Dentists' and Parents' Attitude Toward Nitrous Oxide Use in Kuwait
Affiliations
Affiliations
- Dental Division, Ministry of Health, State of Kuwait, Sulaibikhat, Kuwait.
- Department of Surgical Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, Kuwait University, Safat, Kuwait, and.
- Division of Dental Medicine, CareSouth Carolina, Society Hill, South Carolina.
Abstract
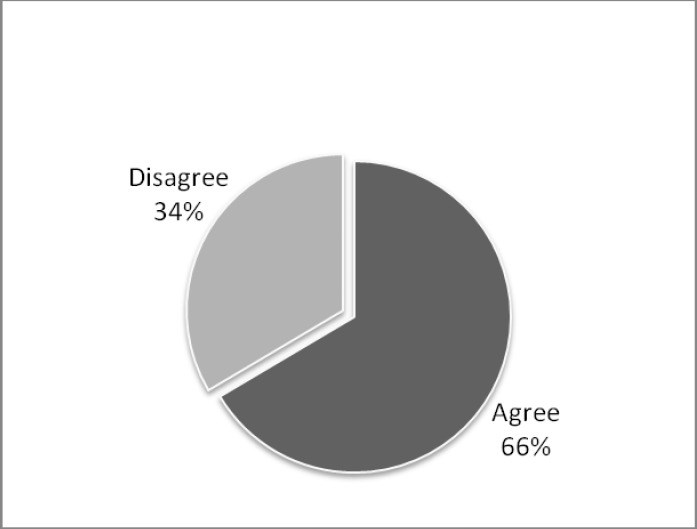
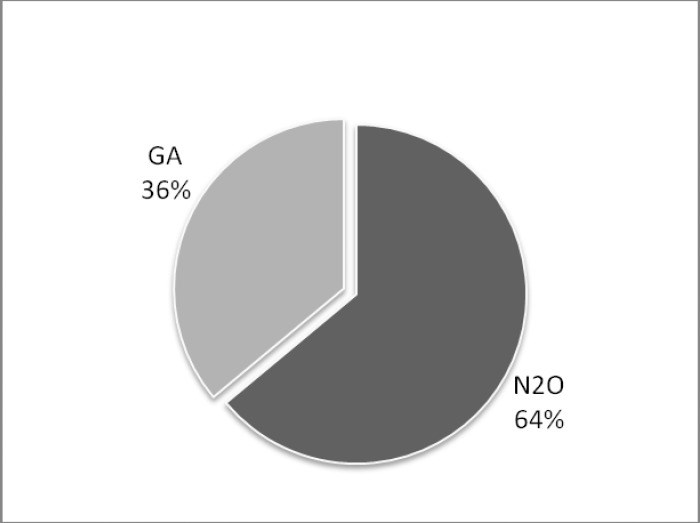
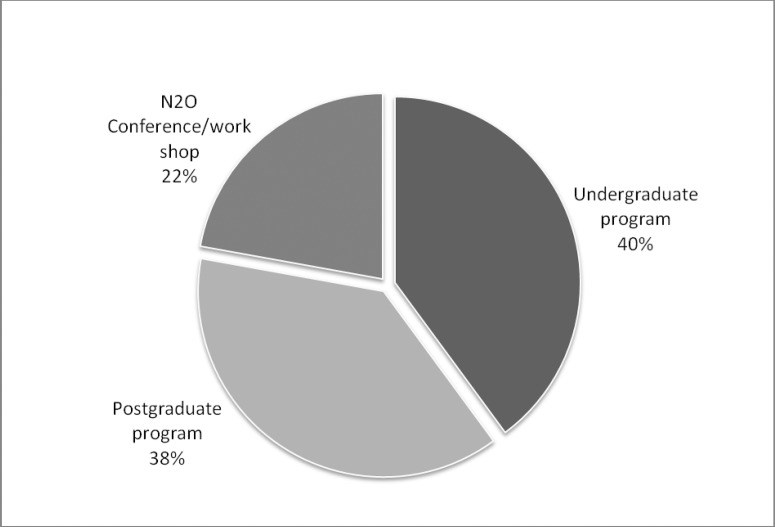
The aim of this study was to investigate the attitude of dentists in Kuwait toward the use of nitrous oxide sedation as a behavior management technique (BMT) for pediatric patients and assess their training in nitrous oxide sedation. In addition, we assessed parents' knowledge of and attitude toward the use of nitrous oxide as a BMT for their children. The objective was to determine if nitrous oxide sedation is being provided and utilized as a means to enhance dental care for pediatric patients. A cross-sectional survey was randomly distributed to both groups of interest: parents accompanying their children to the dentist and licensed dentists in Kuwait. Participants had to meet certain inclusion criteria to be included in the survey and had to complete the entire questionnaire to be part of the analysis. A total of 381 parents completed the questionnaires. The majority of parents responded that they were unaware of nitrous oxide sedation and were not aware of it as a BMT (79%). Two thirds of the parent would accept nitrous oxide sedation if recommended by a dentist treating their children. Two hundred and one dentists completed the survey and met the inclusion criteria. The majority (74.5%) of dentists were willing to use nitrous oxide as a BMT. However, only 6% were utilizing nitrous oxide sedation and providing it to their child patient if indicated. The main reasons for this huge gap are lack of facilities/equipment and lack of training as indicated by the dentists. This study showed that parents are accepting nitrous oxide sedation as a BMT for their children. It also showed the willingness of the dentists to provide such BMT to their patients. The lack of training and lack of equipment are the main barriers to providing such service to the patients. More training courses and more facilities should be provided to eliminate such barriers.
Keywords: Kuwait; Minimal sedation; Nitrous oxide.
Figures
Similar articles
Nitrous oxide inhalation sedation: what do patients, carers and dentists think about it?
Foley J.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2005 Mar;6(1):23-9.PMID: 15839830
Daher A, Hanna RP, Costa LR, Leles CR.BMC Oral Health. 2012 Jul 18;12:21. doi: 10.1186/1472-6831-12-21.PMID: 22808942 Free PMC article.
Wood M.SAAD Dig. 2010 Jan;26:12-22.PMID: 20151606
Sedation for pediatric dental patients.
Webb MD, Moore PA.Dent Clin North Am. 2002 Oct;46(4):803-14, xi. doi: 10.1016/s0011-8532(02)00026-5.PMID: 12436833 Review.
Management of child patient behavior: quality of care, fear and anxiety, and the child patient.
Wilson S.J Endod. 2013 Mar;39(3 Suppl):S73-7. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2012.11.040.PMID: 23439049 Review.
Cited by
Sabbagh HJ, Turkistani JM, Alotaibi HA, Alsolami AS, Alsulami WE, Abdulgader AA, Bagher SM.Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2021 Dec 24;13:531-539. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S340158. eCollection 2021.PMID: 34992465 Free PMC article.
Conscious sedation in dentistry: knowledge and practice among dental professionals in Tanzania.
Sales N, Sohal KS, Moshy JR, Owibingire SS, Deoglas DK, Laizer PJ.J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2021 Dec;21(6):557-564. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2021.21.6.557. Epub 2021 Nov 26.PMID: 34909473 Free PMC article.
Abdulwahab M, Kamal M, AlAli AM.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2021 Nov 12;12:1309-1315. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S331651. eCollection 2021.PMID: 34795547 Free PMC article.
Nitrous Oxide and Midazolam Sedation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Sivaramakrishnan G, Sridharan K.Anesth Prog. 2017 Summer;64(2):59-65. doi: 10.2344/anpr-63-03-06.PMID: 28604098 Free PMC article. Review.