Evaluation of the in vitro activity of ceftaroline, ceftazidime/avibactam and comparator antimicrobial agents against clinical isolates from paediatric patients in Kuwait: ATLAS data 2012-19
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, P.O. Box 24923, Safat 13110, Kuwait.
- Pfizer Gulf FZ LLC, Pfizer Building, PO Box 502749, Dubai Media City, Dubai, UAE.
- Pfizer Inc, 235 E 42nd St, New York, NY 10017, USA.
Abstract
Objectives: To report antimicrobial resistance data for Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens isolated from paediatric patients in three hospitals in Kuwait during 2012-19.
Methods: In vitro activity of antimicrobials against isolates from documented infections was determined using CLSI broth microdilution method and breakpoints at a central laboratory. Enterobacterales and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were screened for β-lactamases using multiplex PCR assays. Phenotypic determination of resistance in Haemophilus influenzae and Gram-positive isolates was performed using standard methodologies.
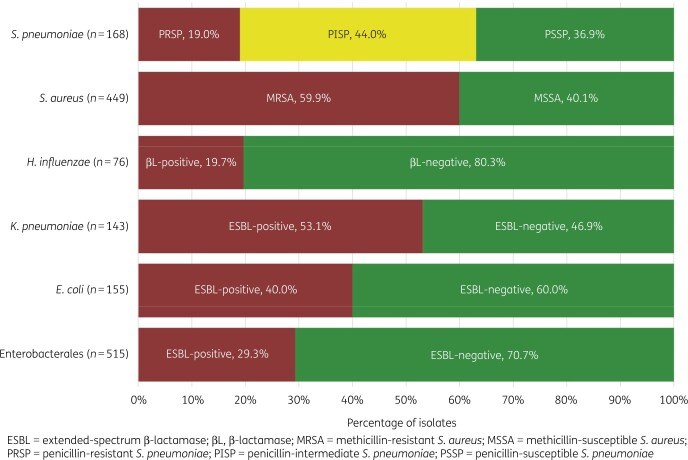
Results: Among 515 Enterobacterales isolates, 29.3% were ESBL-positive; susceptibility was highest to amikacin, ceftazidime/avibactam and meropenem (≥97.4%), regardless of ESBL status. CTX-M-15 was identified in 87.1% of ESBL-positive Escherichia coli and 84.2% of ESBL-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Of 111 P. aeruginosa isolates, 9.9% were MDR and 12.6% meropenem-resistant (MEM-R). Amikacin and ceftazidime/avibactam had the highest susceptibility rates in the overall group (≥92.8%), with reduced rates among MDR and MEM-R isolates. All 269 MRSA and 180 MSSA isolates were susceptible to daptomycin, linezolid, teicoplanin, tigecycline and vancomycin. All MSSA and 99.3% of MRSA were ceftaroline susceptible. All 168 pneumococcal isolates were susceptible to ceftaroline, linezolid, tigecycline and vancomycin. H. influenzae and Streptococcus pyogenes ceftaroline susceptibility rates were ≥93.3% and ≥95.6%.
Conclusions: Most isolates of Enterobacterales (including resistant phenotypes) and P. aeruginosa from Kuwait during 2012-19 were susceptible to ceftazidime/avibactam. Ceftaroline was active against most Gram-positive isolates, including resistant phenotypes, and ESBL-negative Enterobacterales. These results indicate that novel antibiotics such as ceftazidime/avibactam and ceftaroline represent valuable treatment options for paediatric infections, including those caused by MDR organisms.
Figures
Similar articles
Jia P, Zhu Y, Zhang H, Cheng B, Guo P, Xu Y, Yang Q.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Oct 1;22(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02644-5.PMID: 36182895 Free PMC article.
Piérard D, Stone GG.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Jun 23;21(1):600. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06153-0.PMID: 34162341 Free PMC article.
Ko WC, Stone GG.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2020 Apr 1;19(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12941-020-00355-1.PMID: 32238155 Free PMC article.
Zhanel GG, Golden AR, Zelenitsky S, Wiebe K, Lawrence CK, Adam HJ, Idowu T, Domalaon R, Schweizer F, Zhanel MA, Lagacé-Wiens PRS, Walkty AJ, Noreddin A, Lynch Iii JP, Karlowsky JA.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2.PMID: 30712199 Review.
Swaminathan S, Routray A, Mane A.Cureus. 2022 Aug 22;14(8):e28283. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28283. eCollection 2022 Aug.PMID: 36072213 Free PMC article. Review.