaric S.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 11;19(22):14873. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214873.PMID: 36429590 Free PMC article.
Alzahrani AM, Magliah SF, Turkistani HA, Abulaban BA, Sabban MF, Mashat MA, Al Shaikh AM.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Sep 3;81:104550. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104550. eCollection 2022 Sep.PMID: 36147155 Free PMC article.
Bekele BT, Demie TG, Worku F.Pediatric Health Med Ther. 2022 Jun 22;13:243-256. doi: 10.2147/PHMT.S364454. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35769766 Free PMC article.
KMEL References
References
-
- Roze S, Valentine WJ, Zakrzewska KE, et al. Health-economic comparison of continuous insulin infusion with multiple daily injections for the treatment of type 1 diabetes in the UK. Diabet Med. 2005;22:1239–1234. - PubMed
-
- Hoey H, Aanstoot H, Chiarelli F, et al. Good metabolic control is associated with better quality of life in 2,101 adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1923–1928. - PubMed
-
- Varni J, Burwinkle T, Jacobs J, et al. The PedsQL™ in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Reliability and validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory™ Generic Core Scales and type 1 Diabetes Module. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:631–637. - PubMed
-
- Shah N, Shah M, Radovanovic Z. Towards defining socioeconomic and demographic inequalities that may affect health in Kuwait. Med Princ Pract. 1998;7:33–46.
-
- Nunnally JC, Bernstein IR. Psychometric Theory. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1994. pp. 215–255.
-
- Abdul-Rasoul M, AlOtaibi F, AlMahdi M, et al. Reliability and validity of the Arabic version of the PedsQL™ 4.0 Generic Core Score and PedsQL™ Diabetes Module. Int J Diabetes Mellit. 2012;2:301–307.
-
- Kalyva E, Malakonaki E, Eiser C, et al. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1DM): self and parental perception. Pediatr Diabetes. 2011;12:34–40. - PubMed
-
- Graue M, Wentzel-Larsen T, Brue E, et al. The coping styles of adolescents with type 1 diabetes are associated with degree of metabolic control. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1313–1317. - PubMed
-
- Wake M, Hesketh K, Cameron F. The child health questionnaire in children with diabetes: cross-sectional survey of parent and adolescent-reported functional health status. Diabet Med. 2000;17:700–707. - PubMed
-
- Al-Akour N, Khader Y, Shatnawi N. Quality of life and associated factors among Jordanian adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2010;24:43–47. - PubMed
-
- Nardi L, Zucckini S, D'Alberton F, et al. Quality of life, psychological adjustment and metabolic control in youths with type 1 diabetes: a study with self- and parent-report questionnaires. Pediatr Diabetes. 2008;9:496–503. - PubMed
-
- Hanberger L, Ludvigsson J, Nordfeldt S. Health-related quality of life in intensively treated young patients with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009;10:374–381. - PubMed
-
- Wagner VM, Muller-Godeffroy E, von Sengbusch S, et al. Age, metabolic control and type of insulin regimen influence health-related quality of life in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Eur J Pediatr. 2005;164:491–496. - PubMed
-
- Huang G, Palta M, Allen C, et al. Self-rated health among young people with type 1 diabetes in relation to risk factors in a longitudinal study. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;159:364–372. - PubMed
-
- Vanelli M, Chiarelli F, Chiari G, et al. Relationship between metabolic control and quality of life in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Report from two Italian centres for the management of diabetes in childhood. Acta Biomed. 2003;74(suppl 1):13–17. - PubMed
-
- Hesketh K, Wake M, Cameron F. Health-related quality of life and metabolic control in children with type 1 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:415–420. - PubMed